Abstract
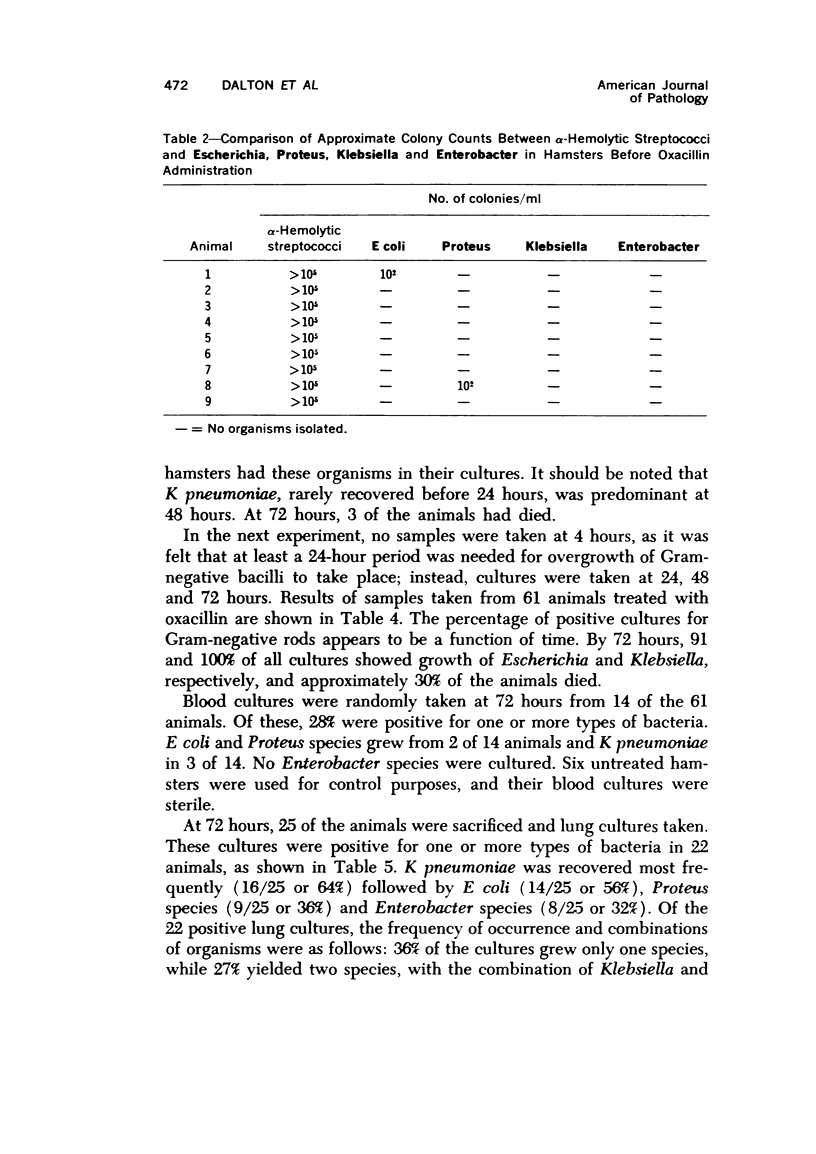
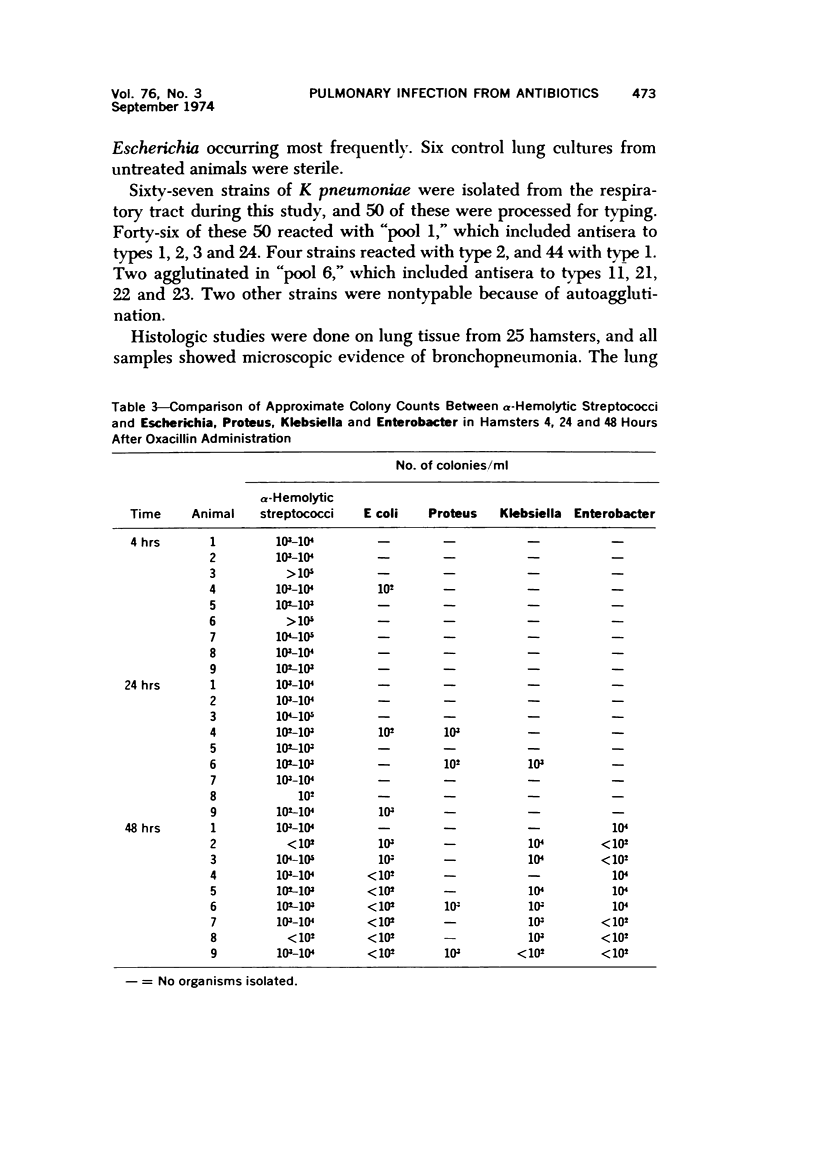
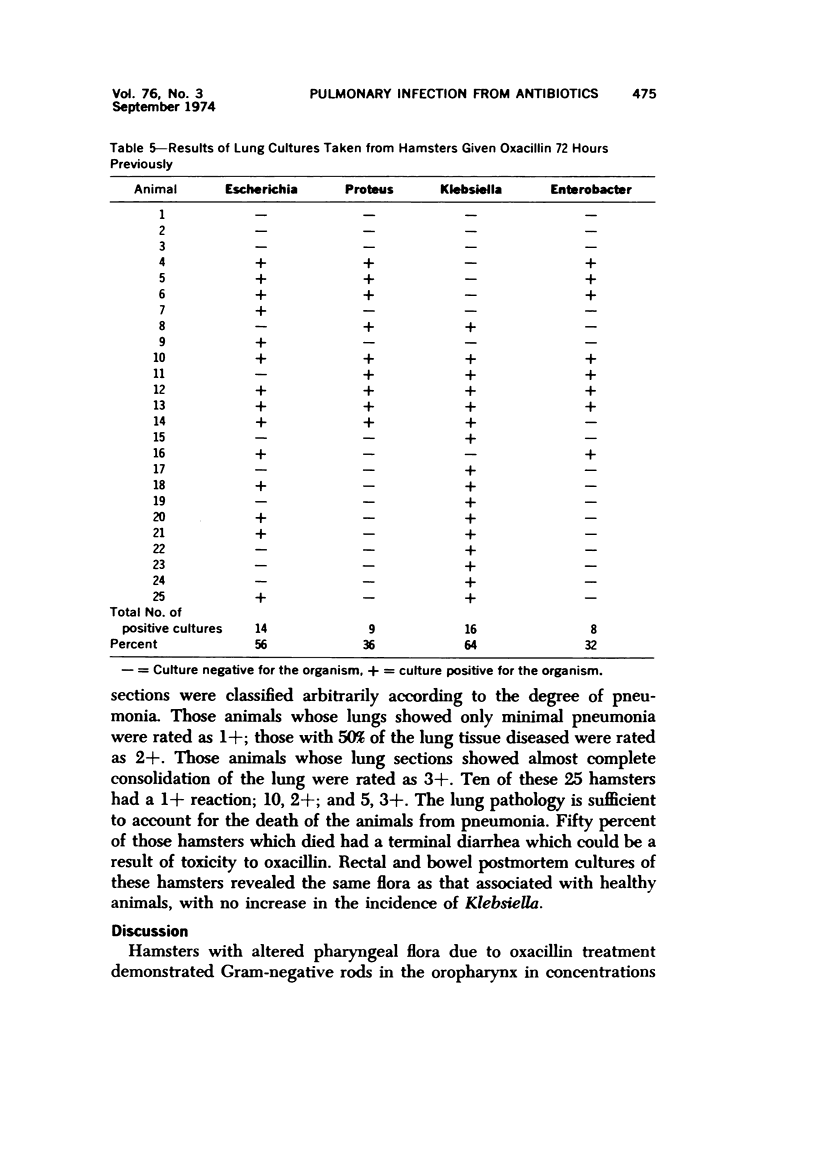
An animal model was used to determine the effect of oxacillin on the pharyngeal bacterial flora and the relationship of this flora to pneumonia. The pharyngeal bacterial flora of 68 healthy Golden Syrian hamsters was determined. A quantitative comparison between Streptococci and Escherichia, Proteus, Klebsiella and Enterobacter from 70 hamsters was made before and at 4, 24, 48 and 72 hours after oxacillin administration. Lung cultures were positive in 22 of 25 hamsters, yielding K pneumoniae type 1 most frequently. Lung histology from 25 hamsters revealed bronchopneumonia. Intestinal postmortem cultures of treated and untreated animals were similar. The importance of throat cultures in diagnosing pneumonia and the value of the hamster model to study the effect of other antibiotics on the temporary flora are demonstrated.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EISENBERG G. M., FLIPPIN H. F., KAYSER H. L., NADEL J., SATHAVARA S., SPIVACK A., WEISS W. Klebsiella in respiratory disease. Ann Intern Med. 1956 Dec;45(6):1010–1026. