Abstract
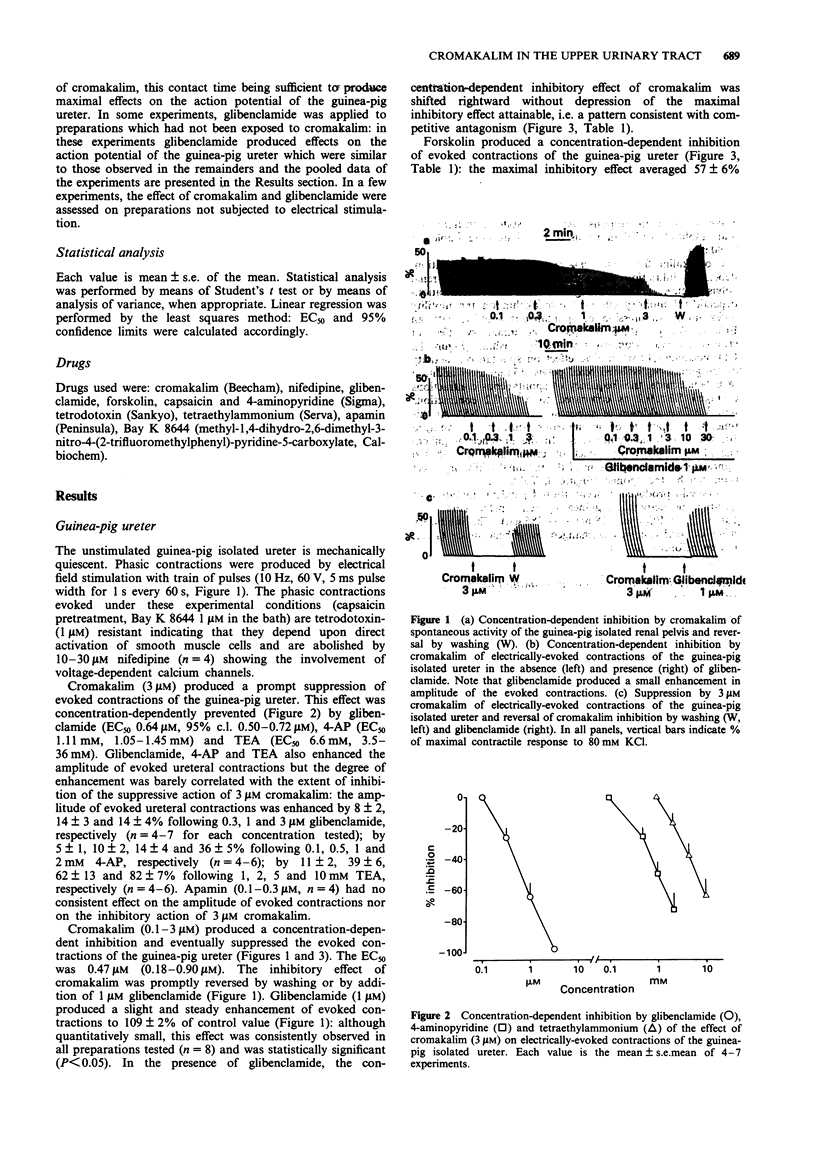
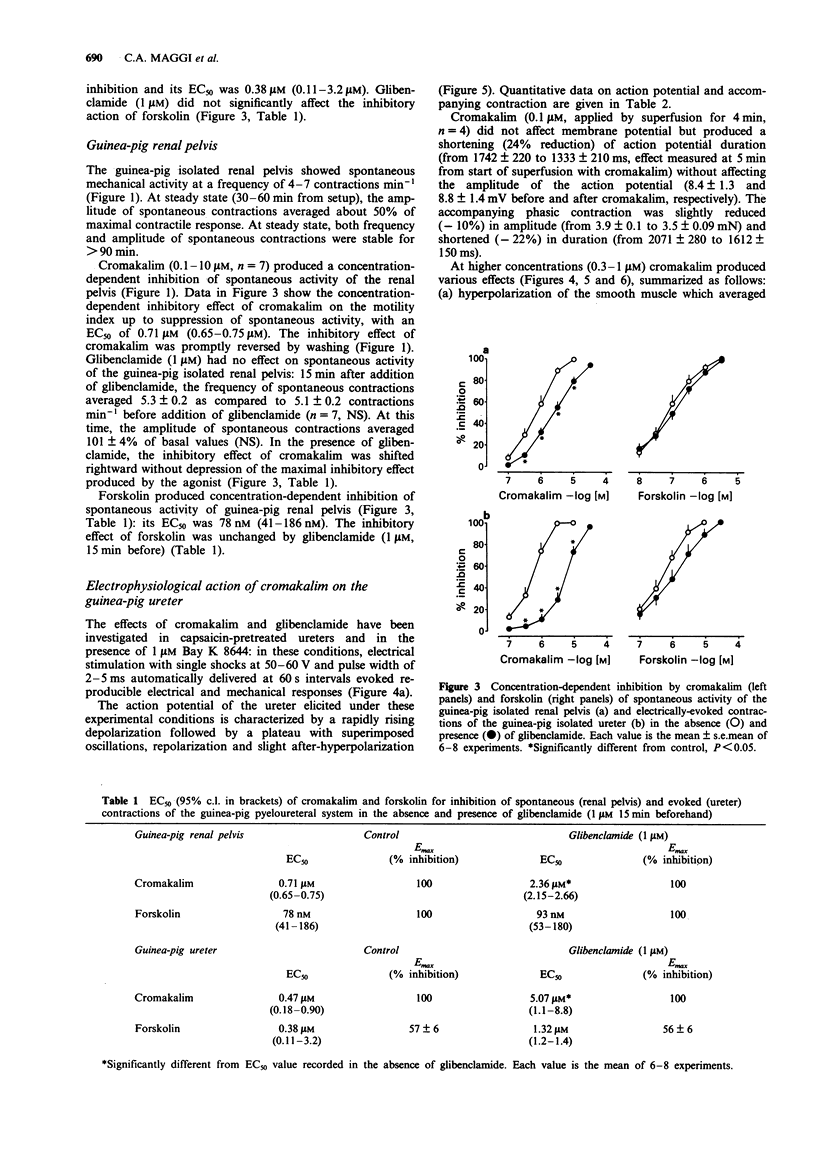
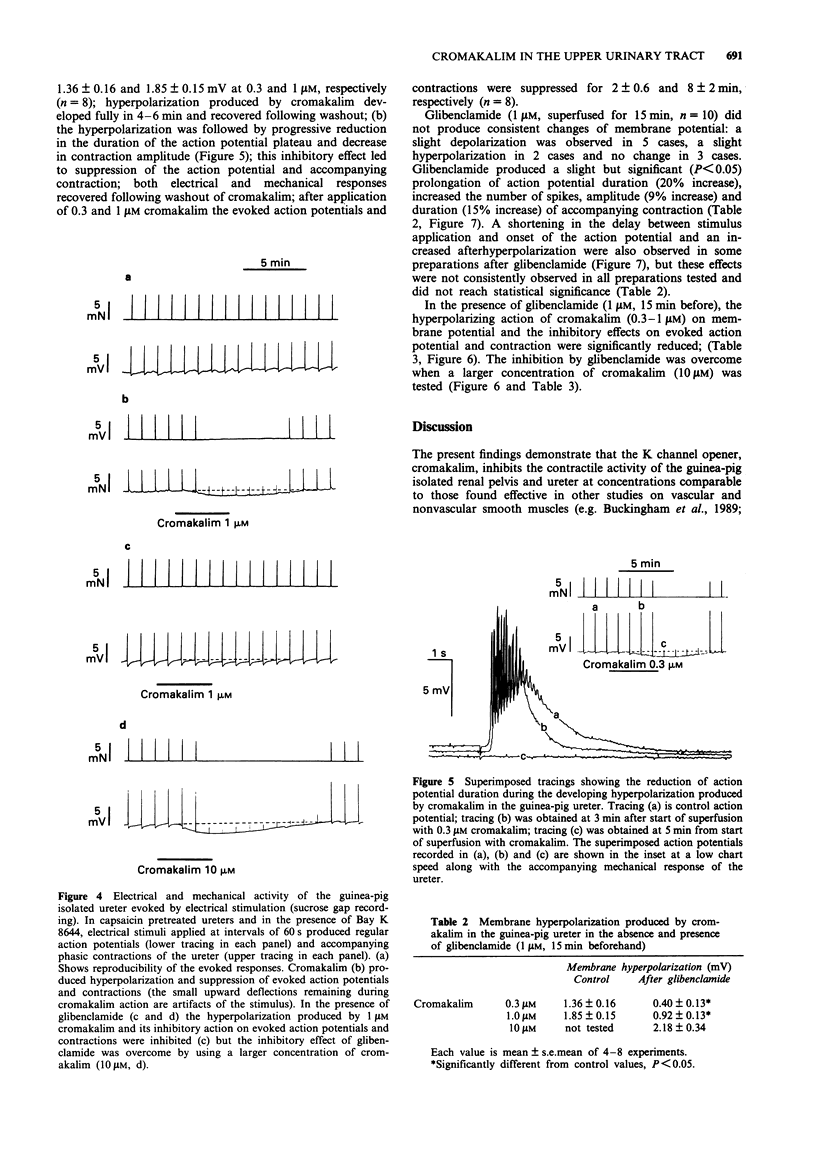
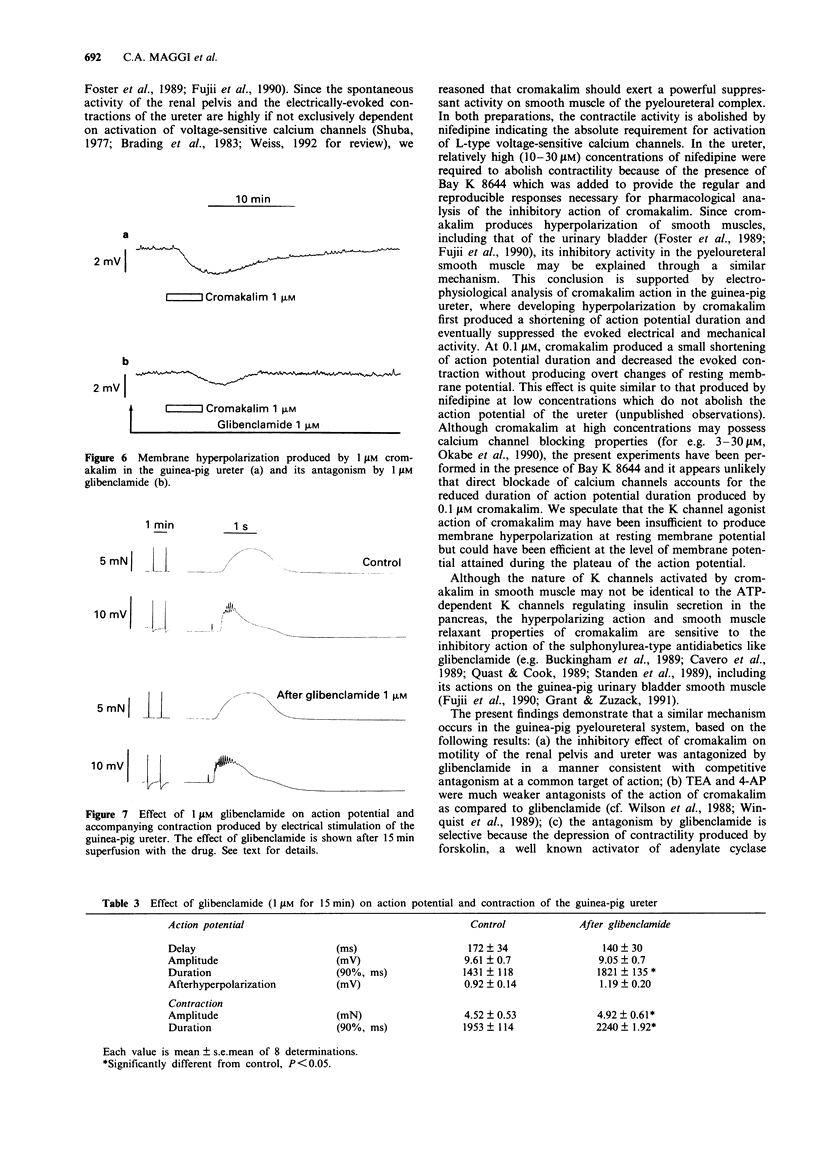
1. We have investigated the effect of the potassium (K) channel opener, cromakalim, on the spontaneous myogenic activity of the guinea-pig isolated renal pelvis and on myogenic contractions evoked by direct electrical stimulation of the guinea-pig isolated ureter. 2. In the presence of Bay K 8644 (1 microM), electrical stimulation of the guinea-pig ureter (10 Hz for 1 s, pulse width 5 ms, 60 V) produced regular tetrodotoxin-(1 microM) resistant phasic contractions which were suppressed by 3 microM cromakalim. Glibenclamide (0.1-3 microM), 4-aminopyridine (4-AP, 0.1-2 mM) and tetraethylammonium (TEA, 1-10 mM) produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of the effect of cromakalim with the rank order of potency (EC50 in parentheses): glibenclamide (0.64 microM) >> 4-AP (1.11 mM) > TEA (6.6 mM). Apamin (0.1-0.3 microM) was without effect. 3. Cromakalim (0.1-10 microM) produced concentration-dependent inhibition and suppression of spontaneous contractions of the guinea-pig isolated renal pelvis and of evoked contractions of the ureter with EC50 values of 0.71 and 0.47 microM, respectively. 4. Glibenclamide (1 microM) produced a rightward shift of the concentration-response curve to cromakalim in both the renal pelvis and ureter, without producing depression of the maximal inhibitory effect. Glibenclamide did not affect the spontaneous activity of the renal pelvis while it produced a slight enhancement (10-15% increase) of evoked contractions of the ureter. Glibenclamide did not affect the inhibitory action of the adenylate cyclase activator, forskolin, in the renal pelvis or ureter. 5. In electrophysiological experiments (sucrose gap), cromakalim (0.3 and 1 microM) produced hyperpolarization of ureter smooth muscle.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artemenko D. P., Buryi V. A., Vladimirova I. A., Shuba M. F. Modifikatsiia metoda odinarnogo sakharoznogo mostika. Fiziol Zh. 1982 May;28(3):374–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonev A. D., Nelson M. T. ATP-sensitive potassium channels in smooth muscle cells from guinea pig urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 1):C1190–C1200. