Abstract
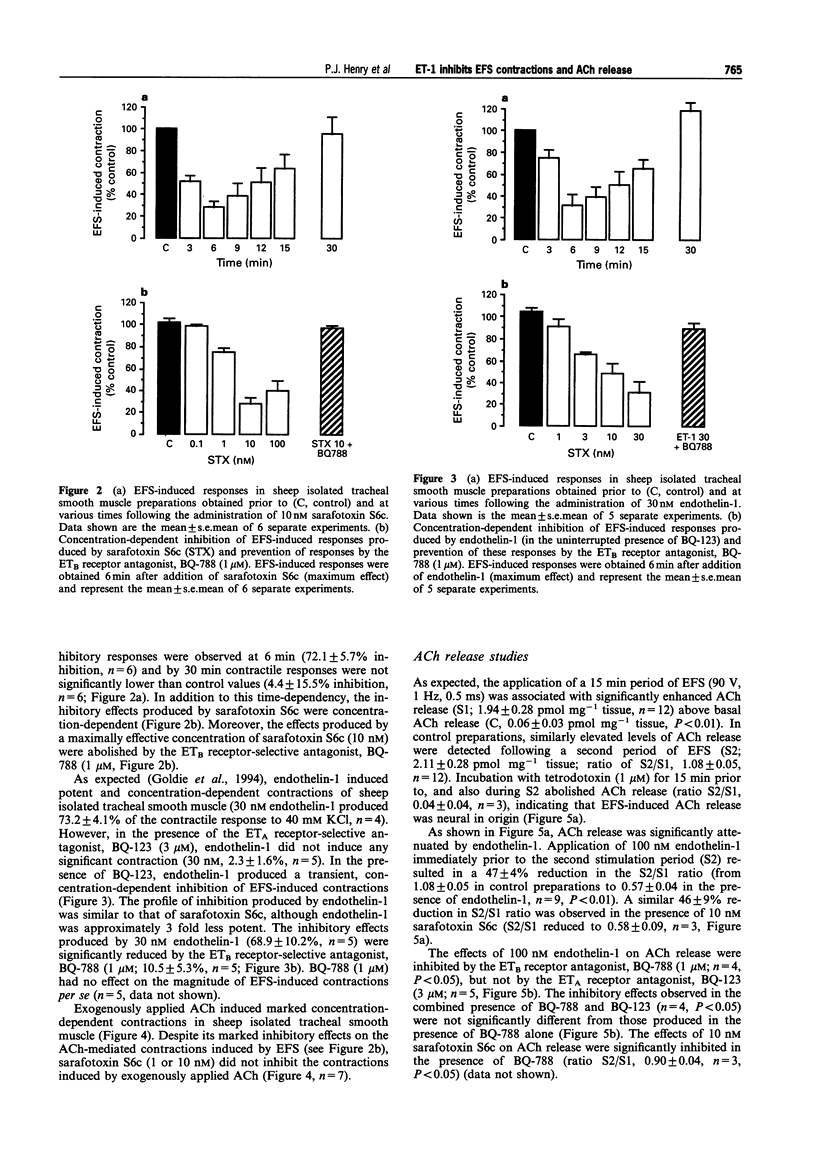
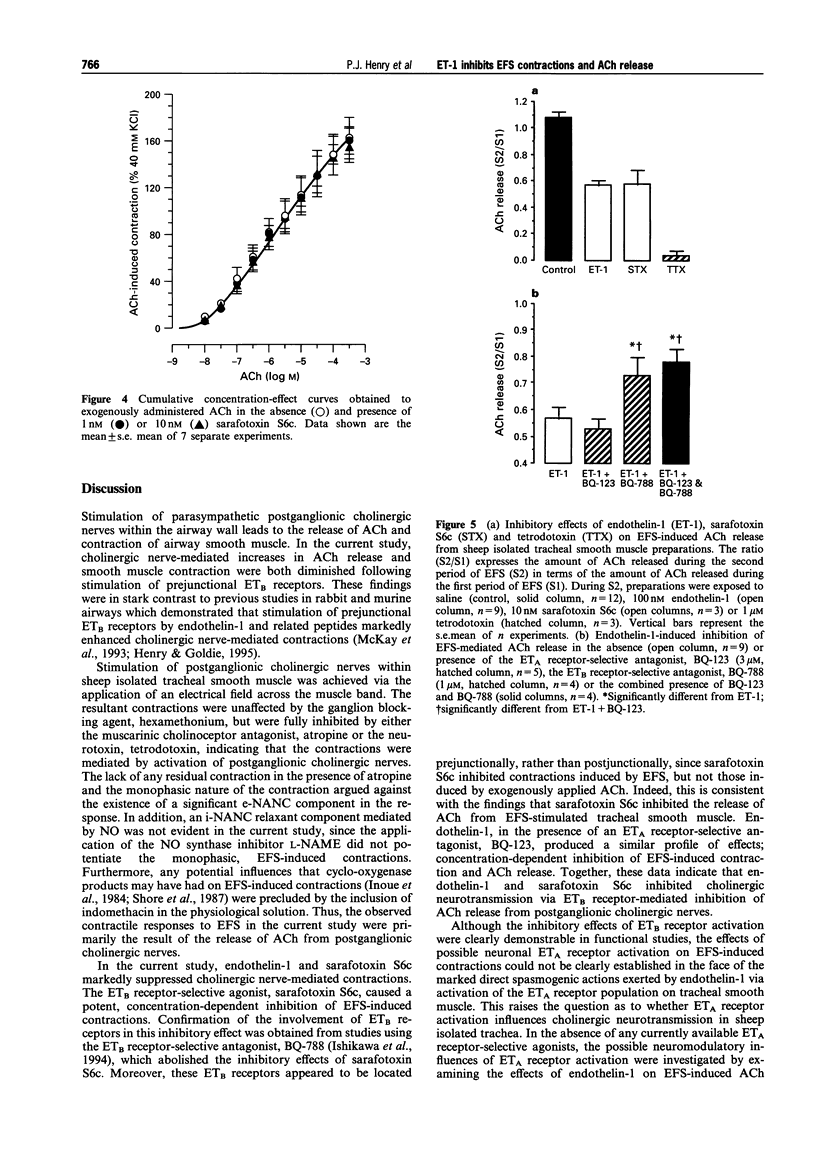
1. The relative roles of ETA and ETB receptor activation on cholinergic nerve-mediated contraction and acetylcholine (ACh) release were examined in sheep isolated tracheal smooth muscle. 2. Electrical field stimulation (EFS; 90 V, 0.5 ms duration, 1 Hz, 10 s train) applied to sheep isolated tracheal smooth muscle strips induced monophasic contractile responses that were abolished by either 1 microM tetrodotoxin or 0.1 microM atropine, but were insensitive to 10 microM hexamethonium and 100 microM L-NAME. Thus, EFS-induced contractions resulted from the spasmogenic actions of ACh released from parasympathetic, postganglionic nerves. 3. As expected, sheep isolated tracheal smooth muscle preparations did not contract in response to the ETB receptor-selective agonist, sarafotoxin S6c (0.1-100 nM). However, sarafotoxin S6c caused a concentration-dependent and transient inhibition of EFS-induced contractions. The inhibitory effect induced by a maximally effective concentration of sarafotoxin S6c (10 nM; 72.1 +/- 5.7%, n = 6) was abolished in the presence of the ETB receptor-selective antagonist BQ-788 (1 microM). Contractile responses to exogenously administered ACh (10 nM-0.3 mM) were not inhibited by sarafotoxin S6c (1 or 10 nM; n = 7). 4. In contrast to sarafotoxin S6c, endothelin-1 induced marked contractions in sheep isolated tracheal smooth muscle. These contractions were inhibited by BQ-123, consistent with an ETA receptor-mediated response. In the presence of BQ-123 (3 microM), endothelin-1 produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of EFS-induced contractions (30 nM endothelin-1, 68.9 +/- 10.2% inhibition, n = 5). These responses were inhibited by 1 microM BQ-788, indicative of an ETB receptor-mediated process. Endothelin-1 was about 3 fold less potent than sarafotoxin S6c. 5. EFS (90 V, 0.5 ms duration, 1 Hz, 15 min train) induced the release of endogenous ACh (1.94 +/- 0.28 pmol mg-1 tissue, n = 12), as assayed by h.p.l.c. with electrochemical detection. EFS-induced release of ACh was inhibited to a similar extent by 100 nM endothelin-1 (47 +/- 4%, n = 9) and 10 nM sarafotoxin S6c (46 +/- 9%, n = 3). These effects of endothelin-1 on ACh release were inhibited by 1 microM BQ-788 alone (n = 4), by BQ-788 in the presence of 3 microM BQ-123 (n = 4), but not by 3 microM BQ-123 alone (n = 5). 6. In summary, sheep isolated tracheal smooth muscle contains two anatomically and functionally distinct endothelin receptor populations. ETA receptors located on airway smooth muscle mediate contraction, whereas ETB receptors appear to exist on cholinergic nerves that innervate tracheal smooth muscle cells and mediate inhibition of ACh release. The inhibitory effect of ETB receptor stimulation on cholinergic neurotransmission is in stark contrast to the enhancing effects hitherto described in the airways.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Modulation of neurotransmission in airways. Physiol Rev. 1992 Jul;72(3):699–729. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.3.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Patacchini R., Barnes P. J., Maggi C. A. Facilitatory effects of selective agonists for tachykinin receptors on cholinergic neurotransmission: evidence for species differences. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):103–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton C. D., Barnes P. J. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways by opioids. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton C. D., Verleden G. M., Ledingham S. J., Yacoub M. H., Barnes P. J. Inhibition of cholinergic neurotransmission in human airways by opioids. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Mar;72(3):1096–1100. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.3.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. L., Johnson P. R., Alouan L., Armour C. L. Neurokinin A with K+ channel blockade potentiates contraction to electrical stimulation in human bronchus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 16;180(2-3):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90315-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. F., Evans T. W., Graf P. D., Nadel J. A. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in canine airways by thromboxane mimetic U46619. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 19;117(3):373–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaker E., Sallustio J., Kohler J., Visner G. Endothelin-1 expression in myenteric neurons cultured from rat small intestine. Regul Pept. 1995 Jan 26;55(2):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(94)00103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. L., Farmer S. G. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission by vasoactive intestinal peptide and peptide histidine isoleucine in guinea-pig tracheal smooth muscle. Pulm Pharmacol. 1989;2(2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(89)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer A. D., Maclagan J. Muscarinic inhibitory receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;83(4):973–978. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16539.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Grayson P. S., Knott P. G., Self G. J., Henry P. J. Predominance of endothelinA (ETA) receptors in ovine airway smooth muscle and their mediation of ET-1-induced contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):749–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães C. L., Rae G. A. Dual effects of endothelins -1, -2 and -3 on guinea pig field-stimulated ileum: possible mediation by two receptors coupled to pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jun;261(3):1253–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. K., Barnes P. J., Meldrum L. A., Maclagan J. Facilitation by tachykinins of neurotransmission in guinea-pig pulmonary parasympathetic nerves. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):274–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. J., Goldie R. G. Potentiation by endothelin-1 of cholinergic nerve-mediated contractions in mouse trachea via activation of ETB receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;114(3):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb17176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. J. Inhibitory effects of nordihydroguaiaretic acid on ETA-receptor-mediated contractions to endothelin-1 in rat trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):561–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Inhibitory histamine H3-receptors on cholinergic nerves in human airways. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 25;163(2-3):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Ito Y., Takeda K. Prostaglandin-induced inhibition of acetylcholine release from neuronal elements of dog tracheal tissue. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:553–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa K., Ihara M., Noguchi K., Mase T., Mino N., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Fukami T., Ozaki S., Nagase T. Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective endothelin B-receptor antagonist, BQ-788. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Pre- and post-junctional actions of procaterol, a beta 2-adrenoceptor stimulant, on dog tracheal tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):268–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbinger H., von Bardeleben R. S., Siefken H., Wolf D. Prejunctional muscarinic receptors regulating neurotransmitter release in airways. Life Sci. 1995;56(11-12):981–987. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(95)00037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay K. O., Armour C. L., Black J. L. Endothelin-3 increases transmission in the rabbit pulmonary parasympathetic nervous system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S181–S184. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi K., Ishikawa K., Yano M., Ahmed A., Cortes A., Abraham W. M. Endothelin-1 contributes to antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1995 Sep;79(3):700–705. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1995.79.3.