Abstract
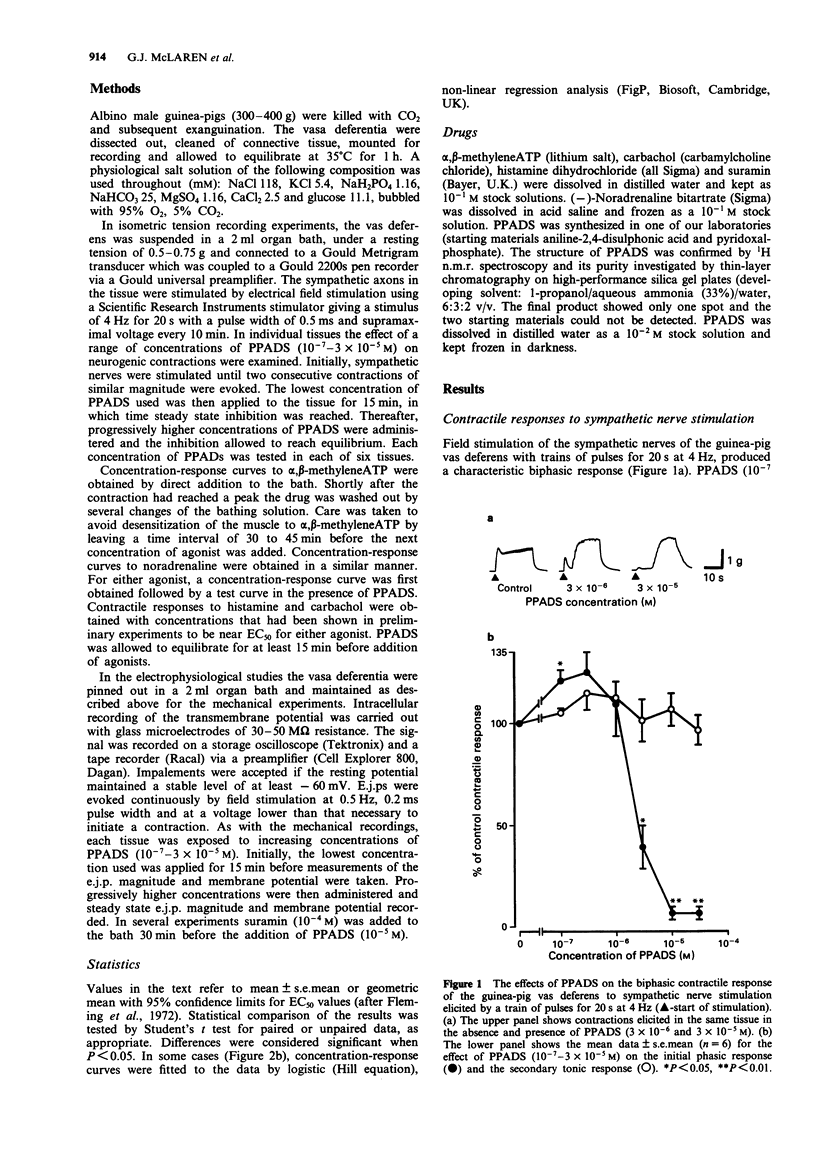
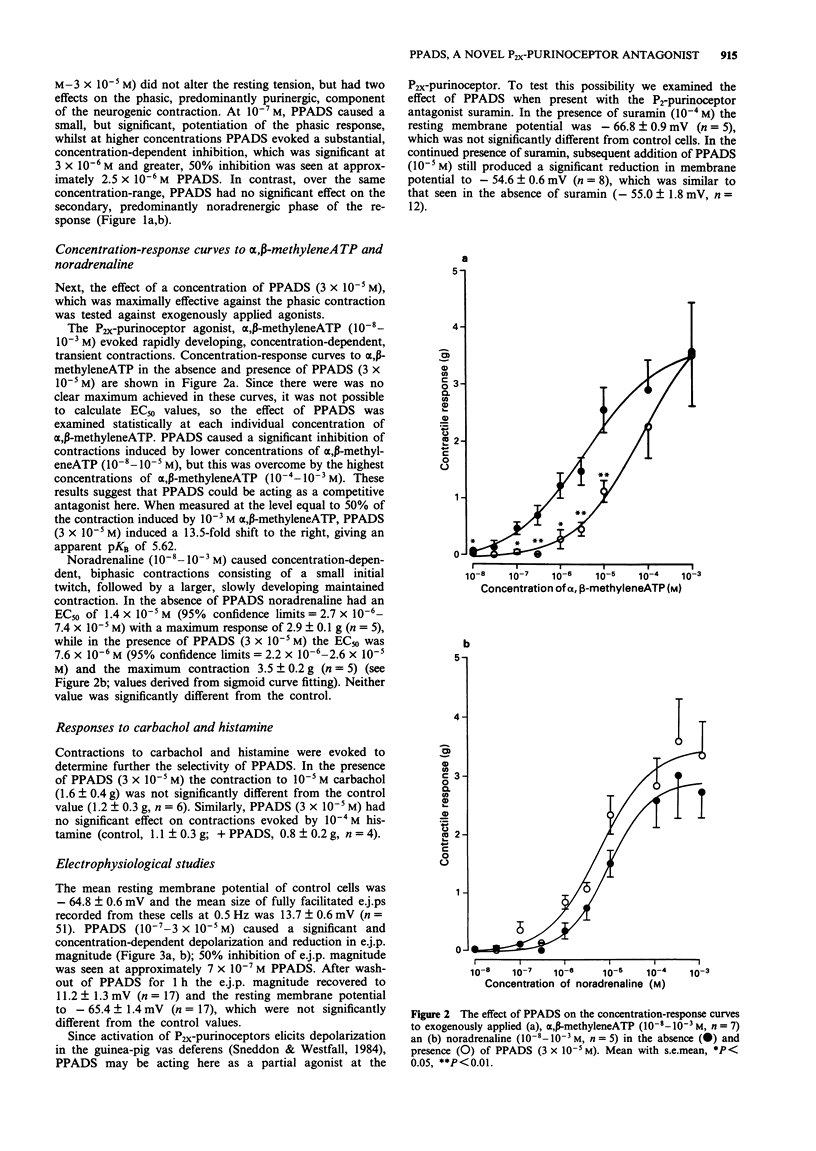
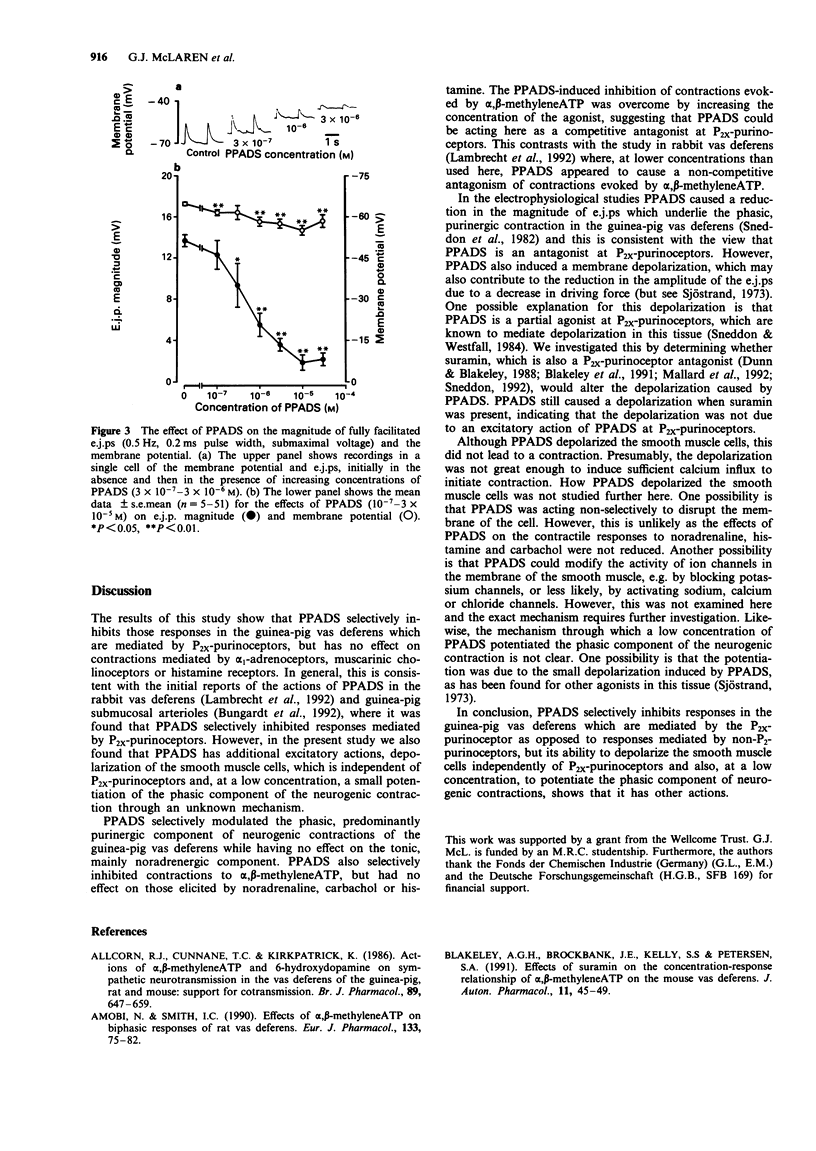
1. Pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS) was investigated for its ability to act as an antagonist at P2x-purinoceptors which mediate neurogenic excitatory junction potentials (e.j.ps) and contractions in the guinea-pig isolated vas deferens. 2. PPADS (10(-7) M) caused a small potentiation of the phasic, predominantly purinergic component of contractions evoked by symapthetic nerve stimulation, but higher concentrations of PPADS (3 x 10(-6)-3 x 10(-5) M) elicited a substantial and significant concentration-dependent inhibition. In contrast, over the same concentration-range, PPADS had no effect on the tonic, predominantly noradrenergic phase. 3 PPADS (3 x 10(-5) M) also inhibited contractile responses to exogenous alpha,beta-methyleneATP (10(-8)-10(-3)M), a P2x-purinoceptor agonist, without affecting the responses to exogenous noradrenaline (10(-8)-10(-3) M), carbachol (10(-5) M) or histamine (10(-4) M). 4. PPADS (10(-7)-3 x 10(-5) M) produced a concentration-dependent reduction in e.j.p. magnitude and resting membrane potential. The maximum effect was seen at 10(-5) M PPADS, which reduced e.j.p. magnitude from 13.7 +/- 0.6 mV (n = 12) to 1.8 +/- 0.7 mV (n = 12) and membrane potential from -64.8 +/- 0.6 mV (n = 51) to -55.0 +/- 1.8 mV (n = 12). 5. The PPADS-induced depolarization was not inhibited by the P2x-purinoceptor antagonist, suramin (10(-4) M). This indicates that the depolarization was not due to an agonist action of PPADS at P2x-purinoceptors. 6. The results support the proposal that PPADS is a selective antagonist at P2x purinoceptors as opposed to non-P2-purinoceptors in the guinea-pig vas deferens, but its ability to cause membrane depolarization independently of P2x-purinoceptors and also, at a low concentration, to potentiate the phasic component of the neurogenic contraction indicates that it has other actions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allcorn R. J., Cunnane T. C., Kirkpatrick K. Actions of alpha, beta-methylene ATP and 6-hydroxydopamine on sympathetic neurotransmission in the vas deferens of the guinea-pig, rat and mouse: support for cotransmission. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;89(4):647–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amobi N., Smith I. C. Effects of alpha,beta-methylene ATP on biphasic responses of rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 6;133(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Brockbank J. E., Kelly S. S., Petersen S. A. Effects of suramin on the concentration--response relationship of alpha, beta-methylene ATP on the mouse vas deferens. J Auton Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;11(1):45–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., Westfall D. P., O'Donnell J. P. Comparison of contractions of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens induced by ATP and related nucleotides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. W., Westfall D. P., De la Lande I. S., Jellett L. B. Log-normal distribution of equiefective doses of norepinephrine and acetylcholine in several tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 May;181(2):339–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes--an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht G., Friebe T., Grimm U., Windscheif U., Bungardt E., Hildebrandt C., Bäumert H. G., Spatz-Kümbel G., Mutschler E. PPADS, a novel functionally selective antagonist of P2 purinoceptor-mediated responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90877-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallard N., Marshall R., Sithers A., Spriggs B. Suramin: a selective inhibitor of purinergic neurotransmission in the rat isolated vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 10;220(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90004-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum L. A., Burnstock G. Evidence that ATP acts as a co-transmitter with noradrenaline in sympathetic nerves supplying the guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug 19;92(1-2):161–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand N. O. Effects of acetylcholine and some other smooth muscle stimulants on the electrical and mechanical responses of the guinea-pig vas deferens to nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Sep;89(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. Inhibition of excitatory junction potentials in guinea-pig vas deferens by alpha, beta-methylene-ATP: further evidence for ATP and noradrenaline as cotransmitters. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 13;100(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Machaly M. Regional variation in purinergic and adrenergic responses in isolated vas deferens of rat, rabbit and guinea-pig. J Auton Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;12(6):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1992.tb00390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P. Suramin inhibits excitatory junction potentials in guinea-pig isolated vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):101–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P., Fedan J. S. Cotransmitters in the motor nerves of the guinea pig vas deferens: electrophysiological evidence. Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.6291151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Astrand P. Discrete events measure single quanta of adenosine 5'-triphosphate secreted from sympathetic nerves of guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Bültmann R., Starke K. Interaction of adenine nucleotides, UTP and suramin in mouse vas deferens: suramin-sensitive and suramin-insensitive components in the contractile effect of ATP. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;342(2):198–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00166965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Noradrenaline-ATP co-transmission in the sympathetic nervous system. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90587-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


