Abstract
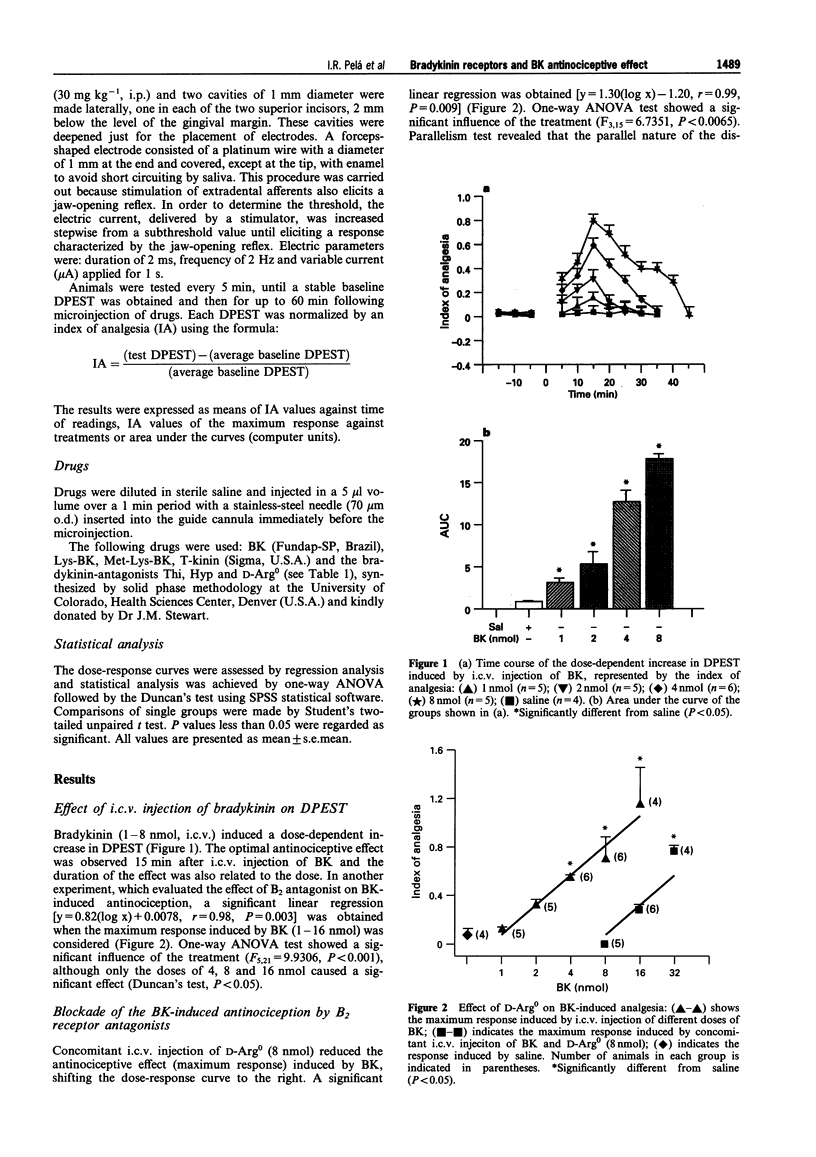
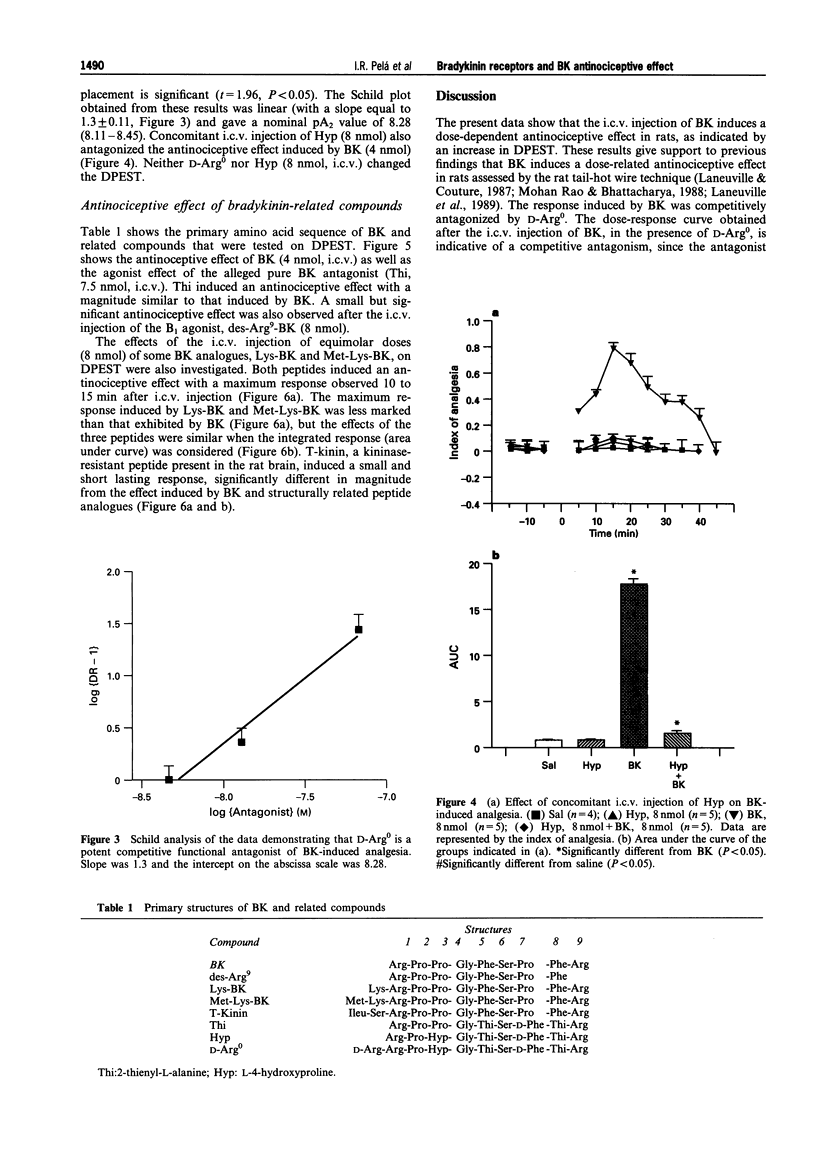
1. The effect of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of bradykinin (BK) and related peptides was tested on the dental pulp electrical stimulation threshold (DPEST) in rats. 2. BK (4, 8 and 16 nmol) induced a dose-dependent increase of DPEST, indicative of an antinociceptive effect. 3. I.c.v. injection of equimolar doses of BK-related peptides, Lys-BK and Met-Lys-BK, also induced an increase of DPEST, but the magnitude of the effect was not as intensive as that induced by BK, when the maximum increase of DPEST was considered. The peptide T-kinin induced a short lasting and weak antinociceptive effect. 4. The B1 agonist, des-Arg9-BK (8 nmol) induced a significant antinociceptive effect, but this was not as intensive as that induced by BK. 5. The B2 antagonist D-Arg0-Hyp3-Thi5,8-D-Phe7-BK (D-Arg0) competitively antagonized the BK-induced antinociception. Likewise, Hyp3-Thi5,8-D-Phe7-BK (Hyp) also antagonized BK effect. However, the compound Thi5,8-D-Phe7-BK (Thi), initially considered a pure BK antagonist, induced an antinociceptive effect, supporting previous observations that this peptide can also act as a partial agonist. 6. It is concluded that the dose-dependent antinociceptive effect induced by i.c.v. injection of BK is mediated by the stimulation of brain B2 receptors.
Full text
PDF
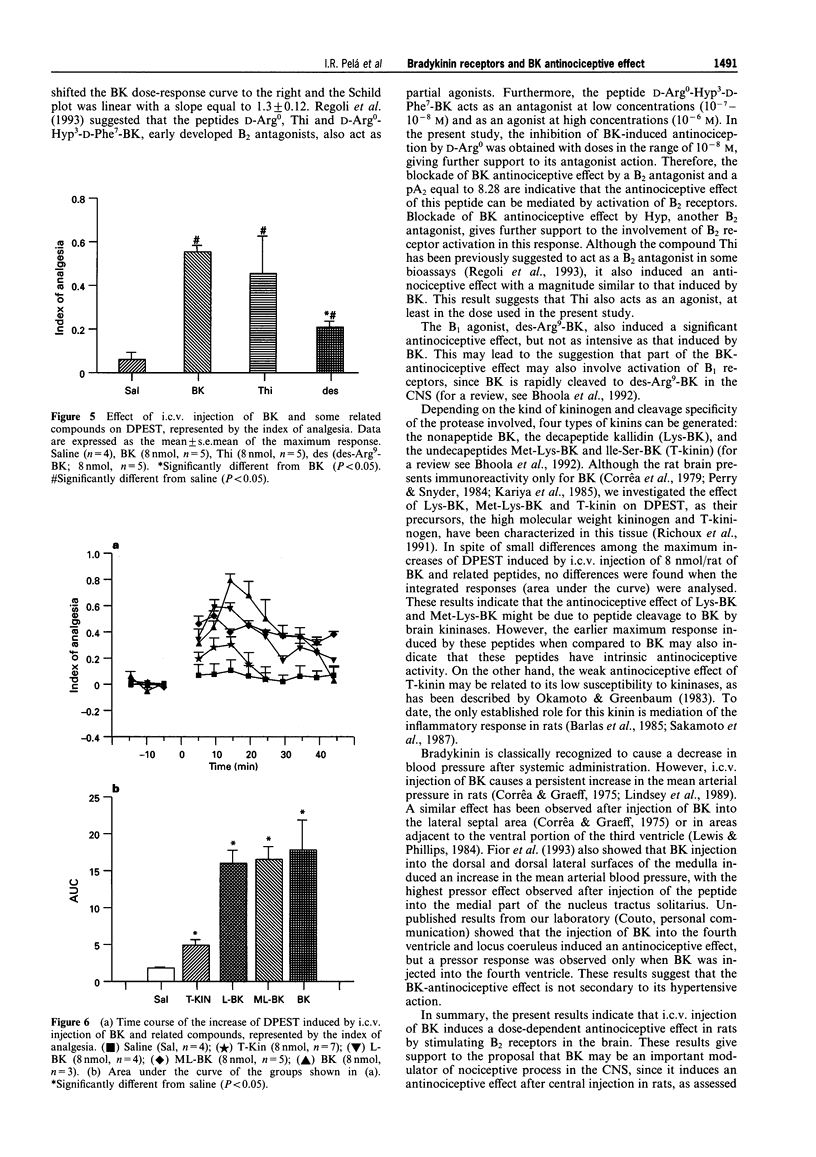

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida e Silva T. C., Pelá I. R. Changes in rectal temperature of the rabbit by intracerebroventricular injection of bradykinin and related kinins. Agents Actions. 1978 Jan;8(1-2):102–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01972410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlas A., Okamoto H., Greenbaum L. M. T-kininogen--the major plasma kininogen in rat adjuvant arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91434-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Figueroa C. D., Worthy K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol Rev. 1992 Mar;44(1):1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdin T. A., Graeff F. G., Pelá I. R. Opioid mediation of the antiaversive and hyperalgesic actions of bradykinin injected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of the rat. Physiol Behav. 1992 Sep;52(3):405–410. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(92)90325-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Chao L., Swain C. C., Tsai J., Margolius H. S. Tissue kallikrein in rat brain and pituitary: regional distribution and estrogen induction in the anterior pituitary. Endocrinology. 1987 Feb;120(2):475–482. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Woodley C., Chao L., Margolius H. S. Identification of tissue kallikrein in brain and in the cell-free translation product encoded by brain mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15173–15178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cholewinski A. J., Stevens G., McDermott A. M., Wilkin G. P. Identification of B2 bradykinin binding sites on cultured cortical astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1456–1458. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa F. M., Graeff F. G. Central mechanisms of the hypertensive action of intraventricular bradykinin in the unanaesthetized rat. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Jan;13(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa F. M., Graeff F. G. Central site of the hypertensive action of bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):670–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa F. M., Innis R. B., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin-like immunoreactive neuronal systems localized histochemically in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1489–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fior D. R., Martins D. T., Lindsey C. J. Localization of central pressor action of bradykinin in medulla oblongata. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):H1000–H1006. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.3.H1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Mantione C. R., Yamamura H. I. Identification of B2 bradykinin binding sites in guinea-pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;147(3):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeff F. G., Pelá I. R., Roch e Silva M. Behavioural and somatic effects of bradykinin injected into the cerebral ventricles of unanaesthetized rabbits. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;37(3):723–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya K., Yamauchi A., Sasaki T. Regional distribution and characterization of kinin in the CNS of the rat. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1892–1897. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laneuville O., Couture R. Bradykinin analogue blocks bradykinin-induced inhibition of a spinal nociceptive reflex in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 4;137(2-3):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laneuville O., Reader T. A., Couture R. Intrathecal bradykinin acts presynaptically on spinal noradrenergic terminals to produce antinociception in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 17;159(3):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. E., Childers S. R., Phillips M. I. [125I]Tyr-bradykinin binding in primary rat brain cultures. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90859-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. E., Phillips M. I. Localization of the central pressor action of bradykinin to the cerebral third ventricle. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):R63–R68. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.1.R63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey C. J., Nakaie C. R., Martins D. T. Central nervous system kinin receptors and the hypertensive response mediated by bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):763–768. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Greenbaum L. M. Isolation and structure of T-kinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):701–708. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. C., Snyder S. H. Identification of bradykinin in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):1072–1080. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHA E SILVA M., Jr, MALNIC G. RELEASE OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE BY BRADYKININ. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Oct;146:24–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. J., Bhattacharya S. K. Hyperthermic effect of centrally administered bradykinin in the rat: role of prostaglandins and serotonin. Int J Hyperthermia. 1988 Mar-Apr;4(2):183–189. doi: 10.3109/02656738809029308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Jukic D., Gobeil F., Rhaleb N. E. Receptors for bradykinin and related kinins: a critical analysis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;71(8):556–567. doi: 10.1139/y93-079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro S. A., Corrado A. P., Graeff F. G. Antinociceptive action of intraventricular bradykinin. Neuropharmacology. 1971 Nov;10(6):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(71)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro S. A., Silva M. R. Antinociceptive action of bradykinin and related kinins of larger molecular weights by the intraventricular route. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;47(3):517–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richoux J. P., Gelly J. L., Bouhnik J., Baussant T., Alhenc-Gelas F., Grignon G., Corvol P. The kallikrein-kinin system in the rat hypothalamus. Immunohistochemical localization of high molecular weight kininogen and T kininogen in different neuronal systems. Histochemistry. 1991;96(3):229–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00271541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto W., Satoh F., Gotoh K., Uehara S. Ile-Ser-bradykinin (T-kinin) and Met-Ile-Ser-bradykinin (Met-T-kinin) are released from T-kininogen by an acid proteinase of granulomatous tissues in rats. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 27;219(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva G. R., Rocha e Silva M. Catatonia induced in the rabbit by intracerebral injection of bradykinin and morphine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;15(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


