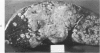
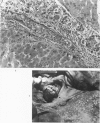
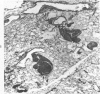
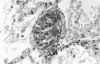
Full text
PDF






















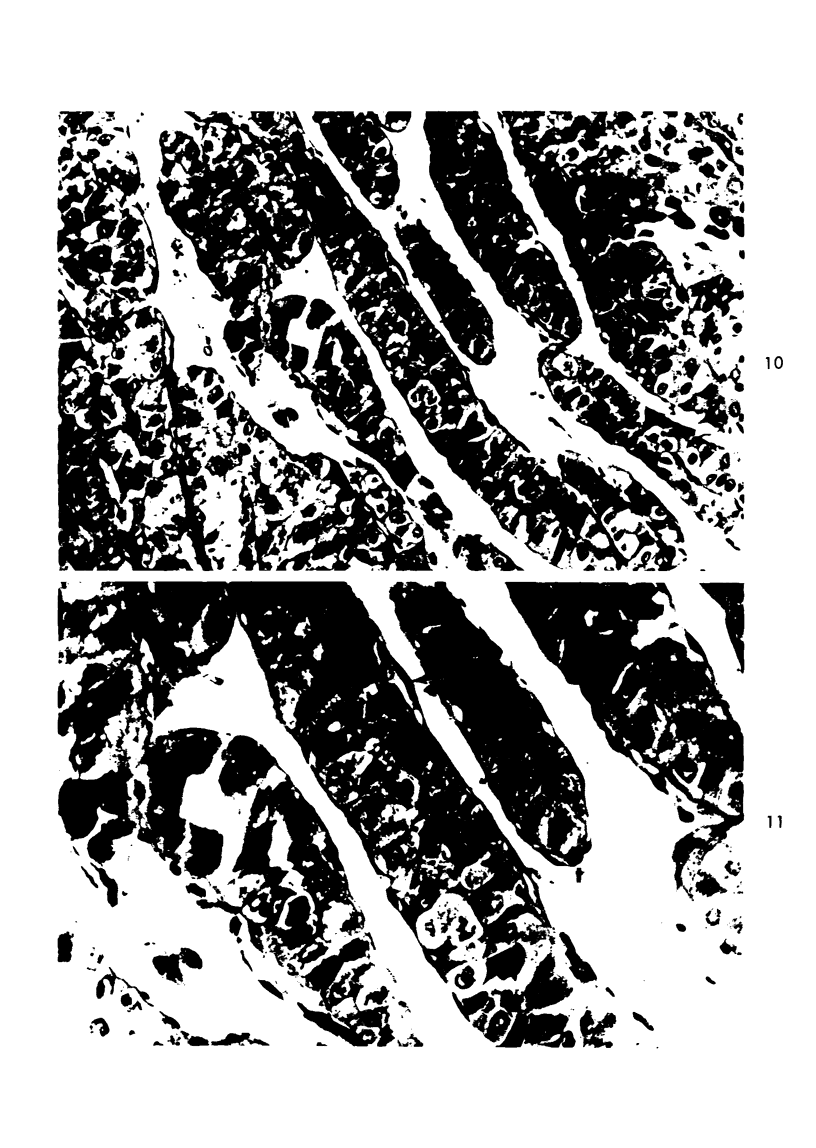
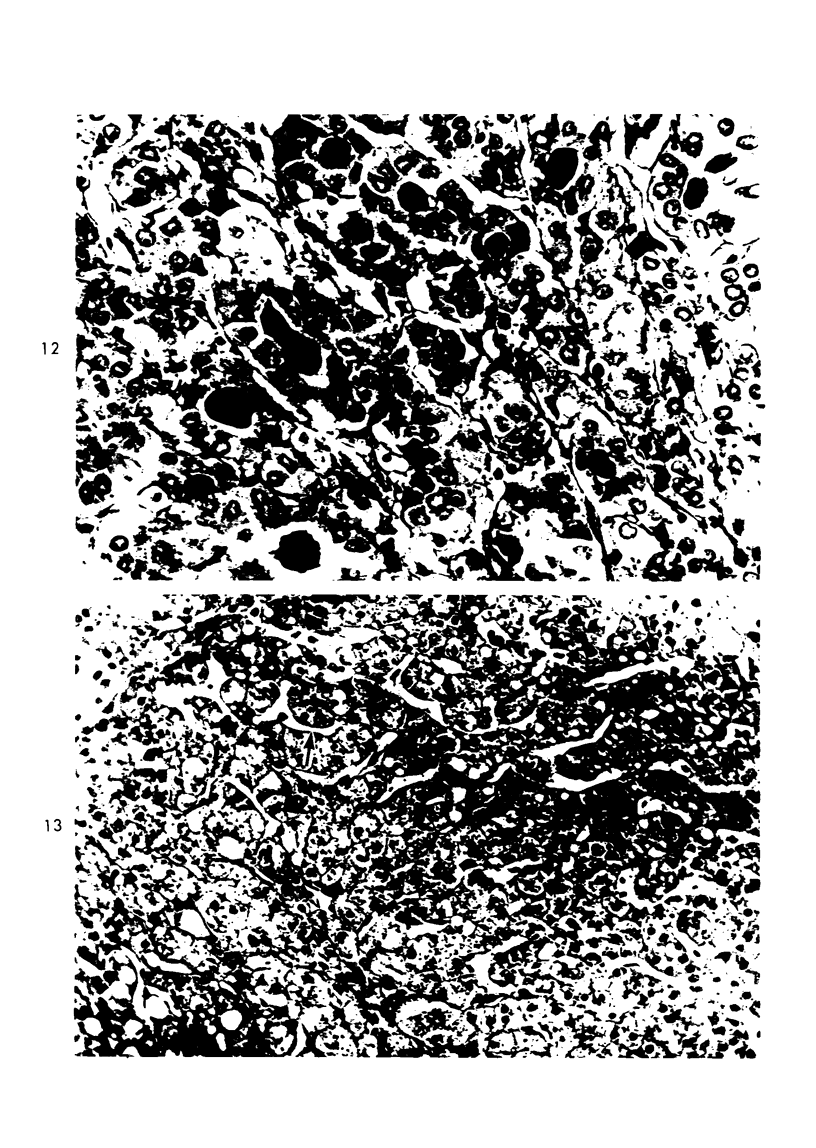
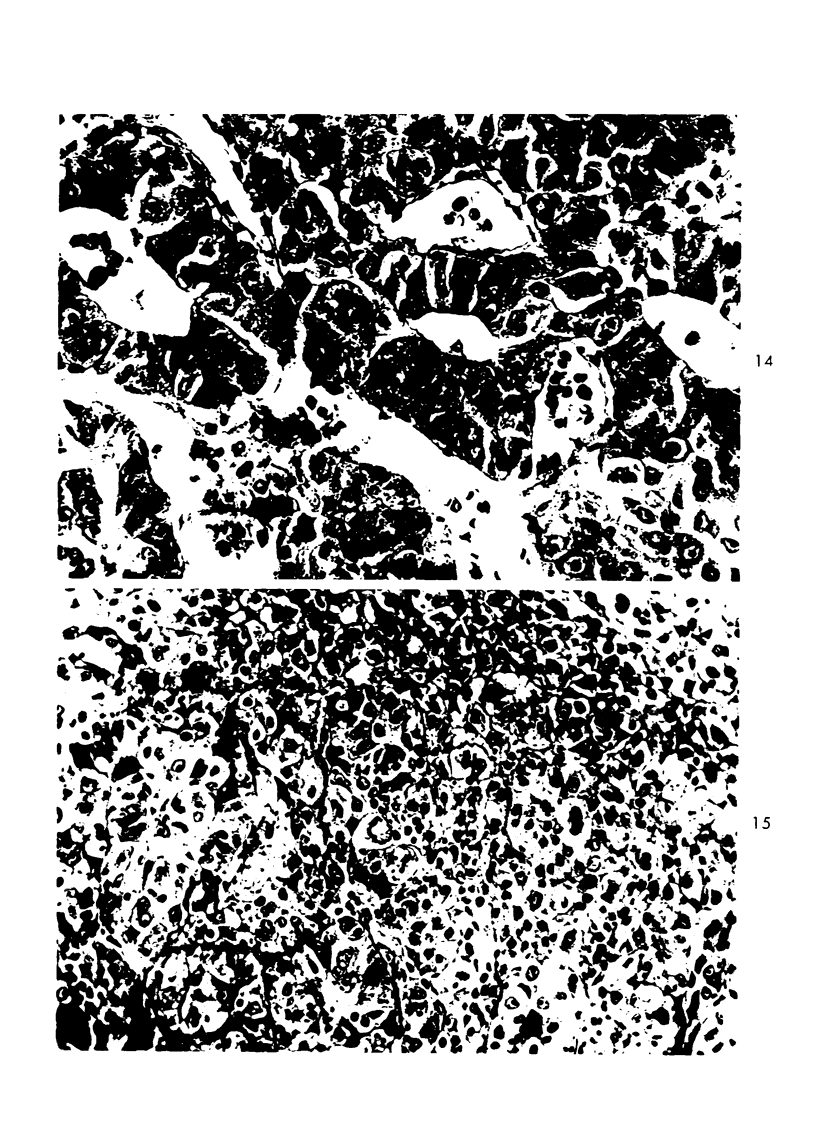
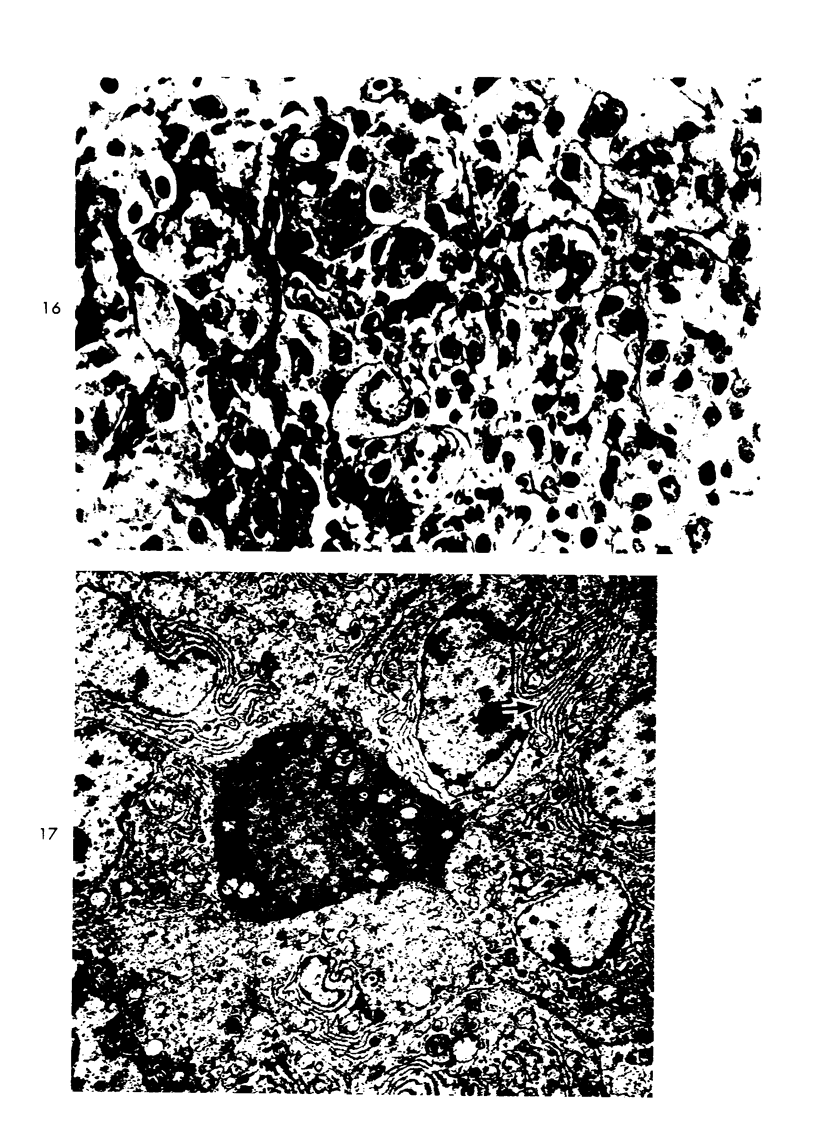
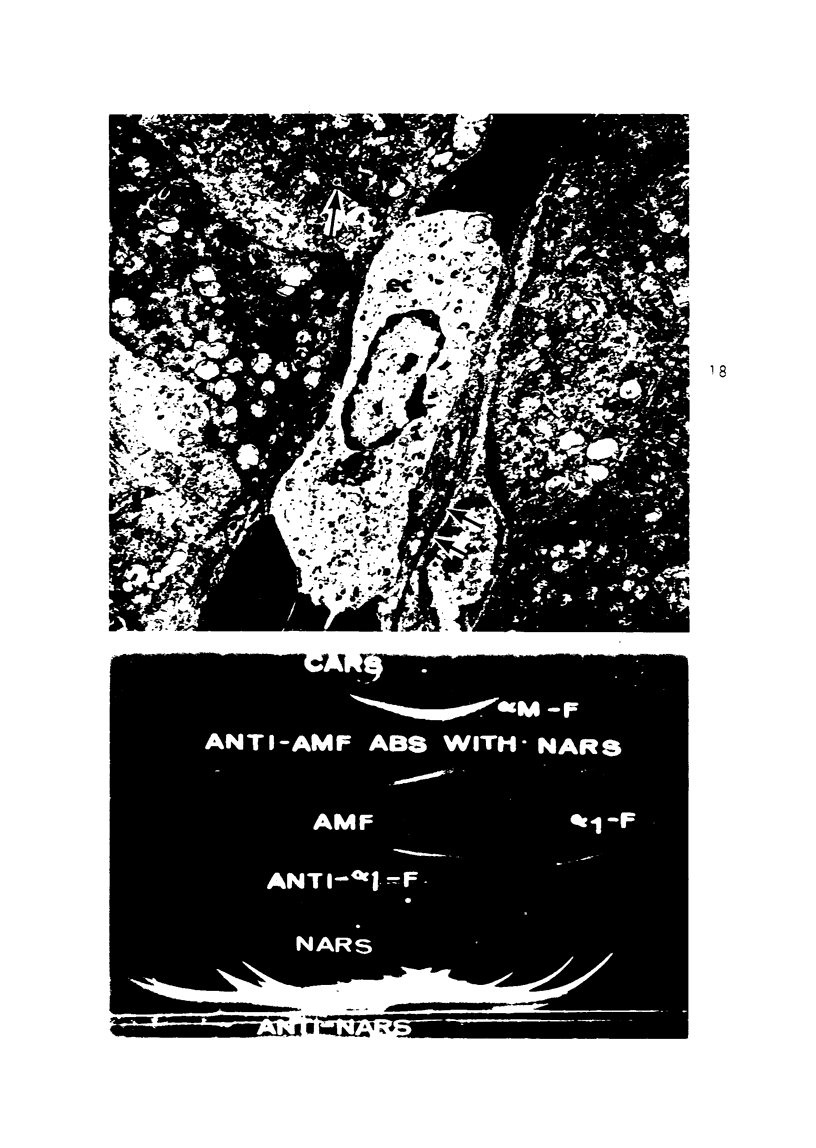

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelev G. I. Alpha-fetoprotein in ontogenesis and its association with malignant tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 1971;14:295–358. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert M. E., Davidson C. S. Mycotoxins. A possible cause of primary carcinoma of the liver. Am J Med. 1969 Mar;46(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert M. E., Hutt M. S., Davidson C. S. Primary hepatoma in Uganda. A prospective clinical and epidemiologic study of forty-six patients. Am J Med. 1969 May;46(5):794–802. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert M. E., Hutt M. S., Wogan G. N., Davidson C. S. Association between aflatoxin content of food and hepatoma frequency in Uganda. Cancer. 1971 Jul;28(1):253–260. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197107)28:1<253::aid-cncr2820280151>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariel I. M., Pack G. T. Treatment of inoperable cancer of the liver by intra-arterial radioactive isotopes and chemotherapy. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):793–804. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<793::aid-cncr2820200534>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTTOMLEY R. H., PITOT H. C., MORRIS H. P. Metabolic adaptations in rat hepatomas. IV. Regulation of threonine and serine dehydrase. Cancer Res. 1963 Mar;23:392–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker F. F., Fox R. A., Klein K. M., Wolman S. R. Chromosome patterns in rat hepatocytes during N-2-fluorenylacetamide carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Jun;46(6):1261–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker F. F., Klein K. M. The effect of L-asparaginase on mitotic activity during N-2-fluorenylacetamide hepatocarcinogenesis: subpopulations of nodular cells. Cancer Res. 1971 Feb;31(2):169–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker F. F., Klein K. M. The synergistic effect of hypoglycemia and L-asparaginase upon transplantable