Abstract
1. We examined the effects of phosphonium, [[4-[[2- [[bis(cyclohexylamino)methylene]amino]-3-(2-naphthalenyl) 1-oxopropyl]amino]-phenyl]-tributyl, chloride, monohydrochloride (WIN 64338), a novel, nonpeptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, on bradykinin-induced contractions of guinea-pig isolated ileum, and guinea-pig and ferret trachea. 2. WIN 64338 potently and competitively antagonized ileal contractions, in response to bradykinin, exhibiting a pA2 value of 7.97 +/- 0.10. The compound was without effect on contractions elicited by methacholine, a muscarinic receptor antagonist. Thus, WIN 64338 is a competitive and selective antagonist of ileal B2 receptors. 3. In contrast, WIN 64338 was completely without effect on bradykinin-induced contractions of guinea-pig or ferret trachea. Thus, even at a concentration of 1 microM, which was sufficient to cause a 100 fold decrease in ileal sensitivity to bradykinin, WIN 64338 failed to shift the bradykinin log concentration-response curves in trachea isolated from either species. 4. These data confirm that WIN 64338 represents the first reported nonpeptide antagonist of guinea-pig ileal B2 receptors. They also provide additional evidence for heterogeneity of bradykinin receptors within the same species (guinea-pig) and, furthermore, indicate that the tracheal bradykinin receptor (B3?) is different from that in ileal tissue (B2).
Full text
PDF
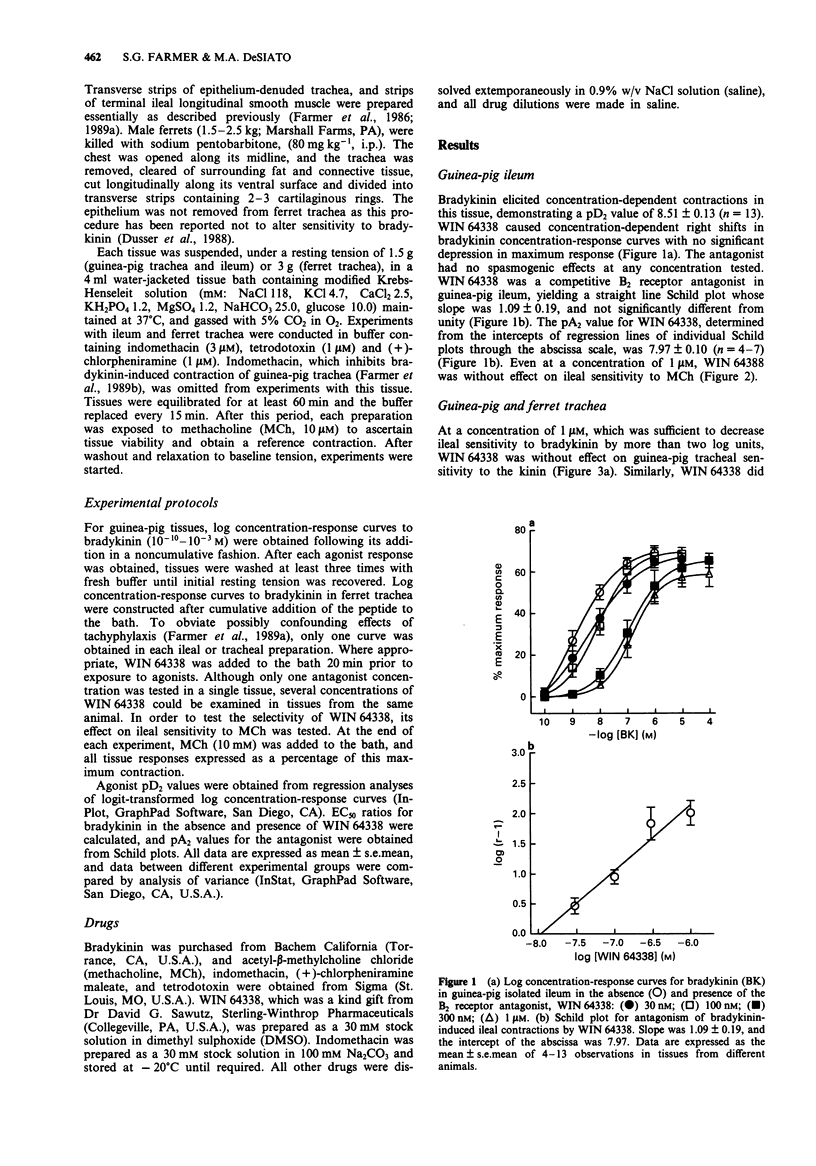
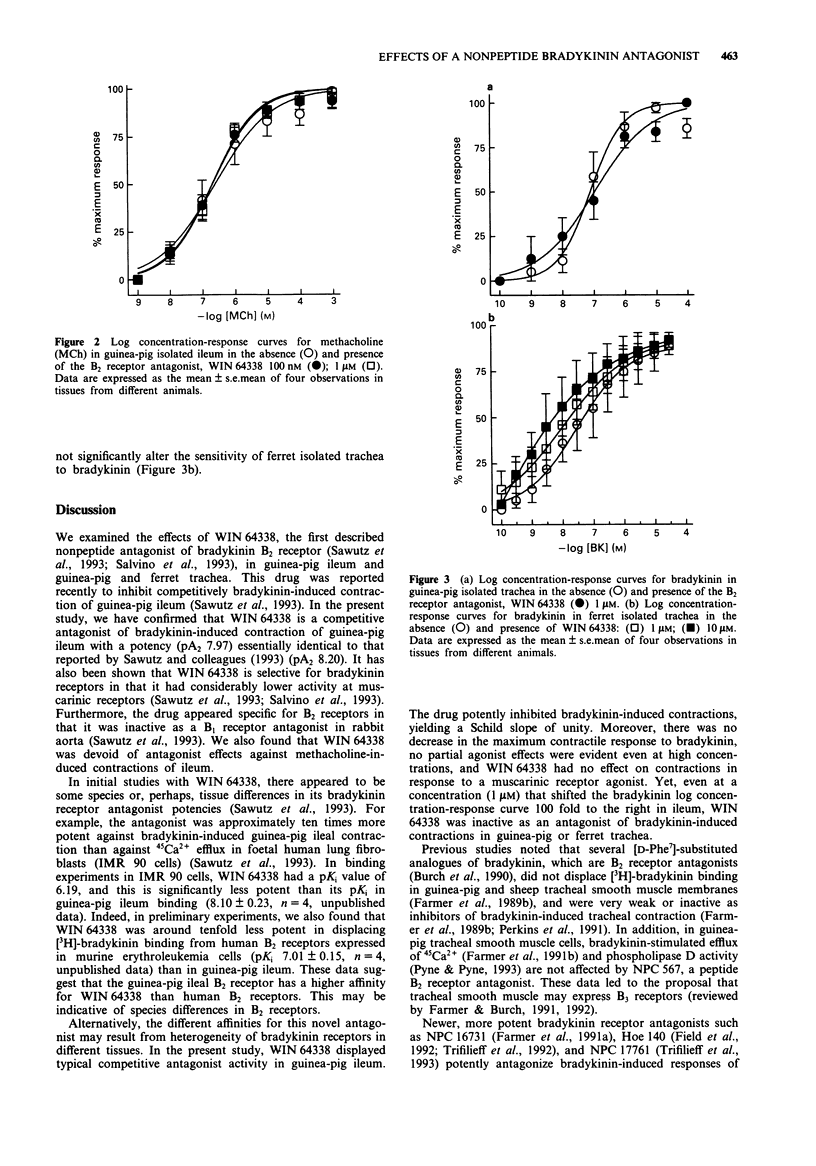

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burch R. M., Farmer S. G., Steranka L. R. Bradykinin receptor antagonists. Med Res Rev. 1990 Apr-Jun;10(2):237–269. doi: 10.1002/med.2610100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Kyle D. J. Recent developments in the understanding of bradykinin receptors. Life Sci. 1992;50(12):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90201-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Nadel J. A., Sekizawa K., Graf P. D., Borson D. B. Neutral endopeptidase and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors potentiate kinin-induced contraction of ferret trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):531–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M. Airway bradykinin receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;629:237–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb37980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M. Biochemical and molecular pharmacology of kinin receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:511–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.002455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Kyle D. J., Martin J. A., Meeker S. N., Togo J. D-Arg[Hyp3-Thi5-D-Tic7-Tic8]-bradykinin, a potent antagonist of smooth muscle BK2 receptors and BK3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):785–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Meeker S. A., Wilkins D. E. Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Ensor J. E., Burch R. M. Evidence that cultured airway smooth muscle cells contain bradykinin B2 and B3 receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;4(3):273–277. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Fedan J. S., Hay D. W., Raeburn D. The effects of epithelium removal on the sensitivity of guinea-pig isolated trachealis to bronchodilator drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;89(2):407–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. L., Hall J. M., Morton I. K. Putative novel bradykinin B3 receptors in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia caeci and trachea. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992;38(Pt 1):540–545. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7321-5_65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M. Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Nov;56(2):131–190. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. J., Martin J. A., Farmer S. G., Burch R. M. Design and conformational analysis of several highly potent bradykinin receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1991 Mar;34(3):1230–1233. doi: 10.1021/jm00107a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Griesbacher T., Eckhardt M., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyne S., Pyne N. J. Differential effects of B2 receptor antagonists upon bradykinin-stimulated phospholipase C and D in guinea-pig cultured tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):477–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Jukic D., Tousignant C., Rhaleb N. E. Kinin receptor classification. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992;38(Pt 1):475–486. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7321-5_60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Nantel F. Direct activation of G proteins. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Oct;11(10):400–401. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90144-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Regoli D., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (HOE 140: D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Qic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90661-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvino J. M., Seoane P. R., Douty B. D., Awad M. M., Dolle R. E., Houck W. T., Faunce D. M., Sawutz D. G. Design of potent non-peptide competitive antagonists of the human bradykinin B2 receptor. J Med Chem. 1993 Aug 20;36(17):2583–2584. doi: 10.1021/jm00069a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff A., Amrani Y., Landry Y., Gies J. P. Comparative action of new highly potent bradykinin receptor antagonists in the guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 3;239(1-3):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)91000-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff A., Da Silva A., Landry Y., Gies J. P. Effect of Hoe 140, a new B2 noncompetitive antagonist, on guinea pig tracheal bradykinin receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Dec;263(3):1377–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


