Abstract
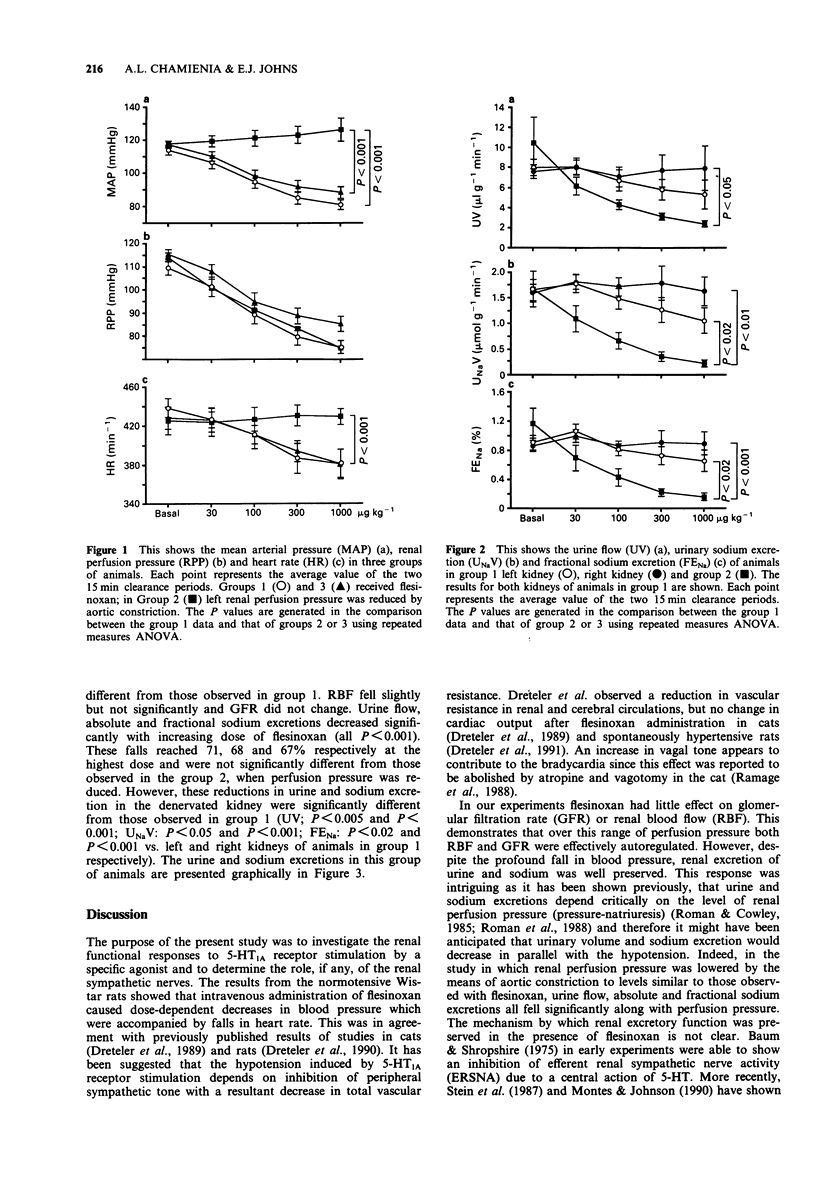
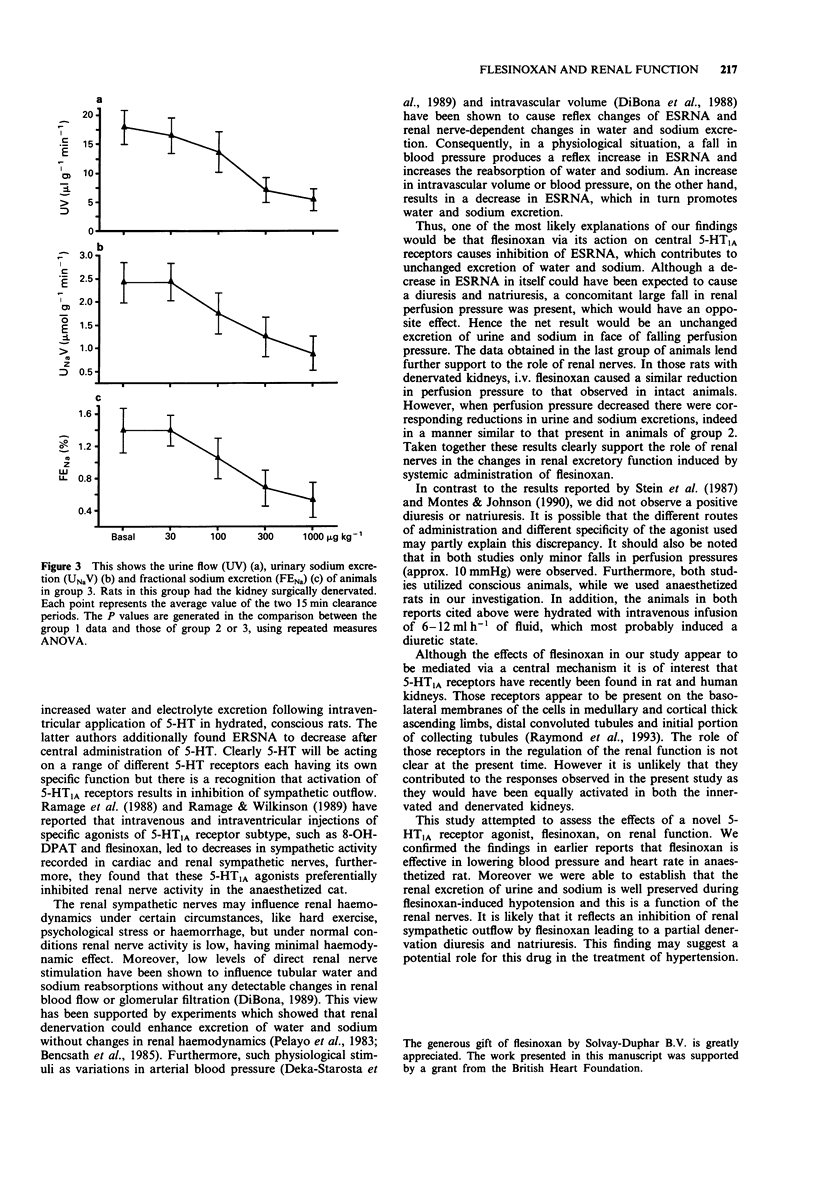
1. The present study was designed to examine the effects of a centrally acting 5-HT1A receptor agonist, flesinoxan, on the cardiovascular system and renal haemodynamics and excretory function. 2. In chloralose-urethane anaesthetized Wistar rats, i.v. administration of bolus doses of flesinoxan, at 30, 100, 300 and 1000 micrograms kg-1, caused significant, dose-dependent decreases in mean arterial pressure, of 33 +/- 2 mmHg (P < 0.001) and heart rate of 57 +/- 9 beats min-1 (P < 0.001) at the highest dose used. Despite this substantial fall in perfusion pressure there were no meaningful changes in the renal excretion of water and sodium. In a second group of rats, reduction of renal perfusion pressure mechanically to the same values as observed in rats given flesinoxan (i.e. 100, 92, 84 and 76 mmHg) produced reductions in urine flow, absolute and fractional sodium excretions reaching a maximum of 74, 86 and 84% respectively (all P < 0.001) at the lowest pressure. These reductions were significantly larger than those seen in the previous group of animals. 3. In the group of rats subjected to renal denervation, flesinoxan produced changes in blood pressure and heart rate which were not different from those observed in intact animals. However, the reduction in pressure was accompanied by significant decreases in urine flow of 71%, absolute sodium excretion of 68% and fractional sodium excretion of 67% (all P < 0.001) at the highest dose, which were all significantly greater than the changes seen in the innervated animals but were not different from those observed when renal perfusion pressure was reduced mechanically.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barajas L., Liu L., Powers K. Anatomy of the renal innervation: intrarenal aspects and ganglia of origin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 May;70(5):735–749. doi: 10.1139/y92-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum T., Shropshire A. T. Inhibition of efferent sympathetic nerve activity by 5-hydroxytryptophan and centrally administered 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1975 Mar;14(3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(75)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bencsáth P., Szénási G., Takács L. Water and electrolyte transport in Henle's loop and distal tubule after renal sympathectomy in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 2):F308–F314. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.2.F308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamienia A. L., Johns E. J. The interaction between atrial natriuretic peptides and angiotensin II in controlling sodium and water excretion in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1893–1898. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12348.