Abstract
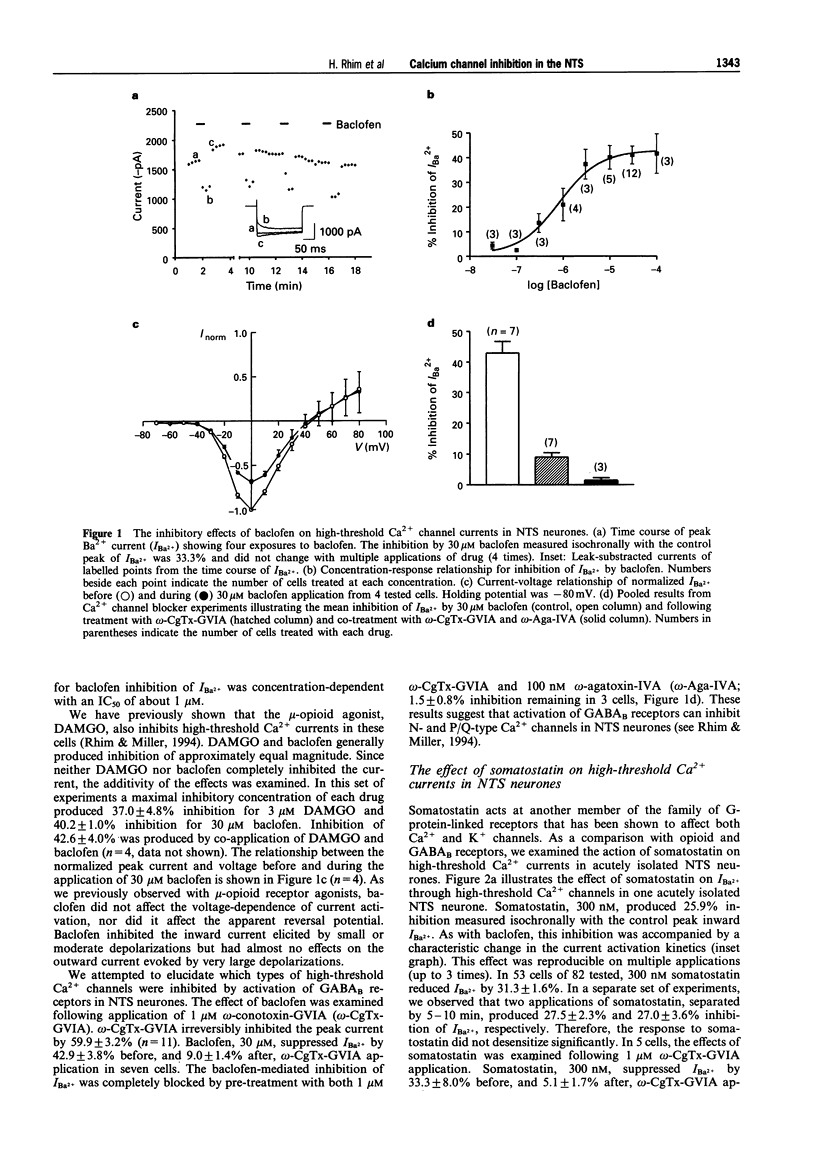
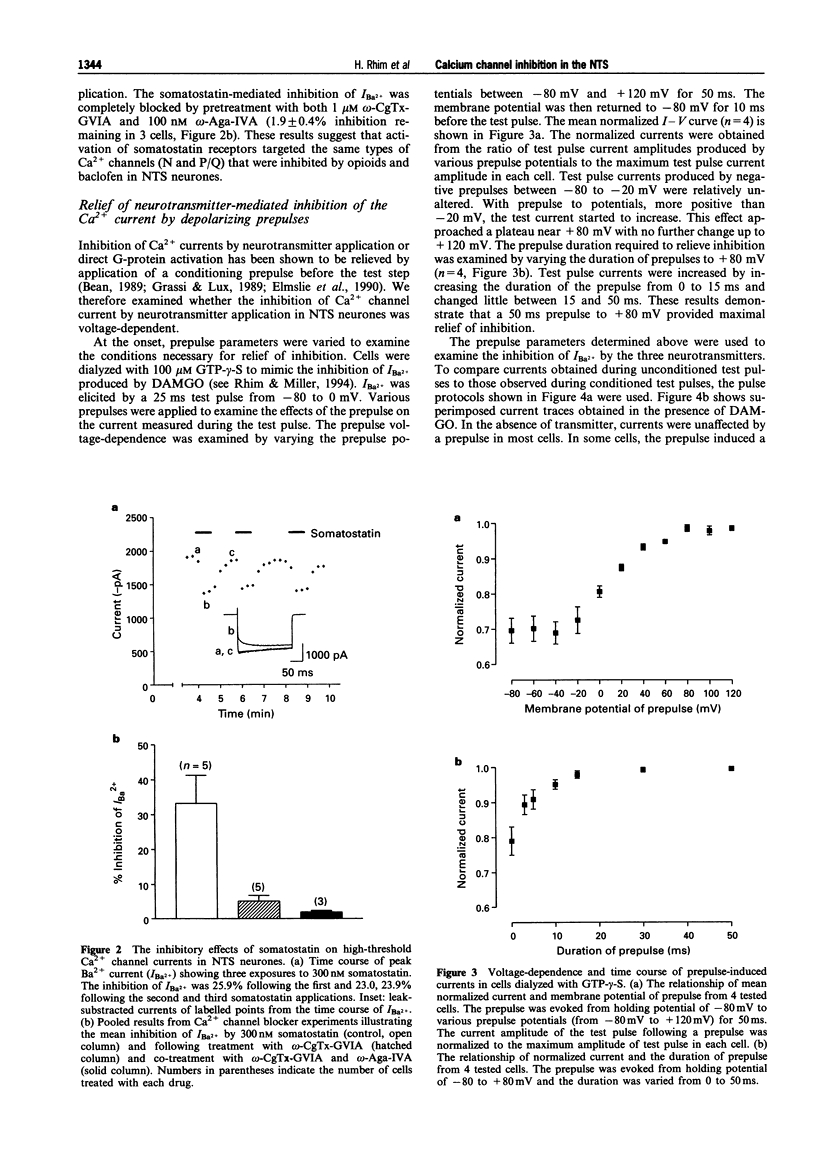
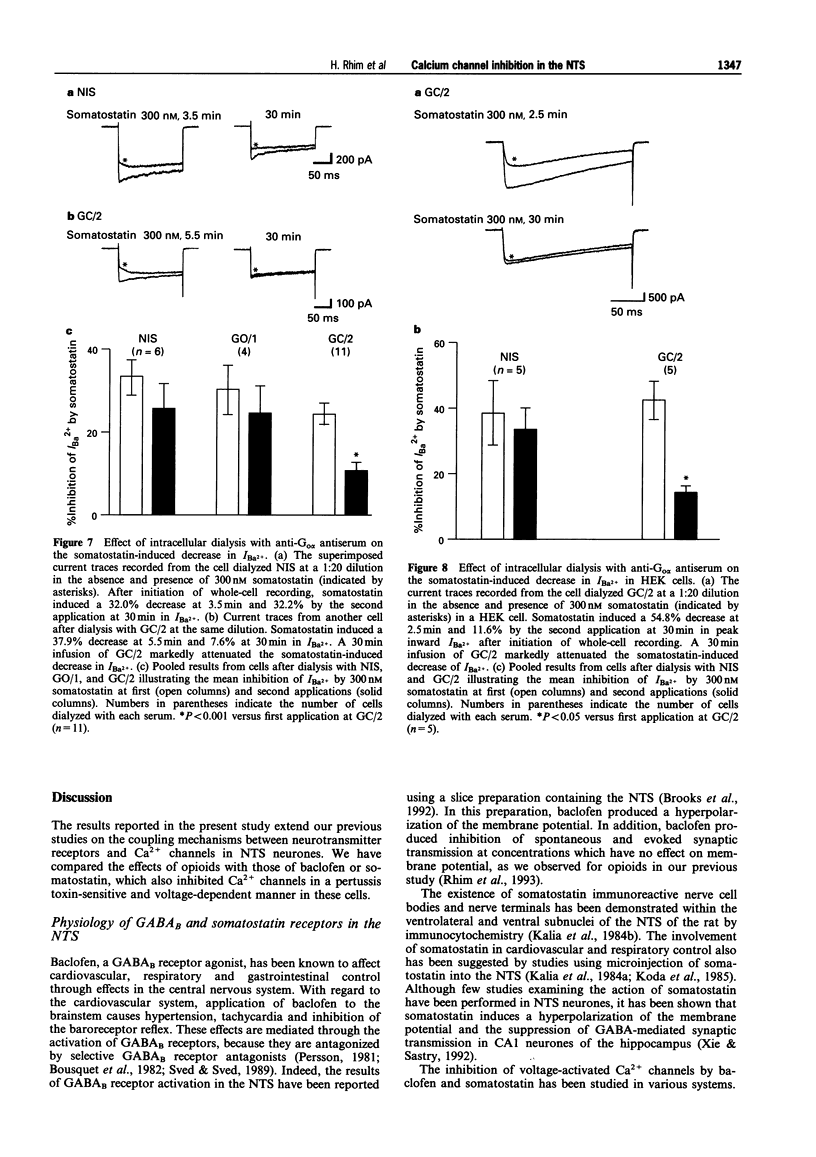
1. High-threshold Ca2+ channel currents were measured every 15 s following a 200 ms voltage step from -80 mV to 0 mV in order to study the coupling mechanism between neurotransmitter receptors and Ca2+ channels in neurones acutely isolated from the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of the rat. 2. Application of 30 microM baclofen (GABAB receptor agonist) caused 38.9 +/- 1.2% inhibition of the peak inward Ba2+ current (IBa2+) in most NTS cells tested (n = 85 of 88). Somatostatin, 300 nM, also reduced IBa2+ by 31.3 +/- 1.6% in 53 cells of 82 tested. 3. Activation of mu-opioid-, GABAB- or somatostatin-receptors inhibited both N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. 4. The inhibition of Ca2+ currents by DAMGo (mu-opioid receptor agonist), baclofen and somatostatin was reduced by treatment with pertussis toxin and partially relieved by application of a 50 ms conditioning prepulse to +80 mV. This suggests that a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein was involved in the neurotransmitter-mediated action in the observed inhibition of Ca2+ currents. 5. Intracellular loading with an antiserum raised against the amino terminus of Go alpha (GC/2) markedly attenuated the somatostatin-induced inhibition, but did not block the DAMGO- and baclofen-induced inhibition. 6. These findings suggest at least two different pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein-mediated pathways are involved in receptor-induced inhibition of Ca2+ currents in the NTS.
Full text
PDF


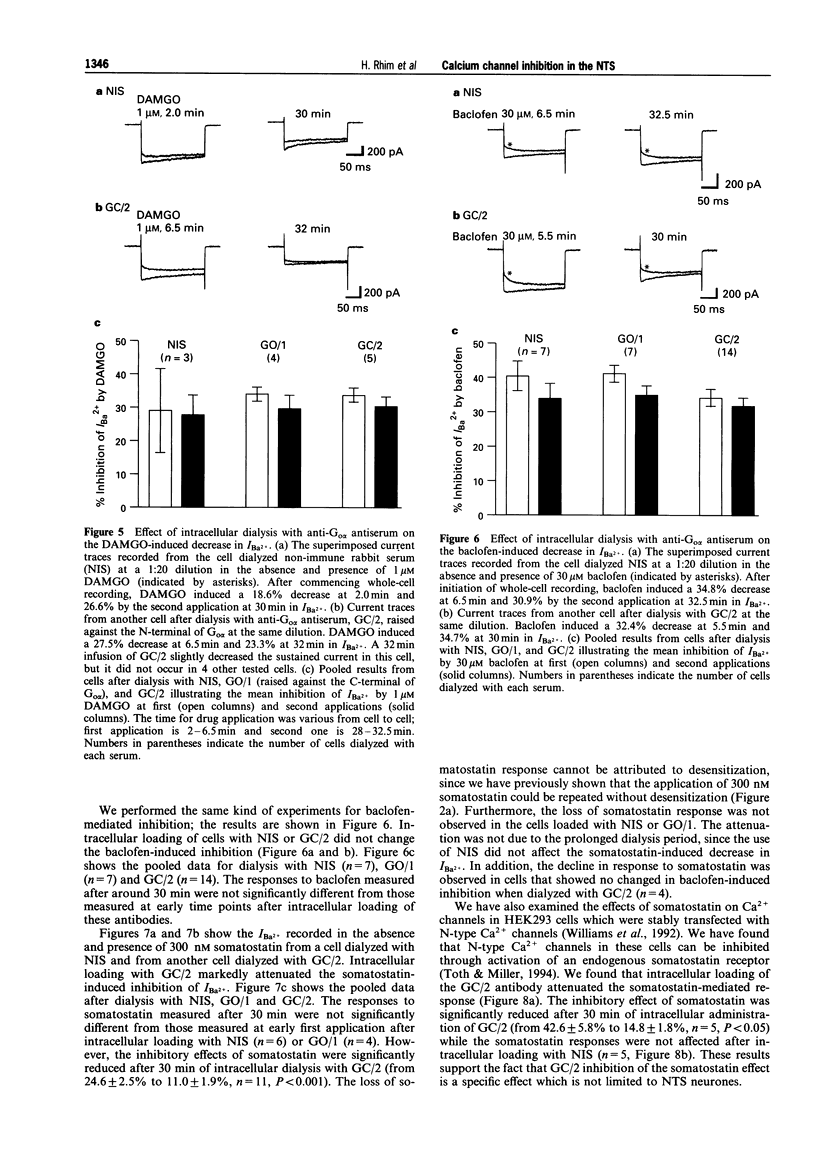



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bernheim L., Hille B. Pertussis toxin and voltage dependence distinguish multiple pathways modulating calcium channels of rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90111-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Bloch R., Schwartz J. Evidence for a neuromodulatory role of GABA at the first synapse of the baroreceptor reflex pathway. Effects of GABA derivatives injected into the NTS. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 May;319(2):168–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00503932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. A., Glaum S. R., Miller R. J., Spyer K. M. The actions of baclofen on neurones and synaptic transmission in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat in vitro. