Abstract
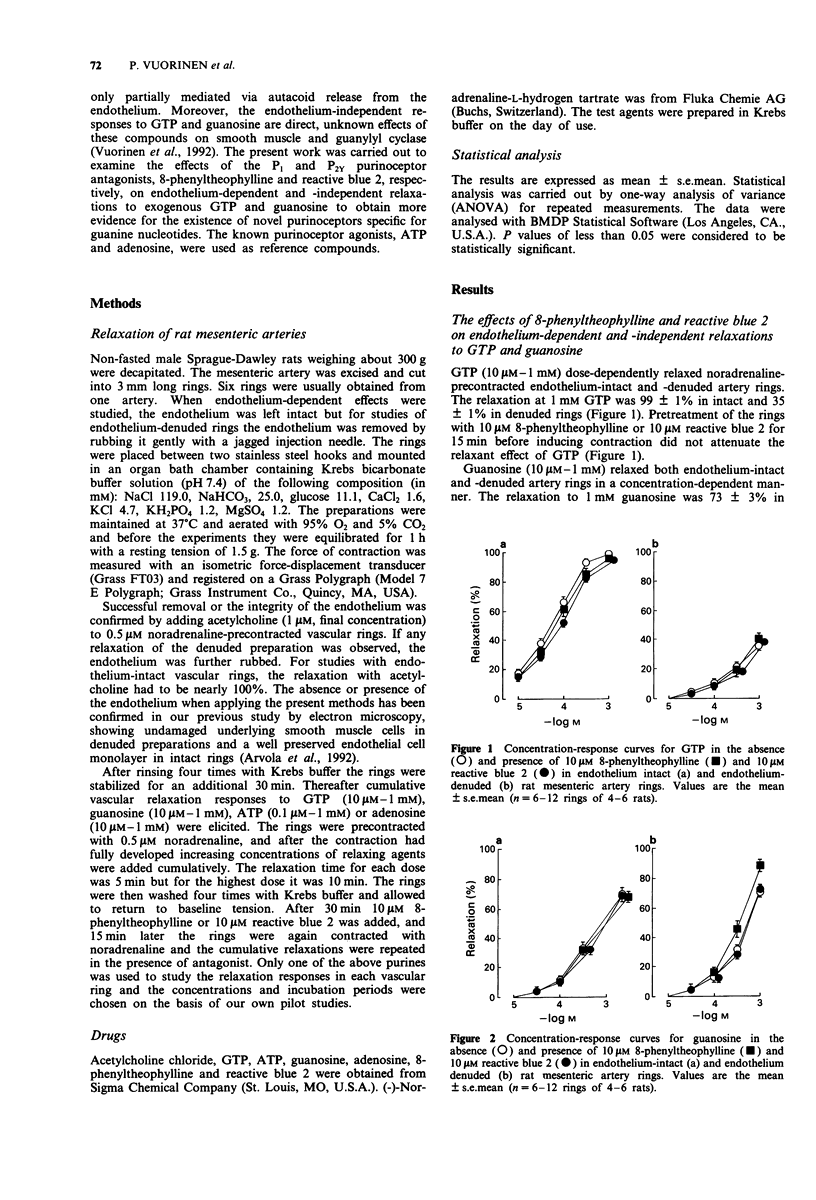
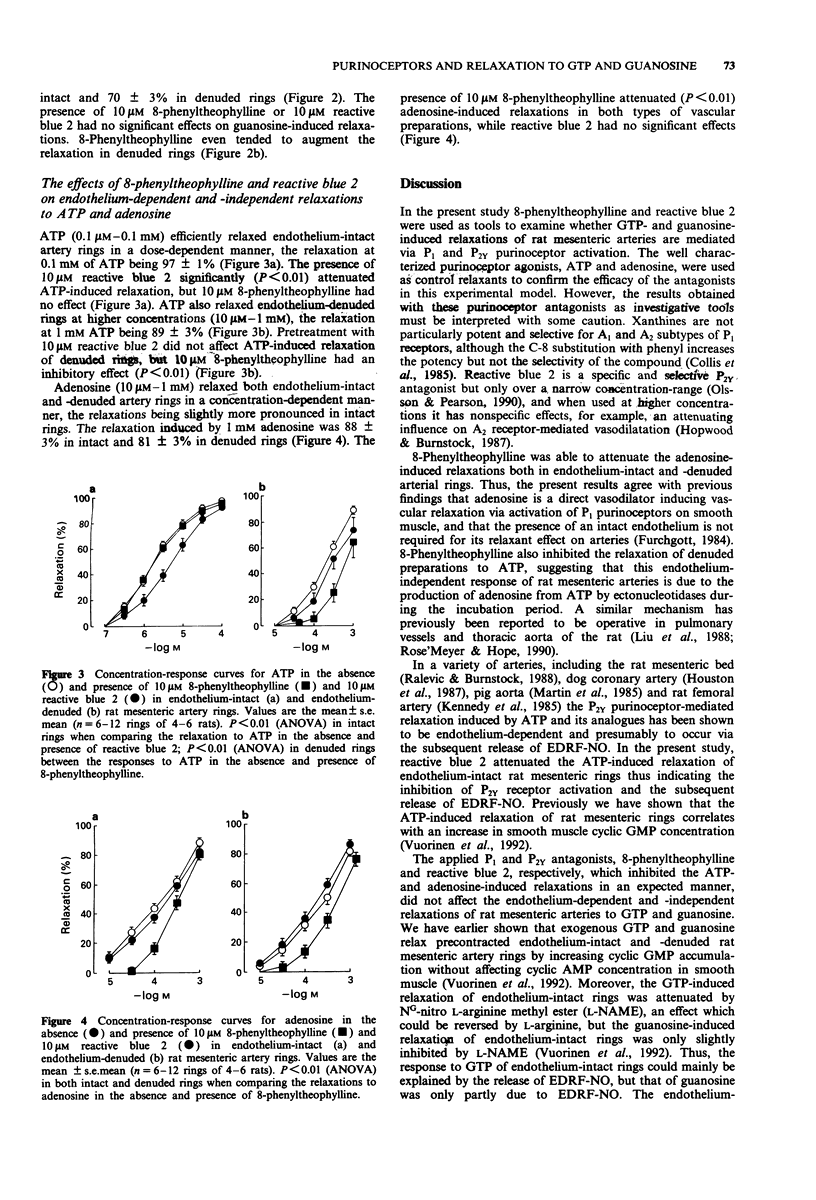
1. Guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP) and guanosine can relax both endothelium-intact and -denuded arterial preparations. In the present work the P1 and P2Y purinoceptor antagonists, 8-phenyltheophylline and reactive blue 2, respectively, were used to study the mechanisms of relaxation responses induced by GTP, guanosine, adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine in noradrenaline-precontracted rat mesenteric artery rings. 2. GTP (10 microM-1mM) dose-dependently relaxed endothelium-intact mesenteric artery rings and also induced moderate relaxation responses in endothelium-denuded preparations. Pretreatment of the rings with 8-phenyltheophylline (10 microM) or reactive blue 2 (10 microM) did not attenuate the relaxant effect of GTP. 3. Guanosine (10 microM-1mM) relaxed both endothelium-intact and -denuded artery rings in a dose-dependent manner. The presence of 8-phenyltheophylline or reactive blue 2 had no effects on guanosine-induced relaxations. 4. ATP-induced (0.1 microM-0.1 mM) relaxation of endothelium-intact artery rings was attenuated by reactive blue 2 while 8-phenyltheophylline was ineffective. ATP also relaxed endothelium-denuded artery rings and this relaxation was inhibited by 8-phenyltheophylline, but not by reactive blue 2. 5. Adenosine-induced (10 microM-1 mM) relaxation of endothelium-intact and -denuded artery rings was attenuated by the presence of 8-phenyltheophylline, but not of reactive blue 2. 6. In conclusion, the endothelium-dependent and -independent relaxations of rat mesenteric arteries to GTP and guanosine are not mediated via P1 and P2Y purinoceptors.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvola P., Pörsti I., Vuorinen P., Pekki A., Vapaatalo H. Contractions induced by potassium-free solution and potassium relaxation in vascular smooth muscle of hypertensive and normotensive rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):157–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeynaems J. M., Pearson J. D. P2 purinoceptors on vascular endothelial cells: physiological significance and transduction mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90039-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Daly J. W., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptor binding: structure-activity analysis generates extremely potent xanthine antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2077–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Warland J. J. P2-purinoceptors of two subtypes in the rabbit mesenteric artery: reactive blue 2 selectively inhibits responses mediated via the P2y-but not the P2x-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coade S. B., Pearson J. D. Metabolism of adenine nucleotides in human blood. Circ Res. 1989 Sep;65(3):531–537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Brown C. M. Adenosine relaxes the aorta by interacting with an A2 receptor and an intracellular site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Palmer D. B., Saville V. L. Comparison of the potency of 8-phenyltheophylline as an antagonist at A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in atria and aorta from the guinea-pig. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;37(4):278–280. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb05063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Role of the intima in cholinergic and purinergic relaxation of isolated canine femoral arteries. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:347–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. The role of endothelium in the responses of vascular smooth muscle to drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:175–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L., Martin W. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta: relationship to stimulation of 86Rb efflux from isolated endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H. Nucleotide metabolism of platelets. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:677–690. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood A. M., Burnstock G. ATP mediates coronary vasoconstriction via P2x-purinoceptors and coronary vasodilatation via P2y-purinoceptors in the isolated perfused rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 7;136(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90777-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston D. A., Burnstock G., Vanhoutte P. M. Different P2-purinergic receptor subtypes of endothelium and smooth muscle in canine blood vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Delbro D., Burnstock G. P2-purinoceptors mediate both vasodilation (via the endothelium) and vasoconstriction of the isolated rat femoral artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 2;107(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laustiola K. E., Vuorinen P., Pörsti I., Metsä-Ketelä T., Manninen V., Vapaatalo H. Exogenous GTP enhances the effects of sodium nitrite on cyclic GMP accumulation, vascular smooth muscle relaxation and platelet aggregation. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991 Jan;68(1):60–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. F., McCormack D. G., Evans T. W., Barnes P. J. Characterization and distribution of P2-purinoceptor subtypes in rat pulmonary vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):1204–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Cusack N. J., Carleton J. S., Gordon J. L. Specificity of P2-purinoceptor that mediates endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham L., Cusack N. J., Pearson J. D., Gordon J. L. Characteristics of the P2 purinoceptor that mediates prostacyclin production by pig aortic endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 10;134(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D. Purine nucleotides as regulators of vessel tone. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Aug;16(4):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bst0160480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Actions mediated by P2-purinoceptor subtypes in the isolated perfused mesenteric bed of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):637–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramagopal M. V., Chitwood R. W., Jr, Mustafa S. J. Evidence for an A2 adenosine receptor in human coronary arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90548-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly W. M., Saville V. L., Burnstock G. An assessment of the antagonistic activity of reactive blue 2 at P1- and P2-purinoceptors: supporting evidence for purinergic innervation of the rabbit portal vein. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 4;140(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose'Meyer R. B., Hope W. Evidence that A2 purinoceptors are involved in endothelium-dependent relaxation of the rat thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):576–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-removal decreases relaxations of canine coronary arteries caused by beta-adrenergic agonists and adenosine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):139–144. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorinen P., Laustiola K. E. Exogenous GTP increases cyclic GMP and inhibits thrombin-induced aggregation of washed human platelets: comparison with ATP, adenosine and guanosine. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992 Oct;71(4):289–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1992.tb00985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorinen P., Pörsti I., Metsä-Ketelä T., Manninen V., Vapaatalo H., Laustiola K. E. Endothelium-dependent and -independent effects of exogenous ATP, adenosine, GTP and guanosine on vascular tone and cyclic nucleotide accumulation of rat mesenteric artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorinen P., Pörsti I., Metsä-Ketelä T., Manninen V., Vapaatalo H., Laustiola K. E. Modification of nitrovasodilator effects on vascular smooth muscle by exogenous GTP and guanosine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;18(6):871–877. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199112000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. D., Angus J. A. Relaxant effects of ATP and adenosine on canine large and small coronary arteries in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 3;143(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90741-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