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.5.C1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F., Burdyga T. V., Scripnyuk Z. D. The effects of papaverine on the electrical and mechanical activity of the guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:79–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham R. E., Hamilton T. C., Howlett D. R., Mootoo S., Wilson C. Inhibition by glibenclamide of the vasorelaxant action of cromakalim in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavero I., Mondot S., Mestre M. Vasorelaxant effects of cromakalim in rats are mediated by glibenclamide-sensitive potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1261–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crépel V., Krnjević K., Ben-Ari Y. Sulphonylureas reduce the slowly inactivating D-type outward current in rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:39–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. The relation between response and the interval between stimuli of the isolated guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):225–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster C. D., Fujii K., Kingdon J., Brading A. F. The effect of cromakalim on the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):281–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K., Foster C. D., Brading A. F., Parekh A. B. Potassium channel blockers and the effects of cromakalim on the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):779–785. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant T. L., Zuzack J. S. Effects of K+ channel blockers and cromakalim (BRL 34915) on the mechanical activity of guinea pig detrusor smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):1158–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H. A modified single sucrose gap. Junction potentials and electrotonic potentials in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. J Pharmacol Methods. 1987 Nov;18(3):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(87)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Muraki K., Watanabe M. Characteristics of transient outward currents in single smooth muscle cells from the ureter of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:301–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Muraki K., Watanabe M. Ionic currents in single smooth muscle cells from the ureter of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama N., Huang S. M., Tomita T., Brading A. F. Effects of cromakalim on the electrical slow wave in the circular muscle of guinea-pig gastric antrum. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1097–1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. J. Identification of the major membrane currents in freshly dispersed single smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:375–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S. Non-adrenergic non-cholinergic excitatory innervation of the guinea-pig isolated renal pelvis: involvement of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent neurons. J Urol. 1992 May;147(5):1394–1398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)37581-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S. The neurotransmitter role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat and guinea-pig ureter: effect of a calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonist and species-related differences in the action of omega conotoxin on calcitonin gene-related peptide release from primary afferents. Neuroscience. 1991;43(1):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90433-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe K., Kajioka S., Nakao K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Weston A. H. Actions of cromakalim on ionic currents recorded from single smooth muscle cells of the rat portal vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):832–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. In vitro and in vivo comparison of two K+ channel openers, diazoxide and cromakalim, and their inhibition by