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-45-6-1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Changing pharyngeal bacterial flora of hospitalized patients. Emergence of gram-negative bacilli. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 20;281(21):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911202812101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass E. H., Green G. M., Goldstein E. Mechanisms of antibacterial action in the respiratory system. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Sep;30(3):488–497. doi: 10.1128/br.30.3.488-497.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Cappel R., Debusscher L., Stilmant M. Pneumonia caused by gram-negative bacilli in hospitalized patients presenting malignant disease. Eur J Cancer. 1971 Aug;7(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(71)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPE W. T. KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIA. A REVIEW OF FORTY-FIVE AND RE-EVALUATION OF THE INCIDENCE AND ANTIBIOTIC SENSITIVITIES. Dis Chest. 1964 Nov;46:599–606. doi: 10.1378/chest.46.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEADS M., ROWE W. P., HASLAM N. M. Alterations in the bacterial flora of the throat during oral therapy with aureomycin. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 Apr;87(4):533–540. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810040058003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson J. R., Finland M. Bacterial colonization and clinical superinfection of the respiratory tract complicating antibiotic treatment of pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):597–624. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson J. R., Finland M. Secondary pulmonary infections following antibiotic therapy for primary bacterial pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:326–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN L., GOLDFIELD M., CHANG TE-WEN Infections occurring during chemotherapy; a study of their frequency, type and predisposing factors. N Engl J Med. 1954 Aug 12;251(7):247–255. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195408122510701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOW E. M. Development of Proteus and Pseudomonas infections during antibiotic therapy. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Jul 26;149(13):1184–1188. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.02930300010003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