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:115–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell V., Berrow N., Dolphin A. C. GABAB receptor modulation of Ca2+ currents in rat sensory neurones by the G protein G(0): antisense oligonucleotide studies. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:1–11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. D., Medzihradsky F. Go mediates the coupling of the mu opioid receptor to adenylyl cyclase in cloned neural cells and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4062–4066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisz R. A., Lux H. D. gamma-Aminobutyric acid-induced depression of calcium currents of chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 May 14;56(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker B. M., Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J. Mutagenesis of the amino terminus of the alpha subunit of the G protein Go. In vitro characterization of alpha o beta gamma interactions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6272–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic D., Hamm H. E. Topographic analysis of antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies to the photoreceptor guanyl nucleotide-binding protein, transducin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10839–10847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diversé-Pierluissi M., Goldsmith P. K., Dunlap K. Transmitter-mediated inhibition of N-type calcium channels in sensory neurons involves multiple GTP-binding proteins and subunits. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Zhou W., Jones S. W. LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90035-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald D. A., Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C., Miller R. J. Differential G protein-mediated coupling of neurotransmitter receptors to Ca2+ channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1185–1193. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Backlund P. S., Jr, Rossiter K., Carter A., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. Purification of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins from brain: identification of a novel form of Go. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7085–7090. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi F., Lux H. D. Voltage-dependent GABA-induced modulation of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger R., Matthews G. Inhibition of calcium influx and calcium current by gamma-aminobutyric acid in single synaptic terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7135–7139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Modulation of ion-channel function by G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R. Double-pulse calcium channel current facilitation in adult rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:181–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G. Somatostatin blocks a calcium current in rat sympathetic ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:221–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Agnati L. F., Hökfelt T., Härfstrand A. Somatostatin produces apnea and is localized in medullary respiratory nuclei: a possible role in apneic syndromes. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 2;296(2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Lang R., Ganten D., Cuello C., Terenius L. Distribution of neuropeptide immunoreactive nerve terminals within the subnuclei of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jan 20;222(3):409–444. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda L. Y., Ling N., Benoit R., Madamba S. G., Bakhit C. Blood pressure following microinjection of somatostatin related peptides into the rat nucleus tractus solitarii. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Yasuda K., Bell G. I., Reisine T. Gi alpha 3 and G(o) alpha selectively associate with the cloned somatostatin receptor subtype SSTR2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10721–10727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. M., Woolkalis M. J., Gerton G. L., Smith R. M., Jarett L., Manning D. R. Subcellular distribution of the alpha subunit(s) of Gi: visualization by immunofluorescent and immunogold labeling. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):1097–1113. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lledo P. M., Homburger V., Bockaert J., Vincent J. D. Differential G protein-mediated coupling of D2 dopamine receptors to K+ and Ca2+ currents in rat anterior pituitary cells. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90273-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire G., Maple B., Lukasiewicz P., Werblin F. Gamma-aminobutyrate type B receptor modulation of L-type calcium channel current at bipolar cell terminals in the retina of the tiger salamander. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10144–10147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie A., Bernheim L., Hille B. Inhibition of N- and L-type calcium channels by muscarinic receptor activation in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90205-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean I., Mullaney I., Brown D. A., Milligan G. Antibodies to the GTP binding protein, Go, antagonize noradrenaline-induced calcium current inhibition in NG108-15 hybrid cells. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon-Johansson A. S., Berrow N., Dolphin A. C. G(o) transduces GABAB-receptor modulation of N-type calcium channels in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Nov;425(3-4):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00374184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Bean B. P. GABAB receptor inhibition of P-type Ca2+ channels in central neurons. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):889–898. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moises H. C., Rusin K. I., Macdonald R. L. mu-Opioid receptor-mediated reduction of neuronal calcium current occurs via a G(o)-type GTP-binding protein. J Neurosci. 1994 Jun;14(6):3842–3851. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-06-03842.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B. A hypertensive response to baclofen in the nucleus tractus solitarii in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;33(4):226–231. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Inglese J., Morales J. M., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Lefkowitz R. J., Bourne H. R., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Activation of the cloned muscarinic potassium channel by G protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):143–146. doi: 10.1038/370143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Glaum S. R., Miller R. J. Selective opioid agonists modulate afferent transmission in the rat nucleus tractus solitarius. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):795–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Miller R. J. Opioid receptors modulate diverse types of calcium channels in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat. J Neurosci. 1994 Dec;14(12):7608–7615. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-12-07608.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:669–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G., Rosenthal W., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. Role of G proteins in calcium channel modulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. S., Hille B. Substance P and somatostatin inhibit calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons via different G protein pathways. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90237-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. S., Wollmuth L. P., Hille B. Angiotensin II inhibits calcium and M current channels in rat sympathetic neurons via G proteins. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1319–1329. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. S., Wollmuth L. P., Hille B. Modulation of Ca2+ channels by PTX-sensitive G-proteins is blocked by N-ethylmaleimide in rat sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 2):7109–7116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-07109.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Shen K. Z., North R. A., Tatsumi H. Inhibition of calcium currents by noradrenaline, somatostatin and opioids in guinea-pig submucosal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved J. C., Sved A. F. Cardiovascular responses elicited by gamma-aminobutyric acid in the nucleus tractus solitarius: evidence for action at the GABAB receptor. Neuropharmacology. 1989 May;28(5):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao K., Yoshii M., Kanda A., Kokubun S., Nukada T. A region of the muscarinic-gated atrial K+ channel critical for activation by G protein beta gamma subunits. Neuron. 1994 Sep;13(3):747–755. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Sanchez S., Rifo M., Gilman A. G., Belardetti F. Inhibition of the omega-conotoxin-sensitive calcium current by distinct G proteins. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):799–809. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90100-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk-Blaszczak M. A., Singer W. D., Gutowski S., Sternweis P. C., Belardetti F. The G protein G13 mediates inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by bradykinin. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1215–1224. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Feldman D. H., McCue A. F., Brenner R., Velicelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90109-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Z., Sastry B. R. Actions of somatostatin on GABA-ergic synaptic transmission in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1992 Sep 25;591(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91703-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeadon M., Kitchen I. Opioids and respiration. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;33(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(89)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Giersbergen P. L., Palkovits M., De Jong W. Involvement of neurotransmitters in the nucleus tractus solitarii in cardiovascular regulation. Physiol Rev. 1992 Jul;72(3):789–824. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.3.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


