Abstract
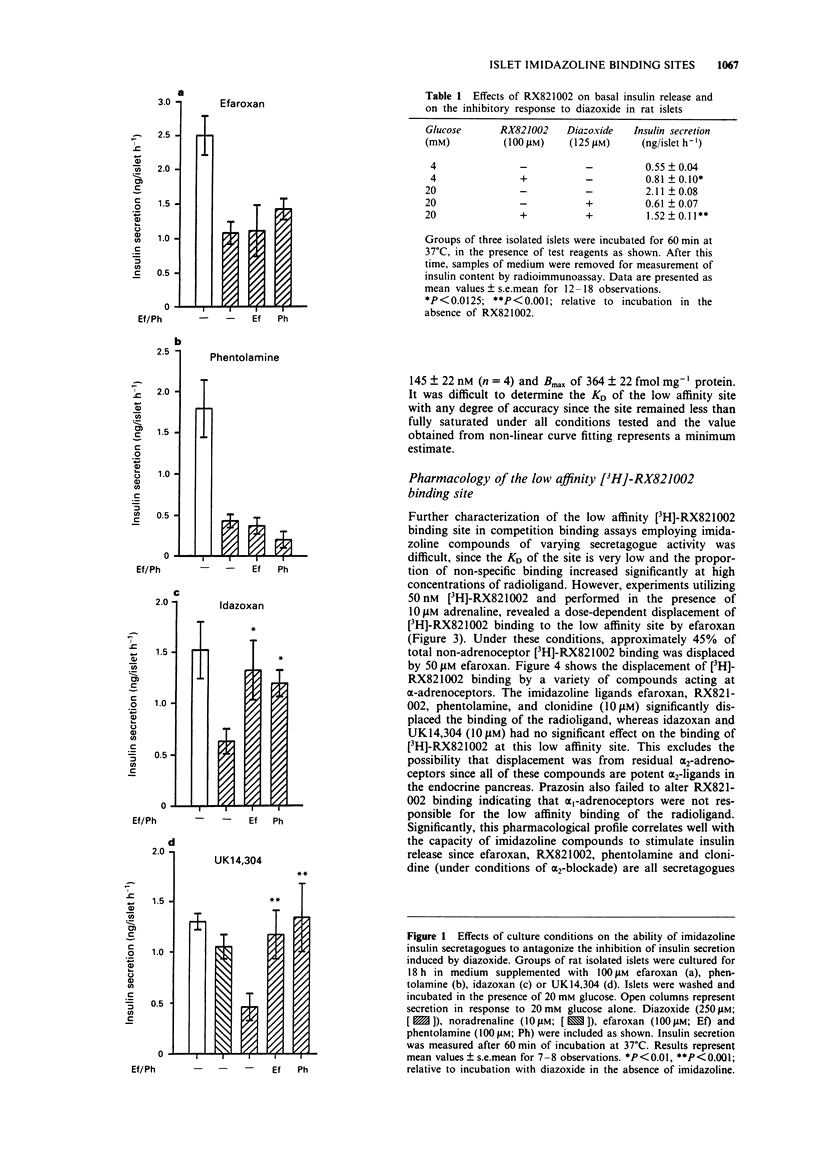
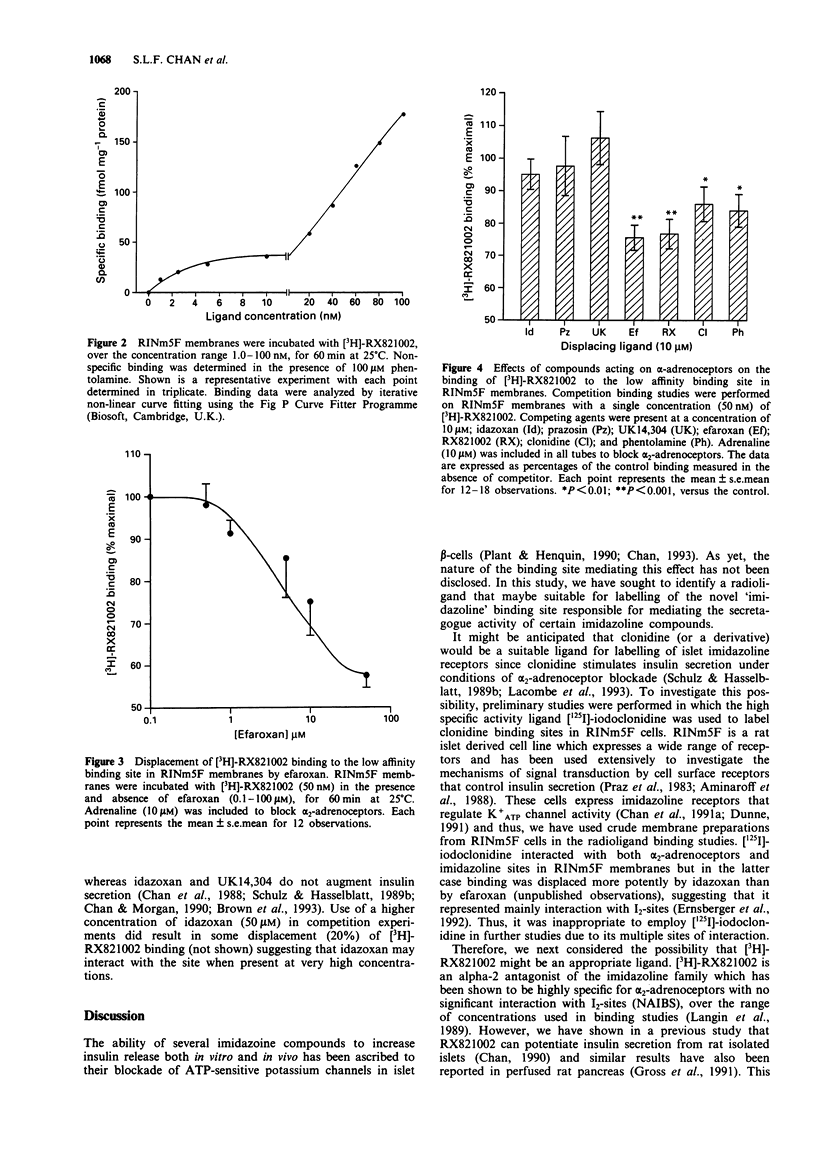
1. The nature of the binding site mediating the insulin secretagogue activity of certain imidazoline compounds remains unclear and the pharmacology of the I1- and I2-imidazoline sites, described in many tissues, does not correlate with the observed responses to imidazolines in islets. In the present paper, we describe further results which support the concept that the islet imidazoline site may represent a novel subtype of imidazoline receptor. 2. Culture of rat isolated islets in the presence of imidazoline secretagogues (either efaroxan or phentolamine) resulted in loss of responsiveness on subsequent re-exposure to these agents. However, culture of islets with either idazoxan or UK14,304 (imidazoline ligands that do not stimulate insulin secretion) did not lead to any loss of response when the islets were subsequently exposed to efaroxan. By contrast, islets cultured with UK14,304 (a potent alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist), displayed loss of sensitivity to noradrenaline, consistent with down-regulation of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. 3. In order to characterize the imidazoline site further, radioligand binding studies were performed in membranes from RINm5F insulinoma cells using [3H]-RX821002, an imidazoline insulin secretagogue that does not interact significantly with imidazoline sites in other tissues. [3H]-RX821002 labelled alpha 2-adrenoceptors with high affinity (2.01 +/- 0.7 nM) but also labelled a second, non-adrenoceptor site with much lower affinity. 4. Under conditions of alpha 2-adrenoceptor blockade (in the presence of adrenaline), efaroxan displaced [3H]-RX821002 binding to the low affinity site, in a dose-dependent manner.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Lundquist I. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor blockade by phentolamine on basal and stimulated insulin secretion in the mouse. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Oct;125(2):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Lagny-Pourmir I., Laburthe M. Mechanism of galanin-inhibited insulin release. Occurrence of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas D. Clonidine-displacing substance (CDS) and its putative imidazoline receptor. New leads for further divergence of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90152-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidet M., Poujeol P., Parini A. Effect of imidazolines on Na+ transport and intracellular pH in renal proximal tubule cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. A., Loweth A. C., Smith S. A., Morgan N. G. Stimulation of insulin secretion by imidazoline