hepatomas of varying growth rates. Cancer Res. 1972 Oct;32(10):2082–2084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank R. J., Tysan I. B. Intra-arterial 131-I-macroaggregated albumin to define intrahepatic tumors: a possible method of quantitating tumor response to therapy. J Nucl Med. 1969 Jul;10(7):514–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasfield R. D., Bowden L., McPeak C. J. Major hepatic resection for malignant neoplasms of the liver. Ann Surg. 1972 Aug;176(2):171–177. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197208000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M. H., Ballard H. S. Hepatoma associated with erythrocytosis. Am J Med. 1966 Feb;40(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher N. L. Experimental aspects of hepatic regeneration. N Engl J Med. 1967 Oct 5;277(14):738–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196710052771405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen R. O., Page L. A., Greenberg R. E. Glycogen storage in a hepatoma: dephosphophosphorylase kinase defect. Pediatrics. 1968 Oct;42(4):694–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell J. A., Wilber J. F. Studies of insulin and growth hormone secretion in a subject with hepatoma and gypoglycemia. Diabetes. 1971 Sep;20(9):607–614. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.9.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoust R. Focal loss of ribonuclease activity in preneoplastic rat liver. Cancer Res. 1972 Nov;32(11):2502–2509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillard B. M. Experience with twenty-six hepatic lobectomies and extensive hepatic resections. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 Aug;129(2):249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S., Ito N., Merkow L., Farber E. Cellular analysis of liver carcinogenesis: the induction of large hyperplastic nodules in the liver with 2-fluorenylacetamide or ethionine and some aspects of their morphology and glycogen metabolism. Cancer Res. 1967 Sep;27(9):1702–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filler R. M., Tefft M., Vawter F., Maddock C., Mitus A. Hepatic lobectomy in childhood: effectws of x-ray and chemotherapy. J Pediatr Surg. 1969 Feb;4(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(69)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALL E. A. Posthepatitic, postnecrotic, and nutritional cirrhosis: a pathologic analysis. Am J Pathol. 