Abstract
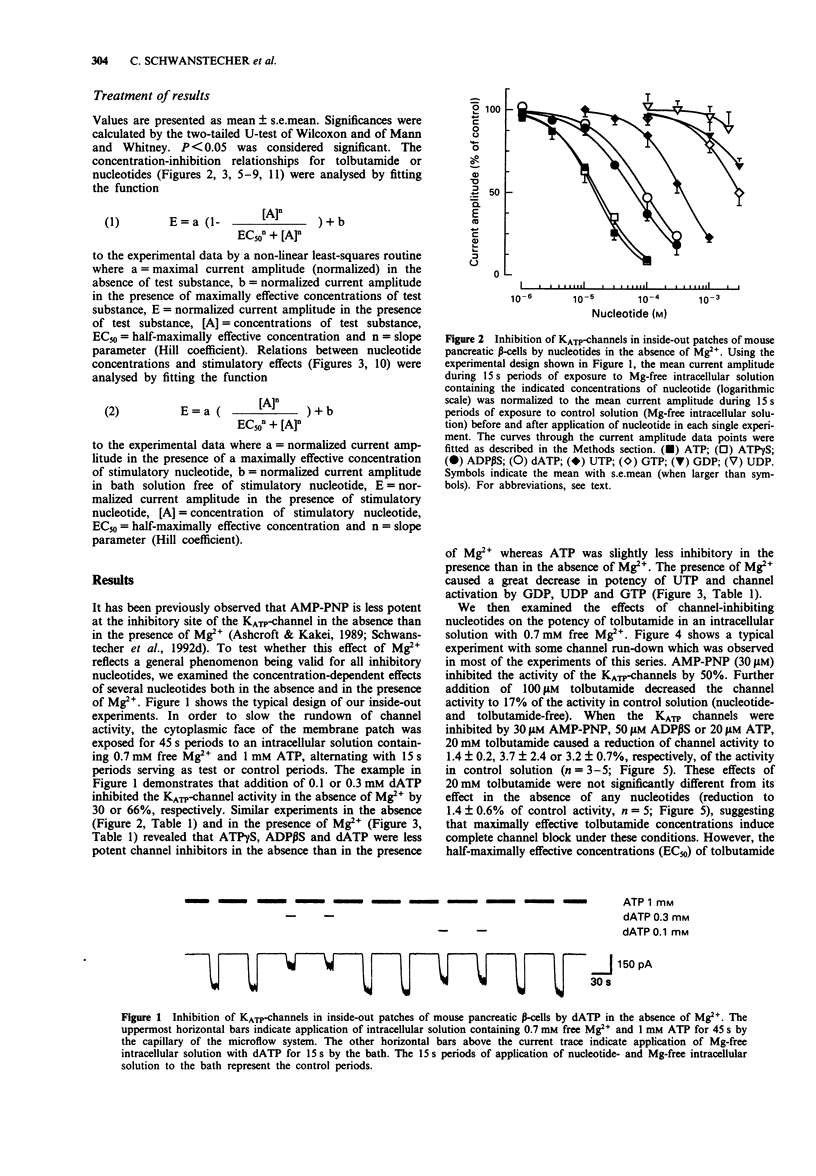
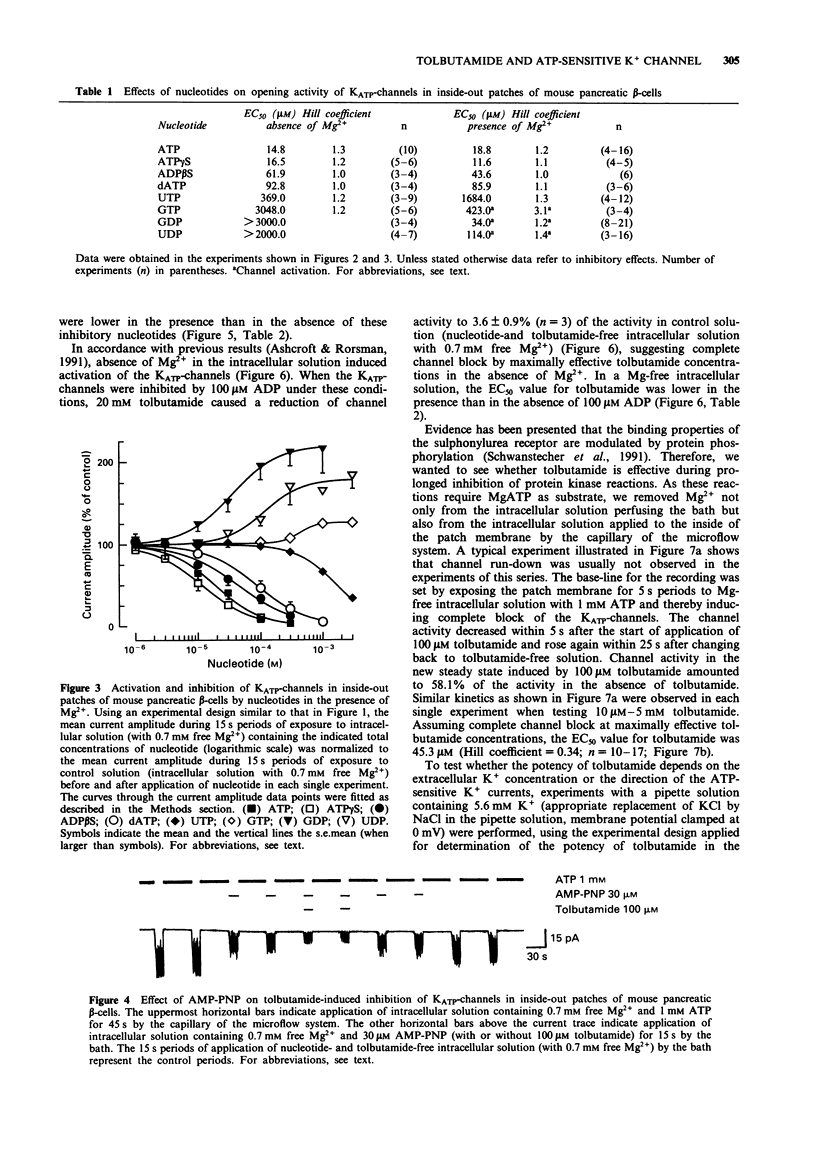
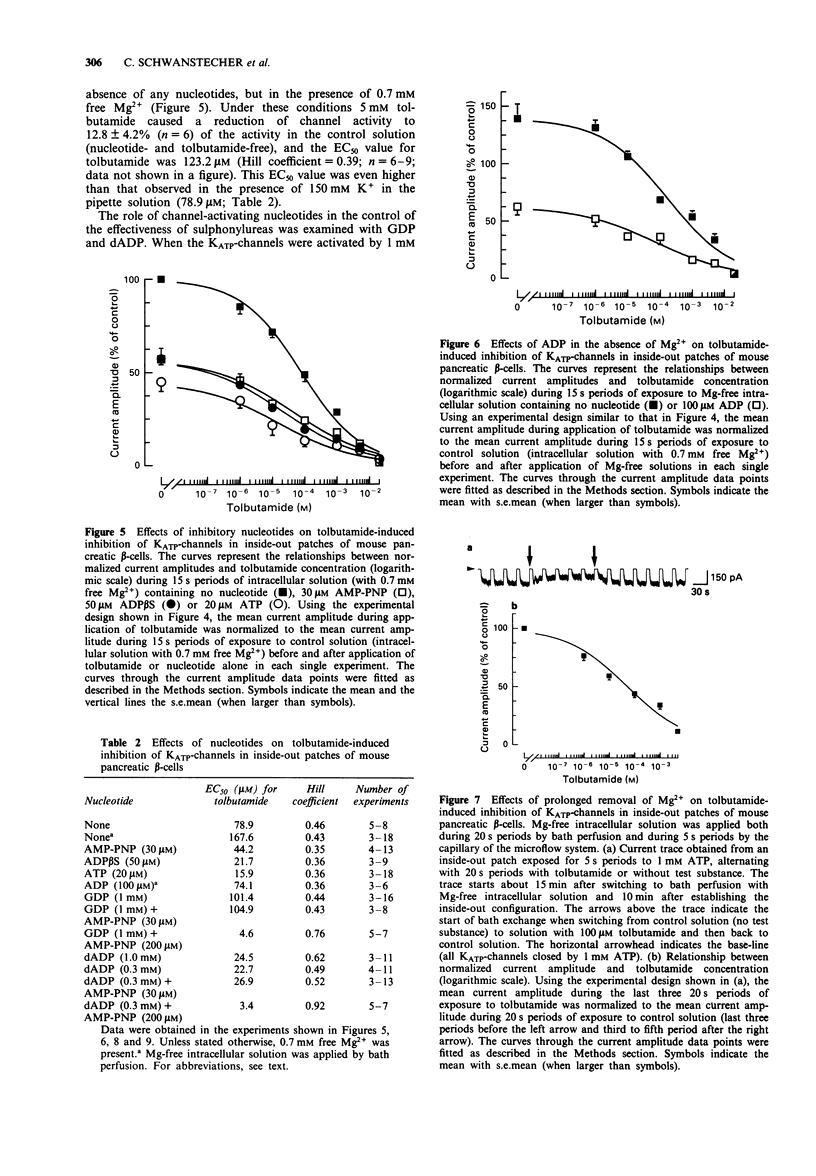
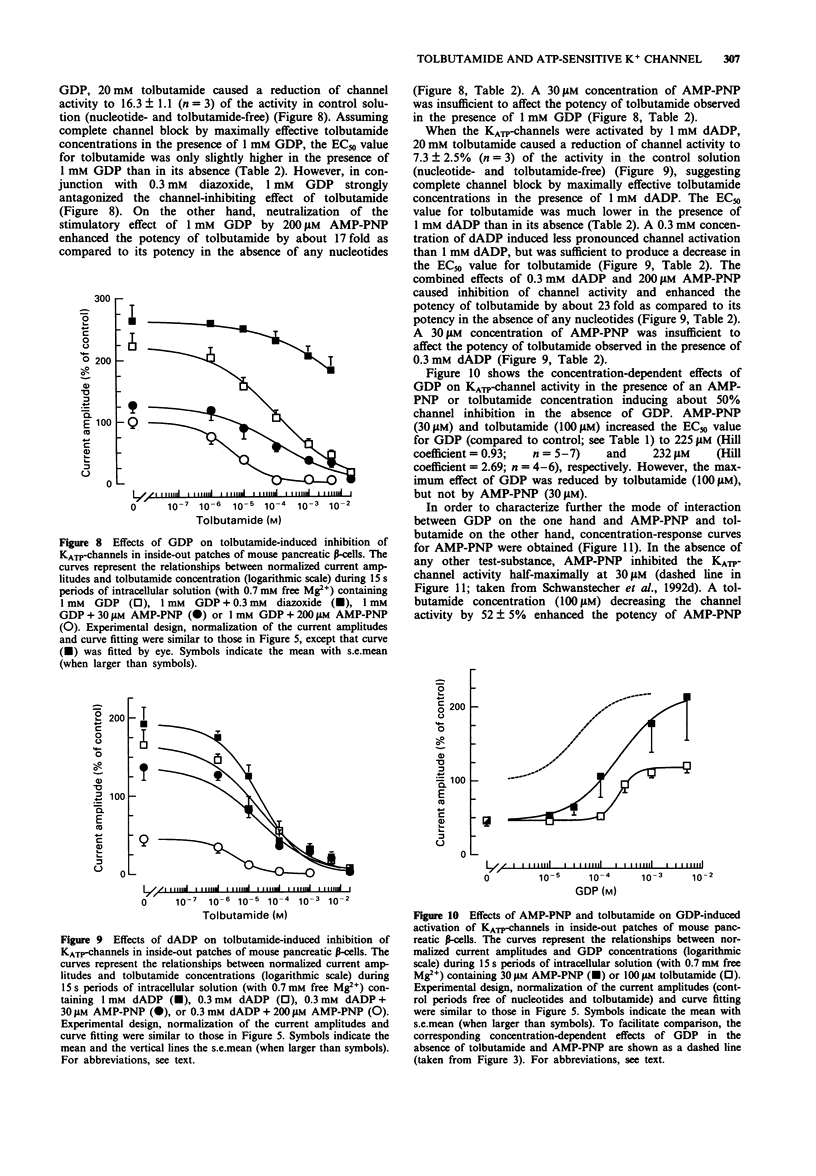
1. In mouse pancreatic beta-cells the role of cytosolic nucleotides in the regulation of the sulphonylurea sensitivity of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive K+ channel (KATP-channel) was examined. Patch-clamp experiments with excised inside-out membrane patches were carried out using an experimental protocol favouring phosphorylation of membrane proteins. 2. In the absence of Mg2+, the KATP-channel-inhibiting potency of cytosolic nucleotides decreased in the order ATP = adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (ATP gamma S) > adenosine 5'-diphosphate (ADP) > adenosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (ADP beta S) = adenylyl-imidodiphosphate (AMP-PNP) > 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-triphosphate (dATP) > uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) > 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-diphosphate (dADP) > guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP) > guanosine 5'-diphosphate (GDP) > uridine 5'-diphosphate (UDP). 3. In the presence of Mg2+, the inhibitory potency of cytosolic nucleotides decreased in the order ATP gamma S > ATP > AMP-PNP > ADP beta S > dATP > UTP. In the presence of Mg2+, the KATP-channels were activated by dADP, GTP, GDP and UDP. 4. Tolbutamide inhibited the KATP-channels not only in the presence but also in the prolonged absence of Mg2+. In nucleotide-free solutions, the potency of tolbutamide was very low. When about half of the KATP-channel activity was inhibited by ATP, AMP-PNP, ADP beta S or ADP (absence of Mg2+), the potency of tolbutamide was increased. 5. Tolbutamide (100 microM) slightly enhanced the channel-inhibiting potency of AMP-PNP and inhibited the channel-activating effect of MgGDP in a non-competitive manner.