compounds is not due to interaction with non-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):312–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Brown C. A., Morgan N. G. Stimulation of insulin secretion by the imidazoline alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist efaroxan is mediated by a novel, stereoselective, binding site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 19;230(3):375–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Dunne M. J., Stillings M. R., Morgan N. G. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist efaroxan modulates K+ATP channels in insulin-secreting cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 29;204(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90833-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Morgan N. G. Stimulation of insulin secretion by efaroxan may involve interaction with potassium channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 25;176(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90137-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L. Role of alpha 2-adrenoceptors and imidazoline-binding sites in the control of insulin secretion. Clin Sci (Lond) 1993 Dec;85(6):671–677. doi: 10.1042/cs0850671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Stillings M. R., Morgan N. G. Mechanisms involved in stimulation of insulin secretion by the hypoglycaemic alpha-adrenergic antagonist, DG-5128. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1545–1551. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90463-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J. Block of ATP-regulated potassium channels by phentolamine and other alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1847–1850. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Jardine E., Reid J. L. Down-regulation of imidazoline sites in rabbit kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 12;243(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90174-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Yakubu M. A., Howie C. A., Reid J. L. Do centrally-acting antihypertensive drugs act at non-adrenergic as well as alpha-2 adrenoceptor sites? Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1992;14(5):815–835. doi: 10.3109/10641969209036221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R. D., Morgan N. G. Evidence for differential effects of noradrenaline and somatostatin on intracellular messenger systems in rat islets of Langerhans. J Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(3):231–237. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0040231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. C., Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Imidazoline antagonists of alpha 2-adrenoceptors increase insulin release in vitro by inhibiting ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe C., Viallard V., Paris H. Identification of alpha 2-adrenoceptors and of non-adrenergic idazoxan binding sites in pancreatic islets from young and adult hamsters. Int J Biochem. 1993 Jul;25(7):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(93)90124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Lafontan M., Stillings M. R., Paris H. [3H]RX821002: a new tool for the identification of alpha 2A-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 11;167(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90751-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon A. C., Stewart M., Olverman H. J., Spedding M., Brown C. M. [3H]p-aminoclonidine and [3H]idazoxan label different populations of imidazoline sites on rat kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 23;232(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90731-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Ernsberger P. Keeping an eye on the I site: imidazoline-preferring receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Taylor K. W. Pentitols and insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj1090333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Gabilondo A. M., Miralles A., Escriba P. V., García-Sevilla J. A. Chronic treatment with the monoamine oxidase inhibitors clorgyline and pargyline down-regulates non-adrenoceptor [3H]-idazoxan binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):597–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Miralles A., Barturen F., Garcia-Sevilla J. A. Characterization of brain imidazoline receptors in normotensive and hypertensive rats: differential regulation by chronic imidazoline drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1000–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Phentolamine and yohimbine inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praz G. A., Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Strauss A. J., Renold A. E. Regulation of immunoreactive-insulin release from a rat cell line (RINm5F). Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):345–352. doi: 10.1042/bj2100345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaury A., Paris H. The insulin-secreting cell line, RINm5F, expresses an alpha-2D adrenoceptor and nonadrenergic idazoxan-binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):417–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. Phentolamine, a deceptive tool to investigate sympathetic nervous control of insulin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;337(6):637–643. doi: 10.1007/BF00175789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


