Abstract
1. The vasoconstrictor effects of uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP), uridine 5'-diphosphate (UDP), uridine 5'-monophosphate (UMP) and uridine were tested in the isolated pulmonary vascular bed of the rat. Comparison was made with the effects of adenine nucleotides, adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), adenosine 5'-diphosphate (ADP), adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) and with adenosine. The effect of P2x-purinoceptor desensitization and blockade was compared on the vascular responses to uracil and adenine nucleotides. 2. At doses ranging from 10(-8) to 10(-5) mol, UTP elicited dose-dependent vasoconstriction. UDP was equiactive to UTP, while UMP and uridine did not show vasomotor activity. Similarly, ATP showed dose-related vasoconstrictor activity. ADP was less potent than ATP in eliciting vasoconstriction, while AMP was active only at the higher doses tested and adenosine was ineffective. 3. Vasoconstriction was produced by ATP analogues with the following order of potency: alpha, beta-methylene ATP > ATP gamma S > beta, gamma-methylene ATP > 2-methylthio ATP > or = ATP. 4. Desensitization of P2x-purinoceptors by the selective agonist alpha, beta-methylene ATP did not modify the vasoconstrictor activity of UTP and UDP and only partially reduced vasoconstrictor responses to ATP, while it abolished vascular responses to alpha, beta-methylene ATP itself. 5. The antagonists of P2-purinoceptors, suramin and pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2', 4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS), did not affect vascular responses to UTP and UDP, but reduced vasoconstriction evoked by beta, gamma-methylene ATP and ATP by about 70 and 30%, respectively. 6. This study demonstrates that uracil nucleotides, UTP and UDP, elicit vasoconstriction in the rat pulmonary vascular bed. In addition to confirming the presence of classical P2x-purinoceptors, these results also suggest the presence of a distinct purinoceptor subtype which mediates UTP- and ATP- evoked vasoconstriction in the rat pulmonary circulation.