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redington A. E., Springall D. R., Ghatei M. A., Lau L. C., Bloom S. R., Holgate S. T., Polak J. M., Howarth P. H. Endothelin in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and its relation to airflow obstruction in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Apr;151(4):1034–1039. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.4.7697227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoden K. J., Meldrum L. A., Barnes P. J. Inhibition of cholinergic neurotransmission in human airways by beta 2-adrenoceptors. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Aug;65(2):700–705. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.2.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serio R., Daniel E. E. Thromboxane effects on canine trachealis neuromuscular function. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 May;64(5):1979–1988. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.5.1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen A., Murray A. G., Mitchelson F. Extraction of acetylcholine and choline from physiological solutions for analysis by HPLC. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1995 Dec;34(4):215–218. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(95)00097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai M., Tsuruoka H., Wakabayashi S., Yamamoto Y., Takayanagi I. Pre- and postjunctional actions of endothelin in the rat iris sphincter preparation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;350(1):63–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00180012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S., Collier B., Martin J. G. Effect of endogenous prostaglandins on acetylcholine release from dog trachealis muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 May;62(5):1837–1844. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.5.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springall D. R., Howarth P. H., Counihan H., Djukanovic R., Holgate S. T., Polak J. M. Endothelin immunoreactivity of airway epithelium in asthmatic patients. Lancet. 1991 Mar 23;337(8743):697–701. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton C. D., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Modulation of neural bronchoconstrictor responses in the guinea pig respiratory tract by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Neuropeptides. 1991 Mar;18(3):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90107-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto M., Inui T., Okada T., Urade Y. Contraction of smooth muscle by activation of endothelin receptors on autonomic neurons. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 21;324(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80134-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki J., Sekizawa K., Graf P. D., Nadel J. A. Cholinergic neuromodulation by prostaglandin D2 in canine airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1396–1400. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka D. T., Grunstein M. M. Effect of substance P on neurally mediated contraction of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):458–463. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosterhout A. J., Hofman G., Woutersen-Van Nijnanten F. M., Nijkamp F. P. 5-HT1-like receptors mediate potentiation of cholinergic nerve-mediated contraction of isolated mouse trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 17;209(3):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90175-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Allcock G. H., Mickley E. J., Vane J. R. Characterization of endothelin receptors mediating the effects of the endothelin/sarafotoxin peptides on autonomic neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens and guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):783–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13880.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Robinson N. E., Wang Z. W., Lu M. C. Catecholamine affects acetylcholine release in trachea: alpha 2-mediated inhibition and beta 2-mediated augmentation. Am J Physiol. 1995 Mar;268(3 Pt 1):L368–L373. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1995.268.3.L368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


