Abstract
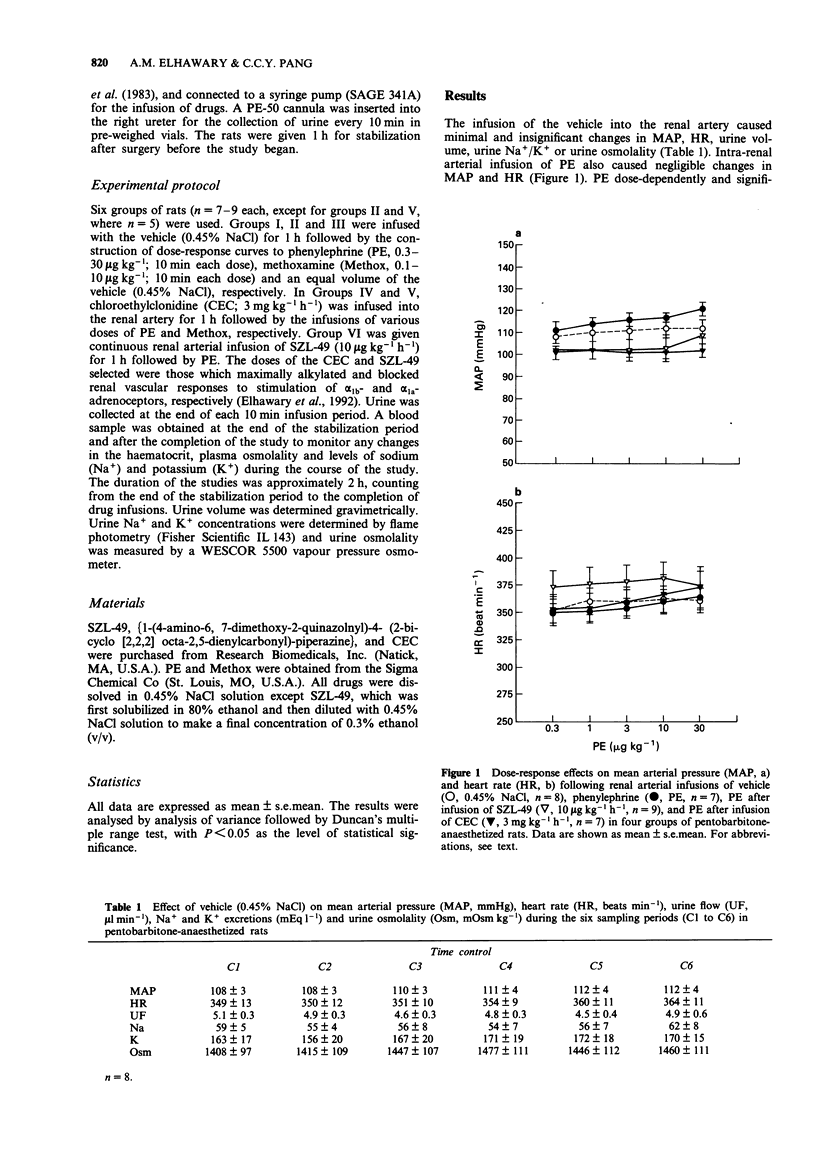
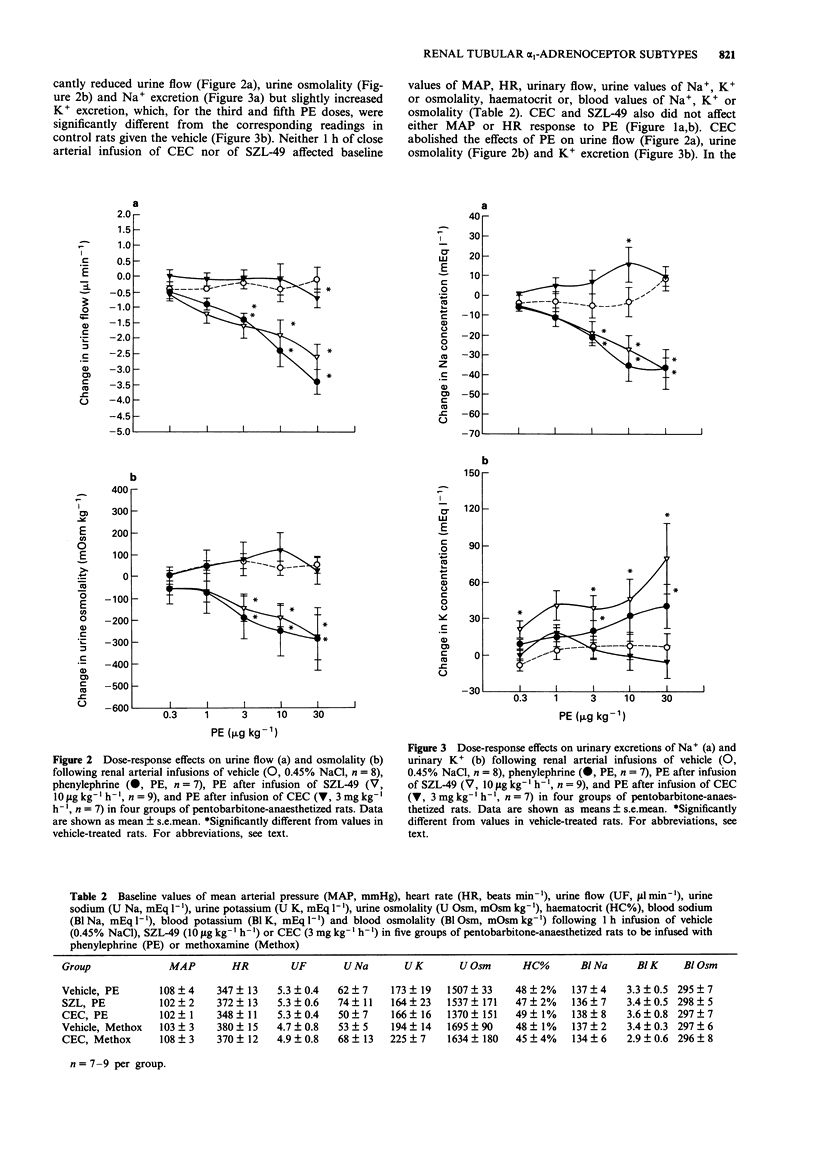
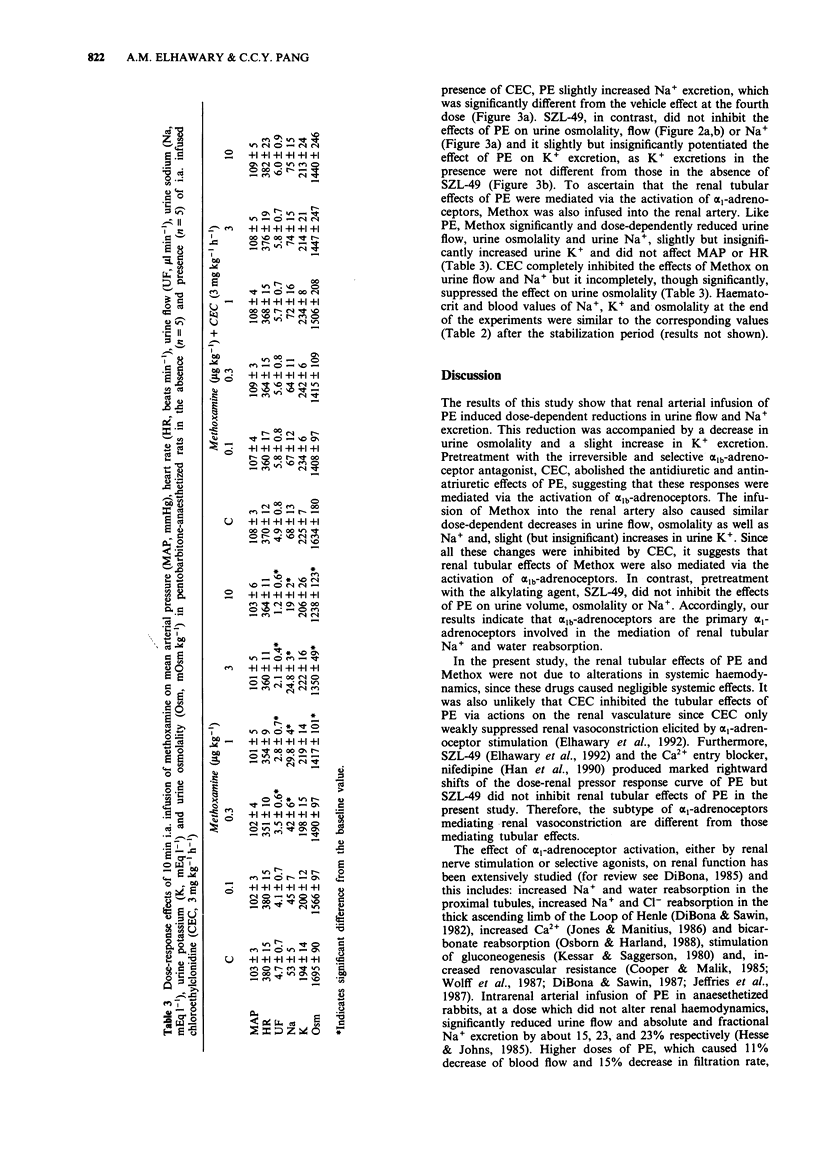
1. It is known that activation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors causes renal vasoconstriction and increased tubular Na+ and water reabsorption, with the alpha 1a-subtype mediating the constrictor effect. 2. This study examines which subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors mediates tubular Na+ and water reabsorption in pentobarbitone-anaesthetized rats. In order to avoid systemic effects, phenylephrine (0.3 to 30 micrograms kg-1), methoxamine (0.1-10 micrograms kg-1) and vehicle were infused into the right renal artery (via the suprarenal artery) of three groups of rats. Two other groups of rats were continuously infused with the irreversible selective alpha 1b-adrenoceptor antagonist, chloroethylclonidine (3 mg kg-1 h-1) for 1 h, prior to the construction of dose-response curves to phenylephrine or methoxamine. Another group was continuously infused with the irreversible selective alpha 1a-adrenoceptor antagonist, SZL-49 (10 micrograms kg-1 h-1) for 1 h, prior to the construction of dose-response curves to phenylephrine. Mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), urine flow, Na+ and K+ excretion, and urine osmolality were monitored. 3. Phenylephrine and methoxamine did not affect MAP or HR but dose-dependently and significantly decreased urine flow, urine osmolality as well as Na+ excretion and, slightly increased K+ excretion, although this was significant only for phenylephrine. 4. The antidiuretic, antinatriuretic and kaliuretic effects of phenylephrine were abolished by pretreatment with chloroethylclonidine, but were not inhibited by SZL-49. The inhibitory effects of methoxamine on urine flow and Na+ excretion were also almost totally abolished by chloroethylclonidine. 5. Our results show that alpha 1b-adrenoceptors mediate renal tubular Na+ and water reabsorption.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babich M., Pedigo N. W., Butler B. T., Piascik M. T. Heterogeneity of alpha 1 receptors associated with vascular smooth muscle: evidence from functional and ligand binding studies. Life Sci. 1987 Aug 10;41(6):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90445-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Malik K. U. Prostaglandin synthesis and renal vasoconstriction elicited by adrenergic stimuli are linked to activation of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the isolated rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Apr;233(1):24–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F. Neural control of renal function: role of renal alpha adrenoceptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7 (Suppl 8):S18–S23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Sawin L. L. Effect of renal nerve stimulation on NaCl and H2O transport in Henle's loop of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):F576–F580. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Sawin L. L. Role of renal alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1987 Jan;9(1):41–48. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhawary A. M., Pettinger W. A., Wolff D. W. Subtype-selective alpha-1 adrenoceptor alkylation in the rat kidney and its effect on the vascular pressor response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):709–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng F., Pettinger W. A., Abel P. W., Jeffries W. B. Regional distribution of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jul 1;258(1):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by chlorethylclonidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Li J., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94116-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse I. F., Johns E. J. The role of alpha-adrenoceptors in the regulation of renal tubular sodium reabsorption and renin secretion in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;84(3):715–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb16154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries W. B., Pettinger W. A. Adrenergic signal transduction in the kidney. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1989;15(1-2):5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Manitius J. A study in the rat of the renal actions of nitrendipine and diltiazem on the adrenergic regulation of calcium and sodium reabsorption. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;89(1):99–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessar P., Saggerson E. D. Evidence that catecholamines stimulate renal gluconeogenesis through an alpha 1-type of adrenoceptor. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):119–123. doi: 10.1042/bj1900119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano E., Nakamura R., Asano Y., Imai M. Distribution of alpha-adrenergic receptors in the rabbit nephron. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1984 Mar;142(3):275–282. doi: 10.1620/tjem.142.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusiak J. W., Pitha J., Piascik M. T. Interaction of a chemically reactive prazosin analog with alpha-1 adrenoceptors of rat tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Apr;249(1):70–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Han C., Abel P. W. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes distinguished by chlorethylclonidine and WB 4101. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz K. H., Garcia C., Hagler H. K. alpha 1-Receptor localization in rat heart and kidney using autoradiography. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):H512–H519. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.3.H512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., Harland R. W. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediation of urinary bicarbonate excretion. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1116–F1121. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Butler B. T., Kusiak J. W., Pitha J., Holtman J. R., Jr Effect of an alkylating analog of prazosin on alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtypes and arterial blood pressure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):878–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. M., Graham R. M., Sagalowsky A., Pettinger W. A. Renal alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors: biochemical and pharmacological correlations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits J. F., Kasbergen C. M., van Essen H., Kleinjans J. C., Struyker-Boudier H. A. Chronic local infusion into the renal artery of unrestrained rats. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):H304–H307. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.244.2.H304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snavely M. D., Insel P. A. Characterization of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes in the rat renal cortex. Differential regulation of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors by guanyl nucleotides and Na. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):532–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J. Renal alpha adrenoceptors. Fed Proc. 1984 Nov;43(14):2917–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan P. R., Fortin T. L., Kelvie S. L. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors in proximal tubules of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F848–F856. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Kispert J., Chin H. M. Sequence of a rat brain cDNA encoding an alpha-1B adrenergic receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1053–1053. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. W., Gesek F. A., Strandhoy J. W. In vivo assessment of rat renal alpha adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):472–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