1960 Mar;36:241–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Zanjani E. D., Zalusky R. A possible mechanism for the erythrocytosis associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in man. Blood. 1970 Feb;35(2):151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESTON W. E., VLAHAKIS G., DERINGER M. K. High incidence of spontaneous hepatomas and the increase of this incidence with urethan in C3H, C3Hf, and C3He male mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Feb;24:425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. N., Chen K. K. Development of hepatic tumors in rats following ingestion of Senecio longilobus. Cancer Res. 1970 Dec;30(12):2881–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higginson J., Svoboda D. J. Primary carcinoma of the liver as a pathologist's problem. Pathol Annu. 1970;5:61–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMPSCHMIDT R. F. MECHANISM OF LIVER CATALASE DEPRESSION IN TUMOR-BEARING ANIMALS: A REVIEW. Cancer Res. 1965 Jan;25:34–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knill-Jones R. P., Buckle R. M., Parsons V., Calne R. Y., Williams R. Hypercalcemia and increased parathyroid-hormone activity in a primary hepatoma. Studies before and after hepatic transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 26;282(13):704–708. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003262821302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Pennington L. F. Tumor hypoglycemia: a heterogeneous disorder. Metabolism. 1970 Jun;19(6):445–452. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroes R., Williams G. M., Weisburger J. H. Early appearance of serum -fetoprotein during hepatocarcinogenesis as a function of age of rats and extent of treatment with 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 1972 Jul;32(7):1526–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAQUEUR G. L. CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS OF CYCAD MEAL AND CYCASIN, METHYLAZOXYMETHANOL GLYCOSIDE, IN RATS AND EFFECTS OF CYCASIN IN GERMFREE RATS. Fed Proc. 1964 Nov-Dec;23:1386–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. I. Cirrhosis and hepatoma in alcoholics. Gut. 1966 Feb;7(1):77–85. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD R. A. Primary carcinoma of the liver; a clinicopathologic study of one hundred eight cases. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1957 Feb;99(2):266–279. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1957.00260020102015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean A. J., Yeung R. T. Further observations on hypoglycaemia in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Med. 1969 Aug;47(2):220–235. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A. Carcinogenesis by chemicals: an overview--G. H. A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res. 1970 Mar;30(3):559–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Sugimura M., Ishida M., Endo Y., Oda T. [Intra-arterial chemotherapy of primary hepatoma and changes in -fetoprotein levels]. Nihon Rinsho. 1972 May;30(5):1201–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Gleich G. J., Hull E. W. Australia antigen and primary liver cancer. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Nov;15(11):983–985. doi: 10.1007/BF02232815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. G., Walker W. C., Mason M. K., Herlinger H., Losowsky M. S. A new syndrome associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1972 Aug;63(2):340–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori W. Cirrhosis and primary cancer of the liver. Comparative study in Tokyo and Cincinnati. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):627–631. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<627::aid-cncr2820200509>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Kimura K., Miura Y., Takaku F. Erythrocytosis associated with carcinoma of the liver (with erythropoietin assay of tumor extract). Am J Med Sci. 1966 Feb;251(2):161–165. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196602000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak N. C., Chawla V., Malaviya A. N., Chandra R. K. -fetoprotein in indian childhood cirrhosis. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):68–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebesar R. A., Pollard J. J., Stone D. L. Angiographic diagnosis of malignant disease of the liver. Radiology. 1966 Feb;86(2):284–292. doi: 10.1148/86.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka M., Hironaga K., Fujita T. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of sera from patients with primary liver carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Feb;31(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka M., Ibata T., Okita K., Harada T., Fujita T. Localization of -fetoprotein in hepatoma tissues by immunofluorescence. Cancer Res. 1972 Jan;32(1):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OETTLE A. G. CANCER IN AFRICA, ESPECIALLY IN REGIONS SOUTH OF THE SAHARA. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Sep;33:383–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onuigbo W. I. Cancer permeation: processes, problems, and prospects--a review. Cancer Res. 1973 Apr;33(4):633–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Jr, Dahlin D. C., Stauffer M. H. Malignant hepatoma: evaluation of surgical (including needle biopsy) material from 69 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1970 Jan;45(1):25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C. Recent advances in the mechanism of hepatic carcinogenesis. Prog Liver Dis. 1970;3:77–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primack A., Wilson J., O'Connor G. T., Engelman K., Hull E., Canellos G. P. Hepatocellular carcinoma with the carcinoid syndrome. Cancer. 1971 May;27(5):1182–1189. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197105)27:5<1182::aid-cncr2820270525>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves L. R., Bersohn I., Geddes E. W. Serum alpha-feto-protein and primary cancer of the liver in man. Cancer. 1970 Jun;25(6):1261–1270. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197006)25:6<1261::aid-cncr2820250603>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUATTLEBAUM J. K. Massive resection of the liver. Ann Surg. 1953 Jun;137(6):787–796. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195306000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGEBIEL R. W., MCFARLAND R. B., TAFT E. B. PRIMARY CARCINOMA OF THE LIVER IN RELATION TO CIRRHOSIS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1963 Nov;40:516–520. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/40.5.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smetana K., Gyorkey F., Gyorkey P., Busch H. Studies on nucleoli and cytoplasmic fibrillar bodies of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1972 May;32(5):925–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Francis T. I. Immunoepidemiological and in vitro studies of possible relationships between Australia antigen and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1972 Aug;32(8):1713–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanislawski-Birencwajg M., Uriel J., Grabar P. Association of embryonic antigens with experimentally induced hepatic