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor H. E., Higgins G. A. Cardiovascular effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists injected into the dorsal raphe nucleus of conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 21;182(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90493-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deka-Starosta A., Garty M., Zukowska-Grojec Z., Keiser H. R., Kopin I. J., Goldstein D. S. Renal sympathetic nerve activity and norepinephrine release in rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):R229–R236. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.257.1.R229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Herman P. J., Sawin L. L. Neural control of renal function in edema-forming states. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):R1017–R1024. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1988.254.6.R1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F. Neural control of renal function: cardiovascular implications. Hypertension. 1989 Jun;13(6 Pt 1):539–548. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreteler G. H., Wouters W., Saxena P. R. Comparison of the cardiovascular effects of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist flesinoxan with that of 8-OH-DPAT in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 16;180(2-3):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreteler G. H., Wouters W., Saxena P. R. Systemic and regional hemodynamic effects of the putative 5-HT1A receptor agonist flesinoxan in the cat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;14(5):770–776. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198911000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreteler G. H., Wouters W., Toorop G. P., Jansen J. A., Saxena P. R. Systemic and regional hemodynamic effects of the 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor agonists flesinoxan and 8-hydroxy-2(di-N-propylamino)tetralin in the conscious rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;17(3):488–493. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199103000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradin K., Pettersson A., Hjorth S., Hedner T., Arvidsson L. E., Persson B. Cardiovascular effects in the Sprague-Dawley rat of 8-hydroxy-2(di-N-propylamino) tetralin, a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonist. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;37(4):263–265. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb05057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Schlicker E. Identification and classification of 5-HT1 receptor subtypes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 7):S1–S7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J. The physiology and pharmacology of the renal nerves. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 1991 Mar;85(3):141–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubie M., Drouillat M., Dabiré H., Cherqui C., Schmitt H. Ventrolateral medullary pressor area: site of hypotensive and sympatho-inhibitory effects of (+/-)8-OH-DPAT in anaesthetized dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 7;160(3):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes R., Johnson A. K. Efferent mechanisms mediating renal sodium and water excretion induced by centrally administered serotonin. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):R1267–R1273. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.6.R1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelayo J. C., Ziegler M. G., Jose P. A., Blantz R. C. Renal denervation in the rat: analysis of glomerular and proximal tubular function. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F70–F77. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:45–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Schmidt A. W., Sleight A. J., Harrington M. A. Serotonin receptor "families" in the central nervous system: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:104–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Wilkinson S. J. Evidence that different regional sympathetic outflows vary in their sensitivity to the sympathoinhibitory actions of putative 5-HT1A and alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists in anaesthetized cats. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1157–1164. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Wouters W., Bevan P. Evidence that the novel antihypertensive agent, flesinoxan, causes differential sympathoinhibition and also increases vagal tone by a central action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. R., Kim J., Beach R. E., Tisher C. C. Immunohistochemical mapping of cellular and subcellular distribution of 5-HT1A receptors in rat and human kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):F9–19. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.1.F9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R. J., Cowley A. W., Jr Characterization of a new model for the study of pressure-natriuresis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F190–F198. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R. J., Cowley A. W., Jr, Garcia-Estañ J., Lombard J. H. Pressure-diuresis in volume-expanded rats. Cortical and medullary hemodynamics. Hypertension. 1988 Aug;12(2):168–176. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.12.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. M., Lind R. W., Johnson A. K. Central serotonergic influences on renal electrolyte and water excretion. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Dec;26(12):1685–1692. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters W., Tulp M. T., Bevan P. Flesinoxan lowers blood pressure and heart rate in cats via 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