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kakei M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells: modulation by ATP and Mg2+ ions. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:349–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(2):87–143. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. The sulfonylurea receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 15;1175(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90008-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokvist K., Ammälä C., Ashcroft F. M., Berggren P. O., Larsson O., Rorsman P. Separate processes mediate nucleotide-induced inhibition and stimulation of the ATP-regulated K(+)-channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Feb 22;243(1307):139–144. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Potassium selective ion channels in insulin-secreting cells: physiology, pharmacology and their role in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J. Protein phosphorylation is required for diazoxide to open ATP-sensitive potassium channels in insulin (RINm5F) secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80734-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis K. D., Gee W. M., Hammoud A., McDaniel M. L., Falke L. C., Misler S. Effects of sulfonamides on a metabolite-regulated ATPi-sensitive K+ channel in rat pancreatic B-cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):C1119–C1127. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.6.C1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1043–1052. doi: 10.1007/BF01971450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski R. Z., Ashford M. L. ATP-sensitive K(+)-channel run-down is Mg2+ dependent. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jun 22;240(1298):397–410. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski R. Z., Ashford M. L. Nucleotide-dependent activation of KATP channels by diazoxide in CRI-G1 insulin-secreting cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):34–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski R. Z., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Dual effects of diazoxide on ATP-K+ currents recorded from an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1039–1050. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson O., Ammälä C., Bokvist K., Fredholm B., Rorsman P. Stimulation of the KATP channel by ADP and diazoxide requires nucleotide hydrolysis in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:349–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Nichols C. G. Nucleotide modulation of the activity of rat heart ATP-sensitive K+ channels in isolated membrane patches. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:193–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Shosaku T., Zünkler B. J., Trube G. Dual effects of ATP on K+ currents of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Feb;408(2):133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00581342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Burgfeld J., Goerke F., Rennicke M., Schwanstecher M., Wallasch A., Zünkler B. J., Lenzen S. Control of insulin secretion by sulfonylureas, meglitinide and diazoxide in relation to their binding to the sulfonylurea receptor in pancreatic islets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 15;38(8):1217–1229. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Heipel C., Rosenberger F., Scheffer K., Zünkler B. J., Schwanstecher C. Tolbutamide-sensitivity of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;342(5):566–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00169047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Schwanstecher M., Schwanstecher C. Pancreatic and extrapancreatic sulfonylurea receptors. Horm Metab Res. 1992 Dec;24(12):549–554. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro V. L., Hermes J. D., Cleland W. W. Stability constants of Mg2+ and Cd2+ complexes of adenine nucleotides and thionucleotides and rate constants for formation and dissociation of MgATP and MgADP. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5262–5271. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher C., Dickel C., Ebers I., Lins S., Zünkler B. J., Panten U. Diazoxide-sensitivity of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher M., Behrends S., Brandt C., Panten U. The binding properties of the solubilized sulfonylurea receptor from a pancreatic B-cell line are modulated by the Mg(++)-complex of ATP. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Aug;262(2):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher M., Brandt C., Behrends S., Schaupp U., Panten U. Effect of MgATP on pinacidil-induced displacement of glibenclamide from the sulphonylurea receptor in a pancreatic beta-cell line and rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;106(2):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher M., Löser S., Rietze I., Panten U. Phosphate and thiophosphate group donating adenine and guanine nucleotides inhibit glibenclamide binding to membranes from pancreatic islets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;343(1):83–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00180681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Studies of the unitary properties of adenosine-5'-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:213–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Ashford M. L., Cook D. L., Hales C. N. The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):474–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Kozlowski R. Z., Carrington C. A., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung R. T., Kurachi Y. On the mechanism of nucleotide diphosphate activation of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in ventricular cell of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Lins S., Ohno-Shosaku T., Trube G., Panten U. Cytosolic ADP enhances the sensitivity to tolbutamide of ATP-dependent K+ channels from pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80925-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


