Abstract
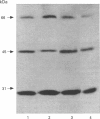
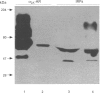
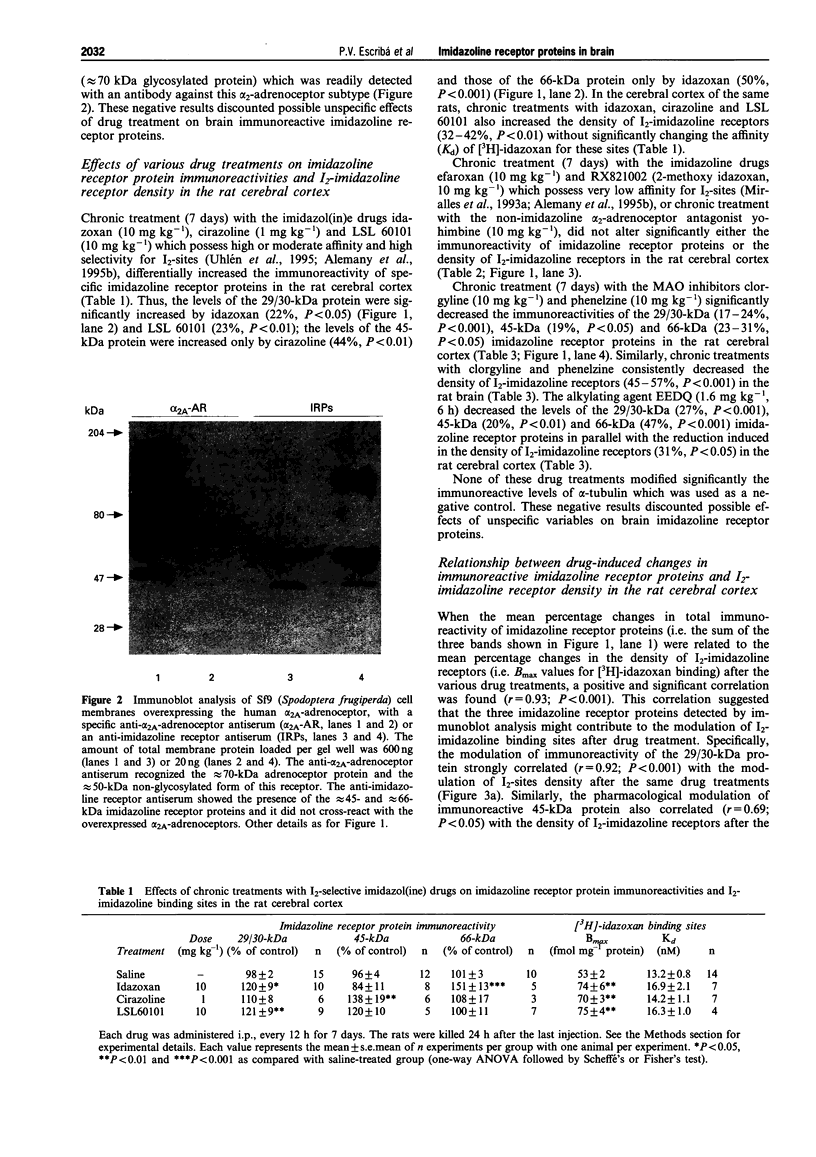
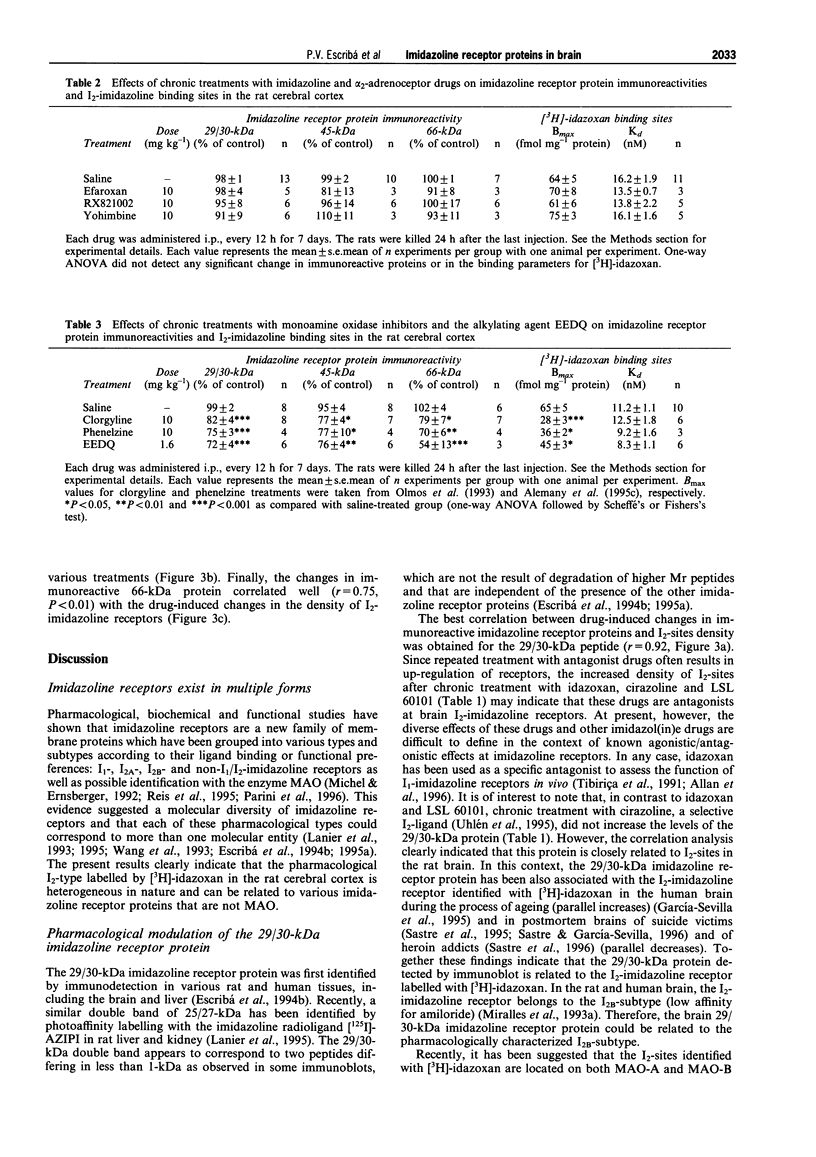
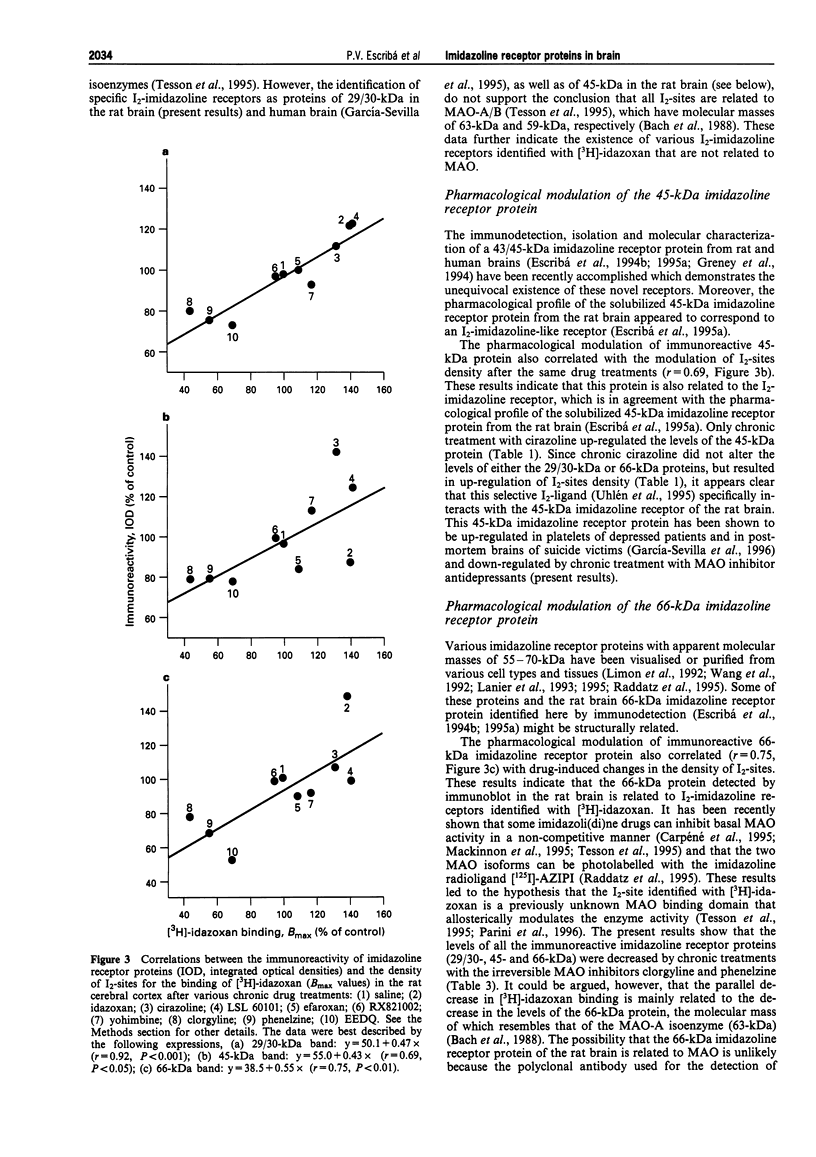
1. The densities of various imidazoline receptor proteins (with apparent molecular masses of approximately 29/30-45- and 66-kDa) were quantitated by immunoblotting in the rat cerebral cortex after various drug treatments. The modulation of these imidazoline receptor proteins was then compared with the changes in the density of non-adrenoceptor [3H]-idazoxan binding sites (I2-sites) induced by the same drug treatments. 2. Chronic treatment (7 days) with the I2-selective imidazol(in)e drugs idazoxan (10 mg kg-1), cirazoline (1 mg kg-1) and LSL 60101 (10 mg kg-1) differentially increased the immunoreactivity of imidazoline receptor proteins. The levels of the 29/30-kDa protein were increased by idazoxan and LSL 60101 (23%), the levels of the 45-kDa protein only by cirazoline (44%) and those of the 66-kDa protein only by idazoxan (50%). These drug treatments also increased the density of I2-sites (32-42%). 3. Chronic treatment (7 days) with efaroxan (10 mg kg-1), RX821002 (10 mg kg-1) and yohimbine (10 mg kg-1), which possess very low affinity for I2-imidazoline receptors, did not alter either the immunoreactivity of imidazoline receptor proteins or the density of I2-sites. 4. Chronic treatment (7 days) with the monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors clorgyline (10 mg kg-1) and phenelzine (10 mg kg-1) decreased the immunoreactivity of the 29/30-kDa (17-24%), 45-kDa (19%) and 66-kDa (23-31%) imidazoline receptor proteins. The alkylating agent N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1, 2-dihydroquinoline (1.6 mg kg-1, 6 h) also decreased the levels of the three imidazoline receptor proteins (20-47%). These drug treatments consistently decreased the density of I2-sites (31-57%). 5. Significant correlations were found when the mean percentage changes in immunoreactivity of imidazoline receptor proteins were related to the mean percentage changes in the density of I2-sites after the various drug treatments (r = 0.92 for the 29/30-kDa protein, r = 0.69 for the 45-kDa protein and r = 0.75 for the 66-kDa protein). 6. In the rat cerebral cortex the I2-imidazoline receptor labelled by [3H]-idazoxan is heterogeneous in nature and the related imidazoline receptor proteins (29/30-, 45- and 66-kDa) detected by immunoblotting contribute differentially to the modulation of I2-sites after drug treatment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany R., Olmos G., Escribá P. V., Menargues A., Obach R., García-Sevilla J. A. LSL 60101, a selective ligand for imidazoline I2 receptors, on glial fibrillary acidic protein concentration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul 4;280(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemany R., Olmos G., García-Sevilla J. A. The effects of phenelzine and other monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants on brain and liver I2 imidazoline-preferring receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;114(4):837–845. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D. R., Penner S. B., Smyth D. D. Antagonism by idazoxan at low dose but not high dose, of the natriuretic action of moxonidine. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;117(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach A. W., Lan N. C., Johnson D. L., Abell C. W., Bembenek M. E., Kwan S. W., Seeburg P. H., Shih J. C. cDNA cloning of human liver monoamine oxidase A and B: molecular basis of differences in enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4934–4938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Schwartz J. Central cardiovascular effects of alpha adrenergic drugs: differences between catecholamines and imidazolines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jul;230(1):232–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpéné C., Collon P., Remaury A., Cordi A., Hudson A., Nutt D., Lafontan M. Inhibition of amine oxidase activity by derivatives that recognize imidazoline I2 sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Feb;272(2):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Brown C. A., Scarpello K. E., Morgan N. G. The imidazoline site involved in control of insulin secretion: characteristics that distinguish it from I1- and I2-sites. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;112(4):1065–1070. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Eldar-Geva T., Atlas D. Imidazoline binding sites in human placenta: evidence for heterogeneity and a search for physiological function. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):101–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escriba P. V., Sastre M., Garcia-Sevilla J. A. Increased density of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in the postmortem brains of heroin addicts. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Jun;51(6):494–501. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950060058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escribá P. V., Ozaita A., Miralles A., Reis D. J., García-Sevilla J. A. Molecular characterization and isolation of a 45-kilodalton imidazoline receptor protein from the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995 Sep;32(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escribá P. V., Sastre M., García-Sevilla J. A. Disruption of cellular signaling pathways by daunomycin through destabilization of nonlamellar membrane structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7595–7599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escribá P. V., Sastre M., Wang H., Regunathan S., Reis D. J., García-Sevilla J. A. Immunodetection of putative imidazoline receptor proteins in the human and rat brain and other tissues. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Aug 29;178(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M. J., Ernsberger P., Regunathan S., Reis D. J. Regulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene expression by imidazoline receptors in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1995 Sep;65(3):988–997. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65030988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sevilla J. A., Sastre M., Escribá P. V. Age-dependent increases of immunoreactive imidazoline receptors in the human brain: possible association of a 29/30 kDa protein with the I2-imidazoline receptor identified by [3H]idazoxan. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Jan 23;184(2):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)11188-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Molderings G. J. Involvement of presynaptic imidazoline receptors in the alpha 2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of noradrenaline release by imidazoline derivatives. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00251126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier B., Raddatz R., Bakthavachalam V., Coupry I., Neumeyer J. L., Lanier S. M. Structural and ligand recognition properties of imidazoline binding proteins in tissues of rat and rabbit. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;48(4):703–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Ivkovic B., Singh I., Neumeyer J. L., Bakthavachalam V. Visualization of multiple imidazoline/guanidinium-receptive sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):16047–16051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Regunathan S., Barrow C. J., Eshraghi J., Cooper R., Reis D. J. Agmatine: an endogenous clonidine-displacing substance in the brain. Science. 1994 Feb 18;263(5149):966–969. doi: 10.1126/science.7906055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limon I., Coupry I., Lanier S. M., Parini A. Purification and characterization of mitochondrial imidazoline-guanidinium receptive site from rabbit kidney. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21645–21649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Ernsberger P. Keeping an eye on the I site: imidazoline-preferring receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miralles A., Olmos G., Sastre M., Barturen F., Martin I., Garcia-Sevilla J. A. Discrimination and pharmacological characterization of I2-imidazoline sites with [3H]idazoxan and alpha-2 adrenoceptors with [3H]RX821002 (2-methoxy idazoxan) in the human and rat brains. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Mar;264(3):1187–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miralles A., Ribas C., Olmos G., García-Sevilla J. A. Differential effects of the alkylating agent N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline on brain alpha 2-adrenoceptors and I2-imidazoline sites in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 1993 Nov;61(5):1602–1610. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb09793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molderings G. J., Göthert M. Inhibitory presynaptic imidazoline receptors on sympathetic nerves in the rabbit aorta differ from I1- and I2-imidazoline binding sites. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 May;351(5):507–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00171042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molderings G. J., Moura D., Fink K., Bönisch H., Göthert M. Binding of [3H]clonidine to I1-imidazoline sites in bovine adrenal medullary membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;348(1):70–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00168539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Alemany R., Escriba P. V., García-Sevilla J. A. The effects of chronic imidazoline drug treatment on glial fibrillary acidic protein concentrations in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):997–1002. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Gabilondo A. M., Miralles A., Escriba P. V., García-Sevilla J. A. Chronic treatment with the monoamine oxidase inhibitors clorgyline and pargyline down-regulates non-adrenoceptor [3H]-idazoxan binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):597–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Kulkarni R. N., Haque M., MacDermot J. Imidazolines stimulate release of insulin from RIN-5AH cells independently from imidazoline I1 and I2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 1;262(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parini A., Moudanos C. G., Pizzinat N., Lanier S. M. The elusive family of imidazoline binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1996 Jan;17(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(96)81564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piletz J. E., Chikkala D. N., Ernsberger P. Comparison of the properties of agmatine and endogenous clonidine-displacing substance at imidazoline and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Feb;272(2):581–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineda J., Ugedo L., García-Sevilla J. A. Stimulatory effects of clonidine, cirazoline and rilmenidine on locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurones: possible involvement of imidazoline-preferring receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;348(2):134–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00164789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raddatz R., Parini A., Lanier S. M. Imidazoline/guanidinium binding domains on monoamine oxidases. Relationship to subtypes of imidazoline-binding proteins and tissue-specific interaction of imidazoline ligands with monoamine oxidase B. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 17;270(46):27961–27968. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.46.27961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regunathan S., Feinstein D. L., Reis D. J. Expression of non-adrenergic imidazoline sites in rat cerebral cortical astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Apr 15;34(6):681–688. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490340611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastre M., Escribá P. V., Reis D. J., García-Sevilla J. A. Decreased number and immunoreactivity of I2-imidazoline receptors in the frontal cortex of suicide victims. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jul 12;763:520–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb32444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastre M., Ventayol P., García-Sevilla J. A. Decreased density of I2-imidazoline receptors in the postmortem brain of heroin addicts. Neuroreport. 1996 Jan 31;7(2):509–512. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199601310-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. Dual action of clonidine on insulin release: suppression, but stimulation when alpha 2-adrenoceptors are blocked. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):712–714. doi: 10.1007/BF00717749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesson F., Limon-Boulez I., Urban P., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J., Coupry I., Pompon D., Parini A. Localization of I2-imidazoline binding sites on monoamine oxidases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9856–9861. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibiriça E., Feldman J., Mermet C., Gonon F., Bousquet P. An imidazoline-specific mechanism for the hypotensive effect of clonidine: a study with yohimbine and idazoxan. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):606–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Muceniece R., Rangel N., Tiger G., Wikberg J. E. Comparison of the binding activities of some drugs on alpha 2A, alpha 2B and alpha 2C-adrenoceptors and non-adrenergic imidazoline sites in the guinea pig. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995 Jun;76(6):353–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1995.tb00161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Regunathan S., Meeley M. P., Reis D. J. Isolation and characterization of imidazoline receptor protein from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;42(5):792–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Regunathan S., Ruggiero D. A., Reis D. J. Production and characterization of antibodies specific for the imidazoline receptor protein. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;43(4):509–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]