Full text
PDF
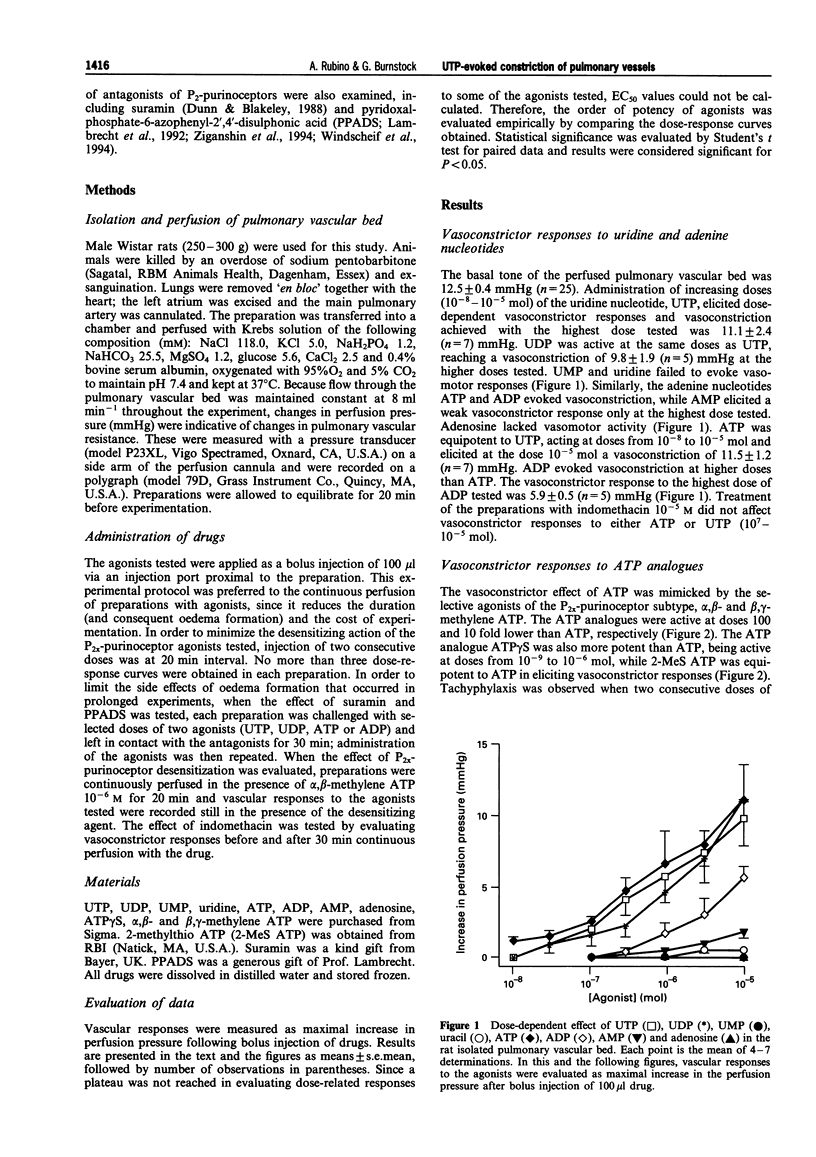
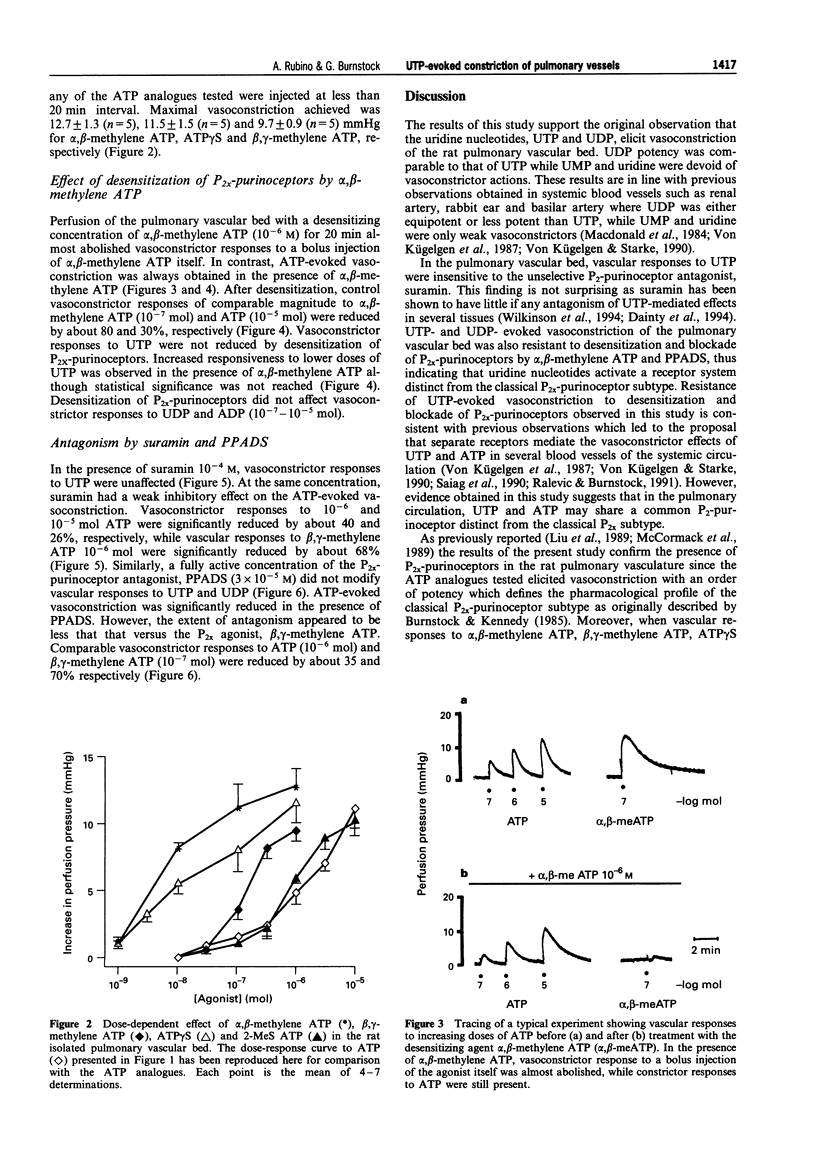
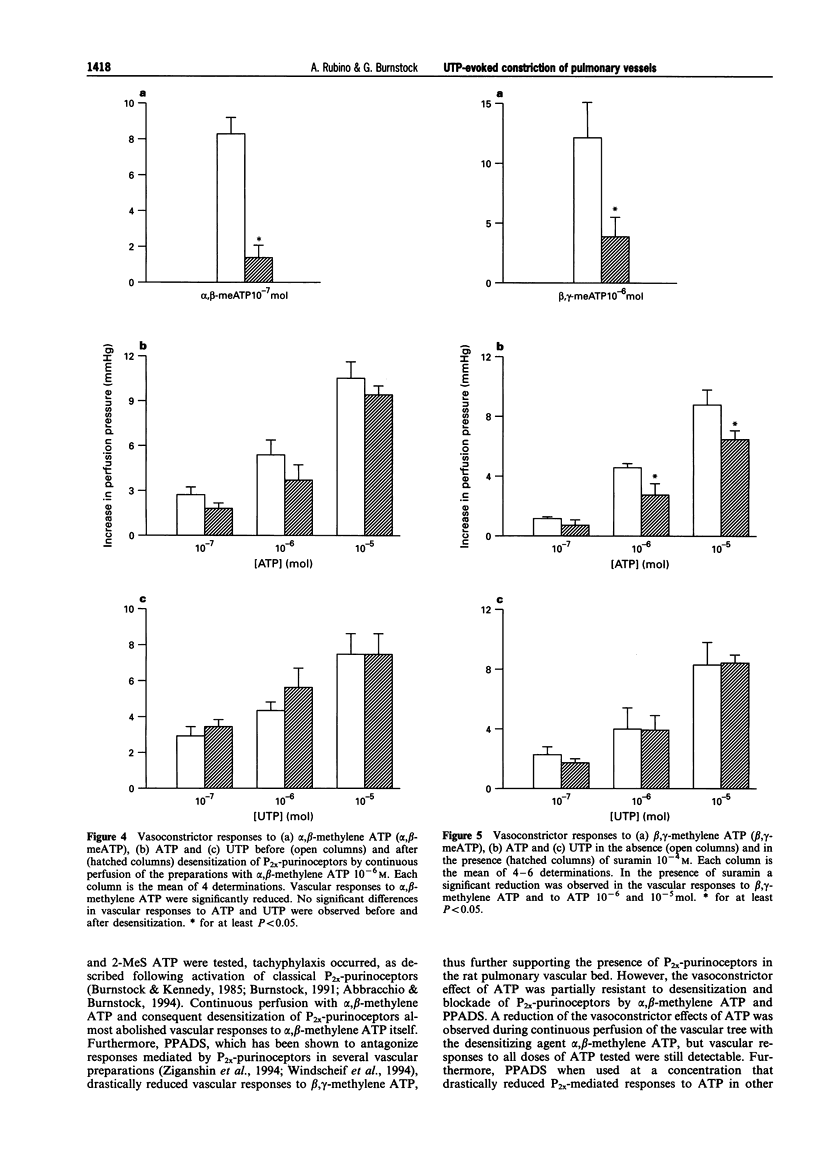
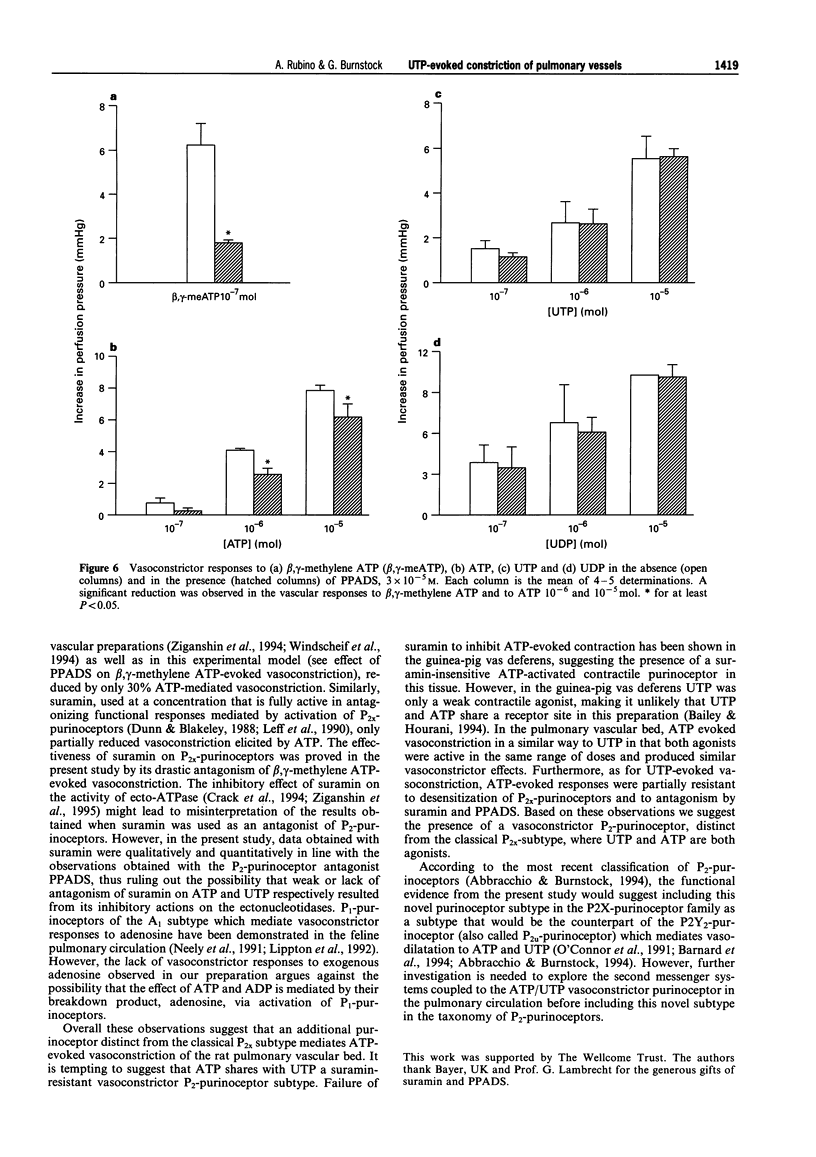

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G. Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors? Pharmacol Ther. 1994;64(3):445–475. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(94)00048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. Differential effects of suramin on P2-purinoceptors mediating contraction of the guinea-pig vas deferens and urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Burnstock G., Webb T. E. G protein-coupled receptors for ATP and other nucleotides: a new receptor family. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Mar;15(3):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crack B. E., Beukers M. W., McKechnie K. C., Ijzerman A. P., Leff P. Pharmacological analysis of ecto-ATPase inhibition: evidence for combined enzyme inhibition and receptor antagonism in P2X-purinoceptor ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1432–1438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht G., Friebe T., Grimm U., Windscheif U., Bungardt E., Hildebrandt C., Bäumert H. G., Spatz-Kümbel G., Mutschler E. PPADS, a novel functionally selective antagonist of P2 purinoceptor-mediated responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90877-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Wood B. E., O'Connor S. E. Suramin is a slowly-equilibrating but competitive antagonist at P2x-receptors in the rabbit isolated ear artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):645–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippton H. L., Hao Q., Hauth T., Hyman A. Mechanisms of signal transduction for adenosine and ATP in pulmonary vascular bed. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 2):H926–H929. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.3.H926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. F., McCormack D. G., Evans T. W., Barnes P. J. Characterization and distribution of P2-purinoceptor subtypes in rat pulmonary vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):1204–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald G., Assef R., Guiffre A., Lo E. Vasoconstrictor effects of uridine and its nucleotides and their inhibition by adenosine. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1984 Jul-Aug;11(4):381–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1984.tb00283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack D. G., Barnes P. J., Evans T. W. Purinoceptors in the pulmonary circulation of the rat and their role in hypoxic vasoconstriction. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely C. F., Haile D. M., Cahill B. E., Kadowitz P. J. Adenosine and ATP produce vasoconstriction in the feline pulmonary vascular bed by different mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Sep;258(3):753–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Effects of purines and pyrimidines on the rat mesenteric arterial bed. Circ Res. 1991 Dec;69(6):1583–1590. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.6.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saïag B., Milon D., Allaín H., Rault B., Van den Driessche J. Constriction of the smooth muscle of rat tail and femoral arteries and dog saphenous vein is induced by uridine triphosphate via 'pyrimidinoceptors', and by adenosine triphosphate via P2x purinoceptors. Blood Vessels. 1990;27(6):352–364. doi: 10.1159/000158829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Involvement of pyrimidinoceptors in the regulation of cell functions by uridine and by uracil nucleotides. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa Y., White R. P., Robertson J. T. Mechanisms of the contractile effect induced by uridine 5-triphosphate in canine cerebral arteries. Stroke. 1983 May-Jun;14(3):347–355. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquilla P. R. Prolonged contraction of isolated human and canine cerebral arteries induced by uridine 5'-triphosphate. Stroke. 1978 Mar-Apr;9(2):133–136. doi: 10.1161/01.str.9.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vials A. J., Burnstock G. Effects of pyrimidines on the guinea-pig coronary vasculature. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. F., McKechnie K., Dainty I. A., Boarder M. R. P2Y purinoceptor and nucleotide receptor-induced relaxation of precontracted bovine aortic collateral artery rings: differential sensitivity to suramin and indomethacin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Feb;268(2):881–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windscheif U., Ralevic V., Bäumert H. G., Mutschler E., Lambrecht G., Burnstock G. Vasoconstrictor and vasodilator responses to various agonists in the rat perfused mesenteric arterial bed: selective inhibition by PPADS of contractions mediated via P2x-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):1015–1021. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin A. U., Hoyle C. H., Lambrecht G., Mutschler E., Bümert H. G., Burnstock G. Selective antagonism by PPADS at P2X-purinoceptors in rabbit isolated blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;111(3):923–929. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin A. U., Ziganshina L. E., King B. E., Burnstock G. Characteristics of ecto-ATPase of Xenopus oocytes and the inhibitory actions of suramin on ATP breakdown. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Jan;429(3):412–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00374157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Häussinger D., Starke K. Evidence for a vasoconstriction-mediating receptor for UTP, distinct from the P2 purinoceptor, in rabbit ear artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;336(5):556–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00169313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Evidence for two separate vasoconstriction-mediating nucleotide receptors, both distinct from the P2x-receptor, in rabbit basilar artery: a receptor for pyrimidine nucleotides and a receptor for purine nucleotides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;341(6):538–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00171734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


