Abstract
1. Lithium salts, used in the treatment of affective disorders, may have adverse effects on glucose tolerance in man, and suppress glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in rats. 2. To study the interaction of these effects with pre-existing diabetes mellitus, plasma glucose and insulin responses to lithium chloride were measured in male Wistar rats made diabetic with intraperitoneal streptozotocin, and in normal controls. 3. In both normal and diabetic anaesthetized rats, intravenous lithium (4 mEq kg-1) caused a rise in plasma glucose. In absolute terms, the rise was greater in diabetic (5.2 mmol l-1) than in normal rats (2.3 mmol l-1). 4. Plasma insulin concentrations were reduced by lithium in normal rats, but the low insulin concentrations measured in the diabetic rats were not significantly changed. 5. After intravenous glucose (0.5 g kg-1), lithium-treated diabetic rats showed a second rise in plasma glucose at 60-90 min without any insulin response, while normal rats showed typically reduced insulin responses and initial glucose disappearance rates. 6. Intravenous glucose reduced plasma glucagon concentrations to a greater extent in normal than in diabetic rats, but lithium induced an equal rise in plasma glucagon in both groups, with a time-course similar to that of the hyperglycaemic effect. 7. The hyperglycaemic action of lithium is greater in the hypoinsulinaemic diabetic rats and appears to involve a stimulation of glucagon secretion in both normal and diabetic animals.
Full text
PDF
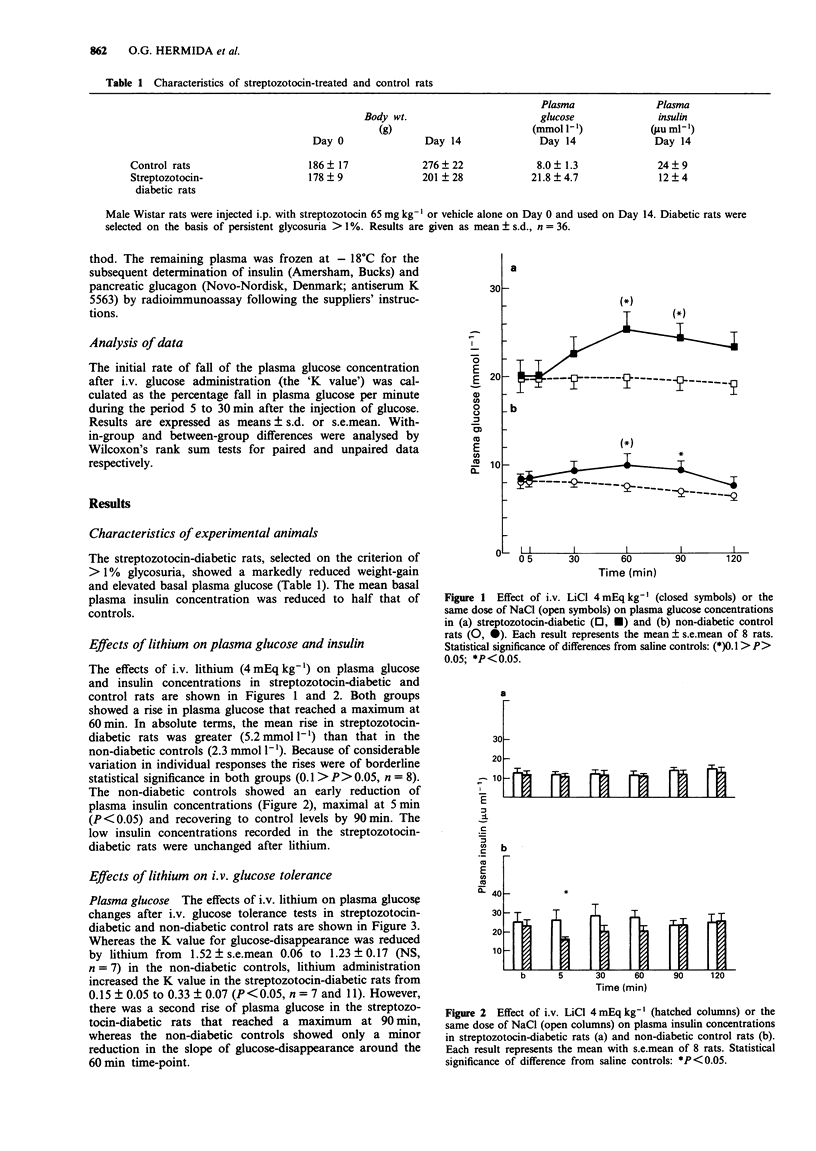
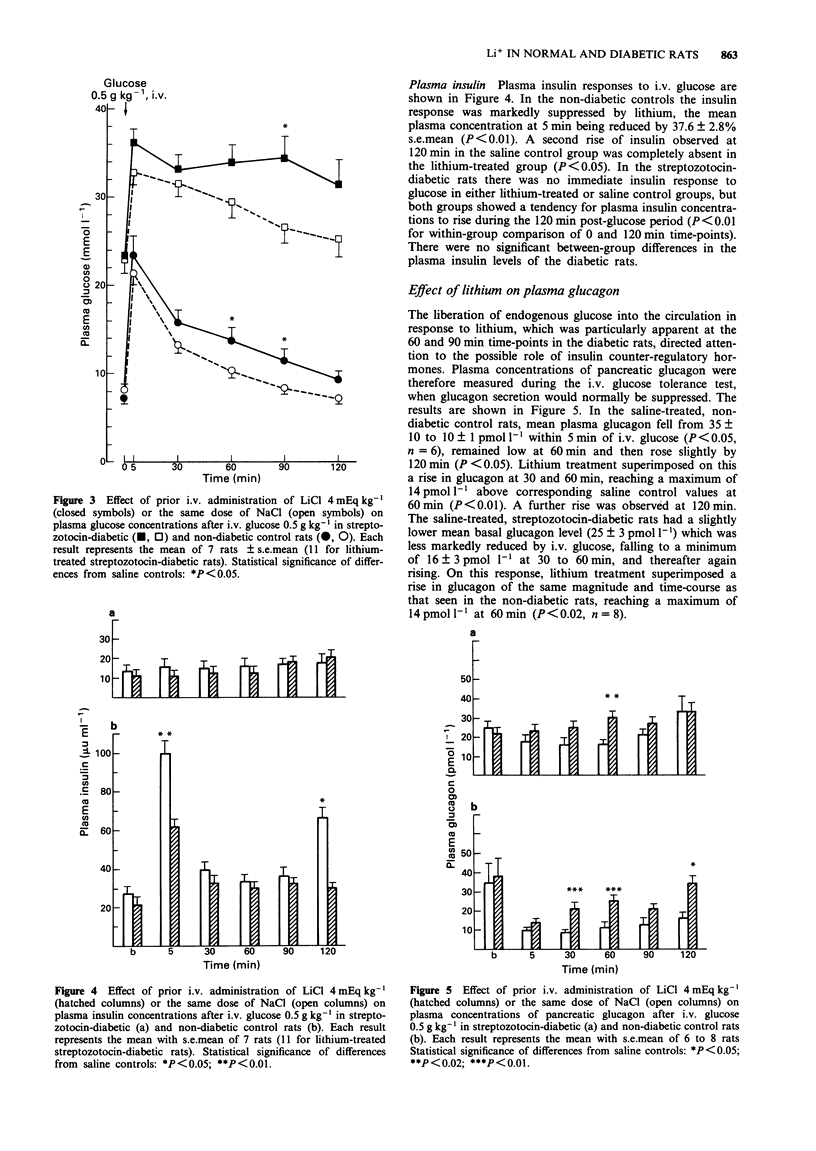


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. H., Jr, Blackard W. G. Effect of lithium on pancreatic islet insulin release. Endocrinology. 1978 Jan;102(1):291–295. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-1-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA G. Influence of ions on the uptake of glucose and on the effect of insulin on it by rat diaphragm. Nature. 1959 Jan 31;183(4657):324–325. doi: 10.1038/183324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya G. Effects of metal ions on the utilization of glucose and on the influence of insulin on it by the isolated rat diaphragm. Biochem J. 1961 May;79(2):369–377. doi: 10.1042/bj0790369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipponi P., Gregorio F., Ferrandina C., Nicoletti I., Mannarelli C., Pippi R., Santeusanio F. Alpha-adrenergic system in the modulation of pancreatic A and B cell function in normal rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1986 Nov-Dec;2(6):325–336. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(86)80069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontela T., Garcia Hermida O., Gómez-Acebo J. Dihydroergotamine, but not naloxone, counteracts lithium as an inhibitor of glucose-induced insulin release in isolated rat islets in vitro. Diabetologia. 1987 Mar;30(3):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00274225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontela T., García Hermida O., Gómez-Acebo J. Blocking effect of naloxone, dihydroergotamine and adrenalectomy in lithium-induced hyperglycaemia and glucose intolerance in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1986 Mar;111(3):342–348. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1110342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontela T., García Hermida O., Gómez-Acebo J. Role of adrenoceptors in vitro and in vivo in the effects of lithium on blood glucose levels and insulin secretion in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García Hermida O., Fontela T., Ghiglione M., Uttenthal L. O. Effect of pertussis pretreatment on plasma glucose and insulin responses to lithium in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1309–1312. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09785.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio F., Filipponi P., Cristallini S., Carloni C., Moretti I., Ferrandina C., Pippi R., Pietropaolo M. Effects of beta non-selective and beta 1 selective adrenergic blocking agents on glucagon secretion from isolated perfused rat pancreas. J Endocrinol Invest. 1986 Jun;9(3):209–215. doi: 10.1007/BF03348100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Hillaire-Buys D., Ribes G., Loubatières-Mariani M. M. Diabetes alters the responses of glucagon secreting cells and vascular bed to isoprenaline and forskolin in vitro in rat pancreas. Life Sci. 1991;48(24):2349–2358. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90272-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. R., Lazarus J. H., Davies C. J., Greenwood R. H. The effect of short term lithium carbonate in Type II diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 1983 Sep;15(9):422–424. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellerup E. T., Thomsen H. G., Plenge P., Rafaelsen O. J. Lithium effect on plasma glucagon, liver phosphorylase-alpha and liver glycogen in rats. J Psychiatr Res. 1970 Oct;8(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(70)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L. Normalization of insulin sensitivity with lithium in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1989 May;38(5):648–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.5.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit F. C., Pipeleers D. G. Differences in adrenergic recognition by pancreatic A and B cells. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):875–877. doi: 10.1126/science.2871625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah J. H., DeLeon-Jones F. A., Schickler R., Nasr S., Mayer M., Hurks C. Symptomatic reactive hypoglycemia during glucose tolerance test in lithium-treated patients. Metabolism. 1986 Jul;35(7):634–639. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah J. H., Pishdad G. The effect of lithium on glucose- and tolbutamide-induced insulin release and glucose tolerance in the intact rat. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1300–1304. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Glucagon and the A cell: physiology and pathophysiology (first two parts). N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 18;304(25):1518–1524. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106183042504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendsborg P. B. Lithium treatment and glucose tolerance in manic-melancholic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1979 Mar;59(3):306–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1979.tb06969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendsborg P. B., Rafaelsen O. J. Lithium in man: effect on glucose tolerance and serum electrolytes. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1973;49(5):601–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1973.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