lesions in the rat. Cancer Res. 1967 Nov;27(11):1990–1997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutnick A. I., London W. T., Blumberg B. S. Australia antigen: a genetic basis for chronic liver disease and hepatoma? Ann Intern Med. 1971 Mar;74(3):443–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATARINOV Iu S. OBNARUZHENIE EMBRIOSPETSIFICHESKOGO ALPHA-GLOBULINA V SYVOROTKE KROVI BOL'NOGO PERVICHNYM RAKOM PECHENI. Vopr Med Khim. 1964 Jan-Feb;10:90–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON W. T., Jr, HIGGINS W. H., Jr Primary carcinoma of the liver. Va Med Mon (1918) 1952 Jun;79(6):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teebor G. W., Becker F. F. Regression and persistence of hyperplastic hepatic nodules induced by N-2-Fluorenylacetamide and their relationship to hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1971 Jan;31(1):1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong M. J., Sun S. C., Schaeffer B. T., Chang N. K., Lo K. J., Peters R. L. Hepatitis-associated antigen and hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Nov;75(5):687–691. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-5-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhouse S. Glycolysis, respiration, and anomalous gene expression in experimental hepatomas: G.H.A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res. 1972 Oct;32(10):2007–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. J. Fine structure and surface adenosinetriphosphatase activity of a human hepatoma. Cancer. 1968 Nov;22(5):1046–1052. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196811)22:5<1046::aid-cncr2820220521>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wogan G. N., Newberne P. M. Dose-response characteristics of aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis in the rat. Cancer Res. 1967 Dec;27(12):2370–2376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L. Differential growth of hepatoma-susceptible liver induced by gene X genome interaction. Cancer Res. 1970 Jun;30(6):1722–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Felten A., Straub P. W., Frick P. G. Dysfibrinogenemia in a patient with primary hepatoma. First observation of an acquired abnormality of fibrin monomer aggregation. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 20;280(8):405–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902202800802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]