Abstract
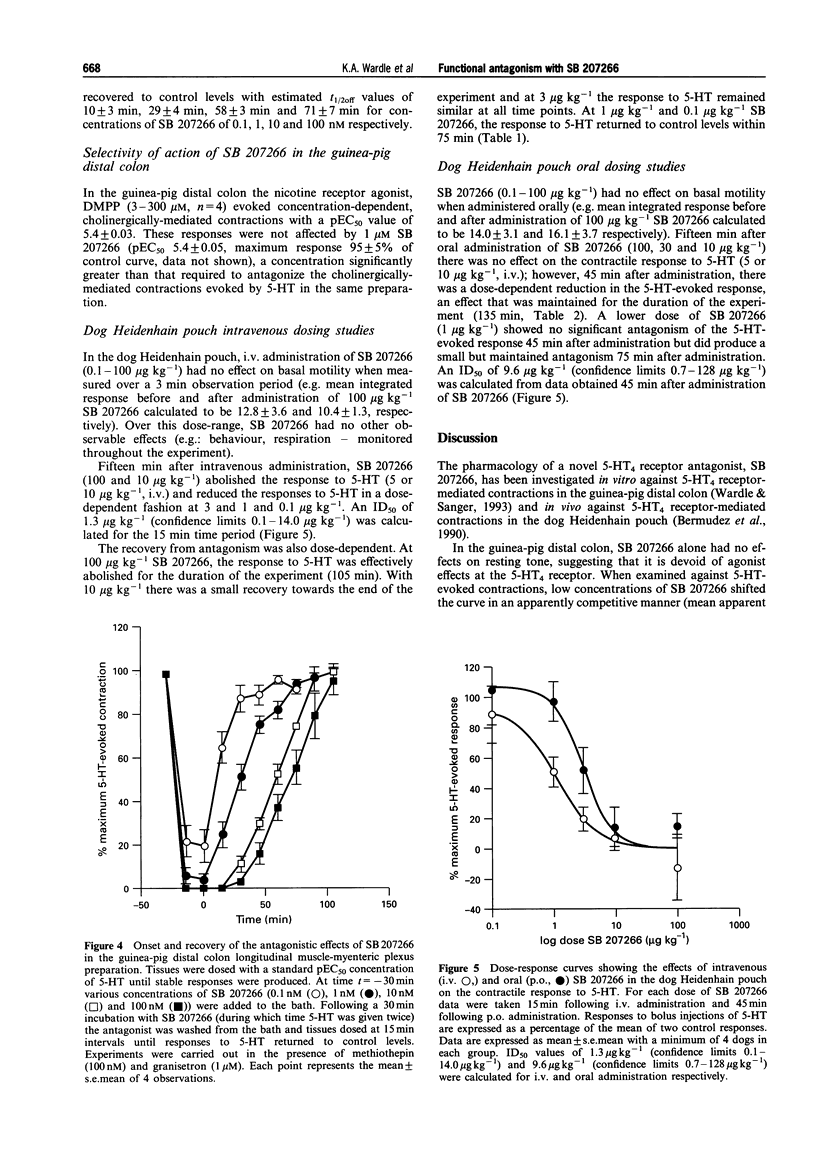
1. The pharmacology of a novel 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, SB 207266 has been evaluated in vitro in the guinea-pig distal colon longitudinal muscle myenteric plexus (LMMP) and in vivo in the dog Heidenhain pouch. 2. SB 207266 is a highly potent antagonist of 5-HT-evoked, cholinergically-mediated contractions in the guinea-pig distal colon. Low concentrations (0.1-10 nM) produced a parallel shift to the right of the concentration-effect curve (apparent pA2 10.6 +/- 0.1) with no significant effect on the maximum response. With higher concentrations of SB 207266 (30 nM and above) the maximum response to 5-HT was reduced. 3. The antagonism seen with SB 207266 cannot be attributed to a non-selective effect since high concentrations (1 microM) had no effect on cholinergically-mediated contractions evoked by the nicotinic receptor agonist DMPP in the same preparation. 4. SB 207266 is not an irreversible antagonist since the effects of the compound were reversible upon washing of the tissue. 5. In the dog Heidenhain pouch, oral (0.1-100 micrograms kg-1) and intravenous (0.1-100 micrograms kg-1) administration of SB 207266 produced a dose-dependent antagonism of the contractions evoked by a bolus intravenous injection of 5-HT. An ID50 for SB 207266 of 1.3 micrograms kg-1 was obtained following i.v. administration and 9.6 micrograms kg-1 following oral administration. 6. The antagonistic effects of SB 207266 (0.1-100 micrograms kg-1) in the dog Heidenhain pouch were long lasting since, following oral administration, the response to 5-HT was reduced for at least 135 min. 7. SB 207266 is a highly potent, highly selective and orally active 5-HT4 receptor antagonist. This compound is the first orally active amide to be identified in this class of antagonists and as such is an important new tool in the evaluation of 5-HT4 receptor function both in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
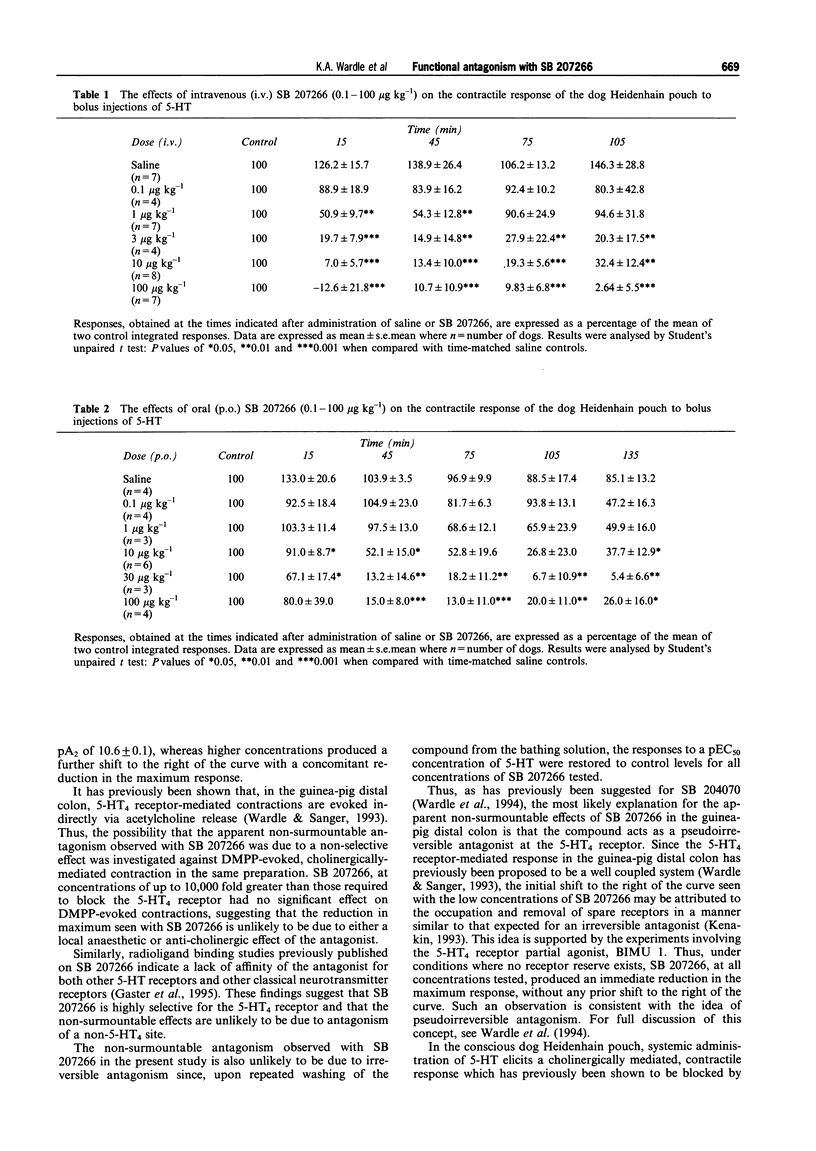
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham S., King B. F., Rushant B., Smith M. I., Gaster L., Sanger G. J. Antagonism by SB 204070 of 5-HT-evoked contractions in the dog stomach: an in-vivo model of 5-HT4 receptor function. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;47(3):219–222. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1995.tb05782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Clarke D. E. The 5-HT4 receptor. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):633–662. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaster L. M., Jennings A. J., Joiner G. F., King F. D., Mulholland K. R., Rahman S. K., Starr S., Wyman P. A., Wardle K. A., Ellis E. S. (1-Butyl-4-piperidinyl)methyl 8-amino-7-chloro-1,4-benzodioxane-5-carboxylate hydrochloride: a highly potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist derived from metoclopramide. J Med Chem. 1993 Dec 10;36(25):4121–4123. doi: 10.1021/jm00077a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaster L. M., Joiner G. F., King F. D., Wyman P. A., Sutton J. M., Bingham S., Ellis E. S., Sanger G. J., Wardle K. A. N-[(1-butyl-4-piperidinyl)methyl]-3,4dihydro-2H-[1,3]oxazino[3,2- a]indole10-carboxamide hydrochloride: the first potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist amide with oral activity. J Med Chem. 1995 Nov 24;38(24):4760–4763. doi: 10.1021/jm00024a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. J., Kilpatrick G. J., Bunce K. T. Development of a radioligand binding assay for 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig and rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):618–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson D. H., Barnard E. A., Hoyer D., Humphrey P. P., Leff P., Shankley N. P. International Union of Pharmacology Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification. IX. Recommendations on terms and symbols in quantitative pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):255–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonini M., Rizzi C. A., Manzo L., Onori L. Novel enteric 5-HT4 receptors and gastrointestinal prokinetic action. Pharmacol Res. 1991 Jul;24(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/1043-6618(91)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle K. A., Ellis E. S., Baxter G. S., Kennett G. A., Gaster L. M., Sanger G. J. The effects of SB 204070, a highly potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, on guinea-pig distal colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):789–794. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle K. A., Sanger G. J. The guinea-pig distal colon--a sensitive preparation for the investigation of 5-HT4 receptor-mediated contractions. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1593–1599. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb14006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