glibenclamide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):261–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U. Effect of the K+ efflux stimulating vasodilator BRL 34915 on 86Rb+ efflux and spontaneous activity in guinea-pig portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve H. L., Vaughan P. F., Peers C. Glibenclamide inhibits a voltage-gated K+ current in the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jan 20;135(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90130-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki N., Karim O. M., Mostwin J. L. Effect of pinacidil on the membrane electrical activity of guinea pig detrusor muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Nov;263(2):816–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuba M. F. The effect of sodium-free and potassium-free solutions, ionic current inhibitors and ouabain on electrophysiological properties of smooth muscle of guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(3):837–851. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Noma A. The ATP-sensitive K+ channel. Prog Neurobiol. 1993 Jul;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(93)90039-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Coldwell M. C., Howlett D. R., Cooper S. M., Hamilton T. C. Comparative effects of K+ channel blockade on the vasorelaxant activity of cromakalim, pinacidil and nicorandil. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 2;152(3):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. Inhibition by sulphonylureas of vasorelaxation induced by K+ channel activators in vitro. J Auton Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;9(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1989.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Heaney L. A., Wallace A. A., Baskin E. P., Stein R. B., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini S., Ben-Ari Y., Ashford M. L. Characterization of sulfonylurea receptors and the action of potassium channel openers on cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig isolated small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Nov;259(2):566–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


