Abstract
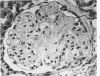
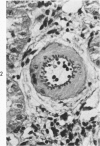
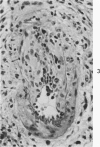
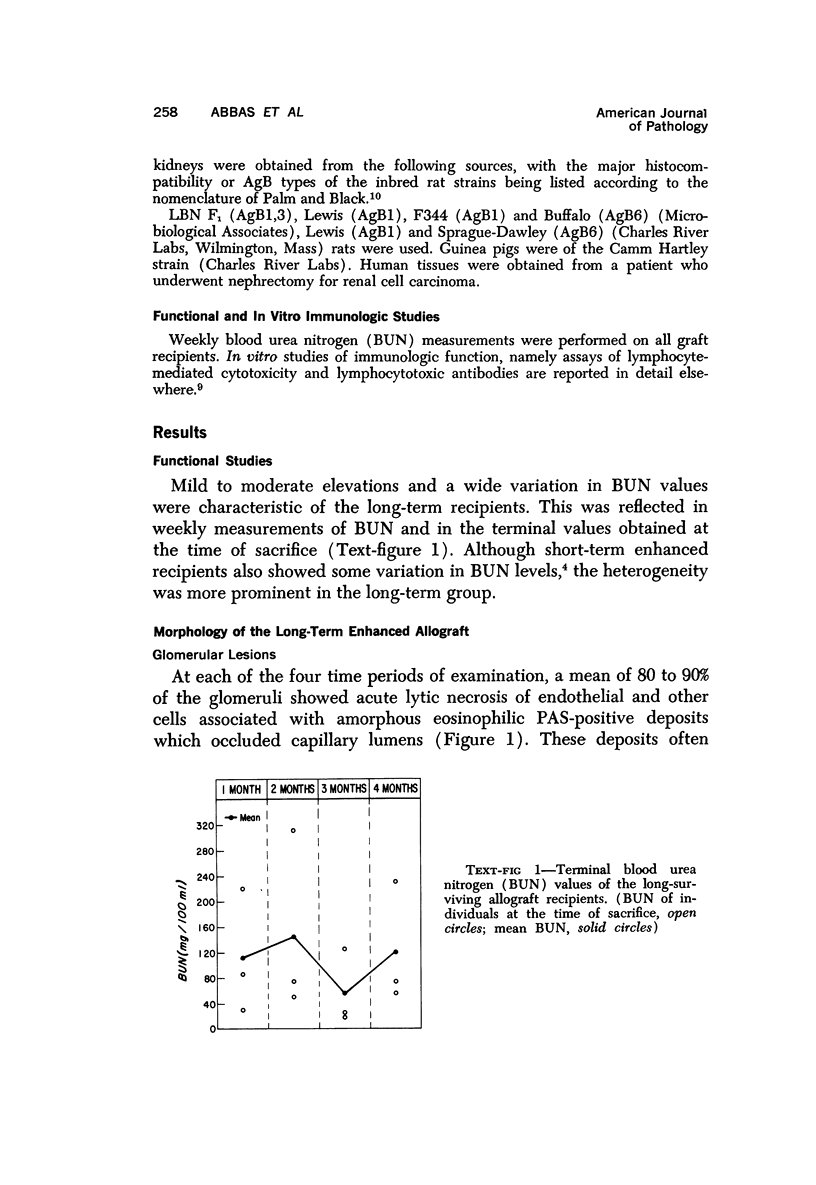
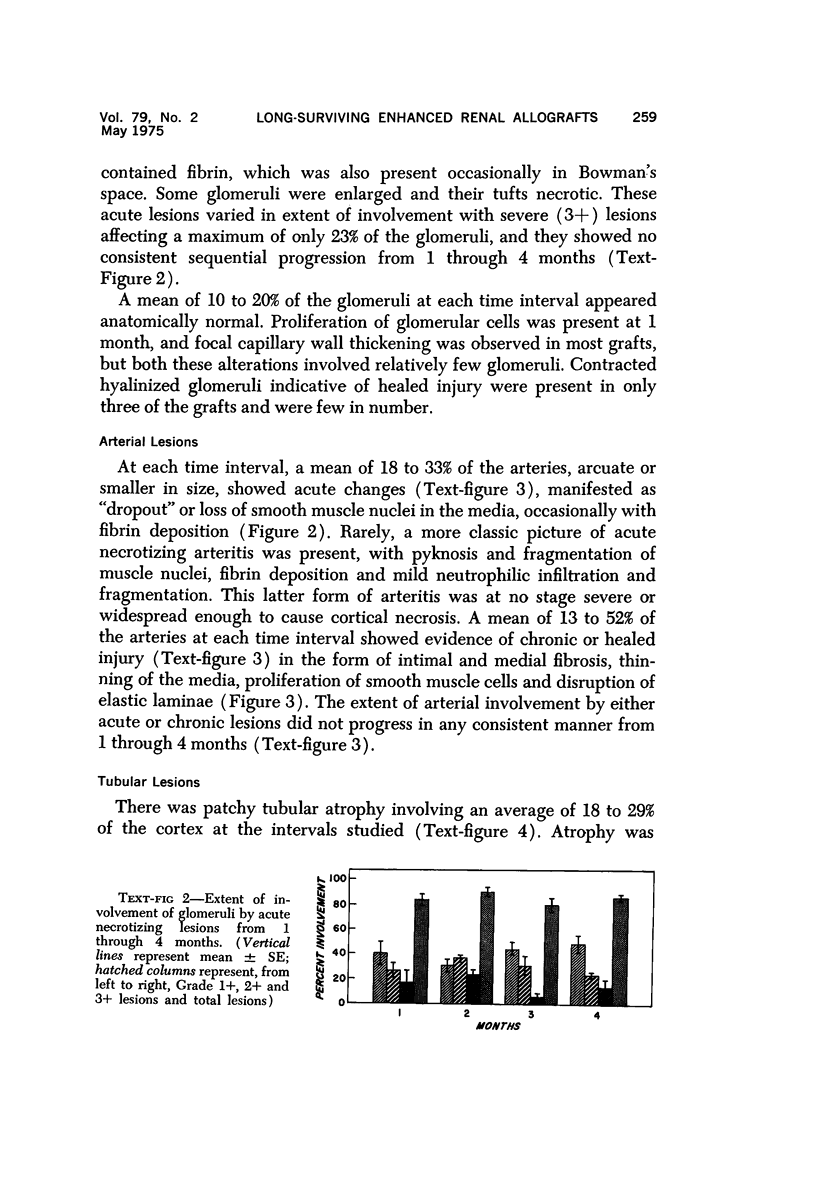
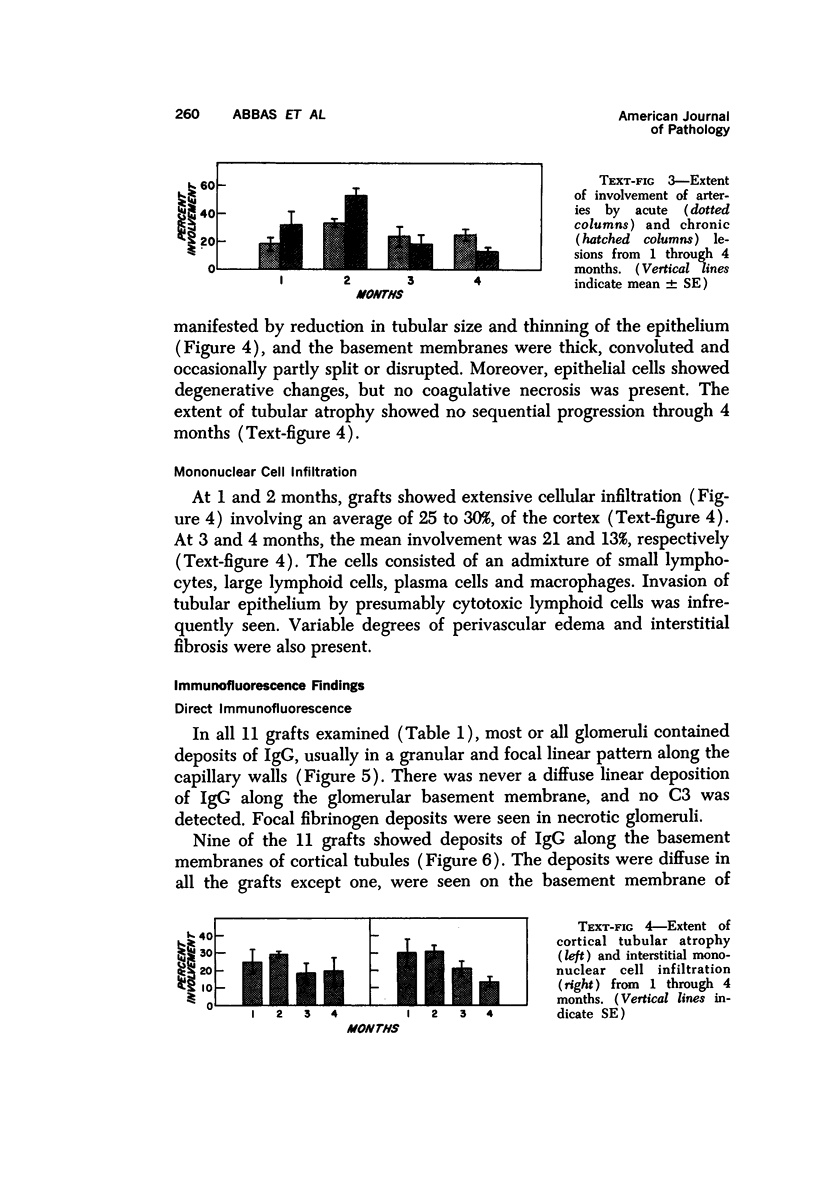
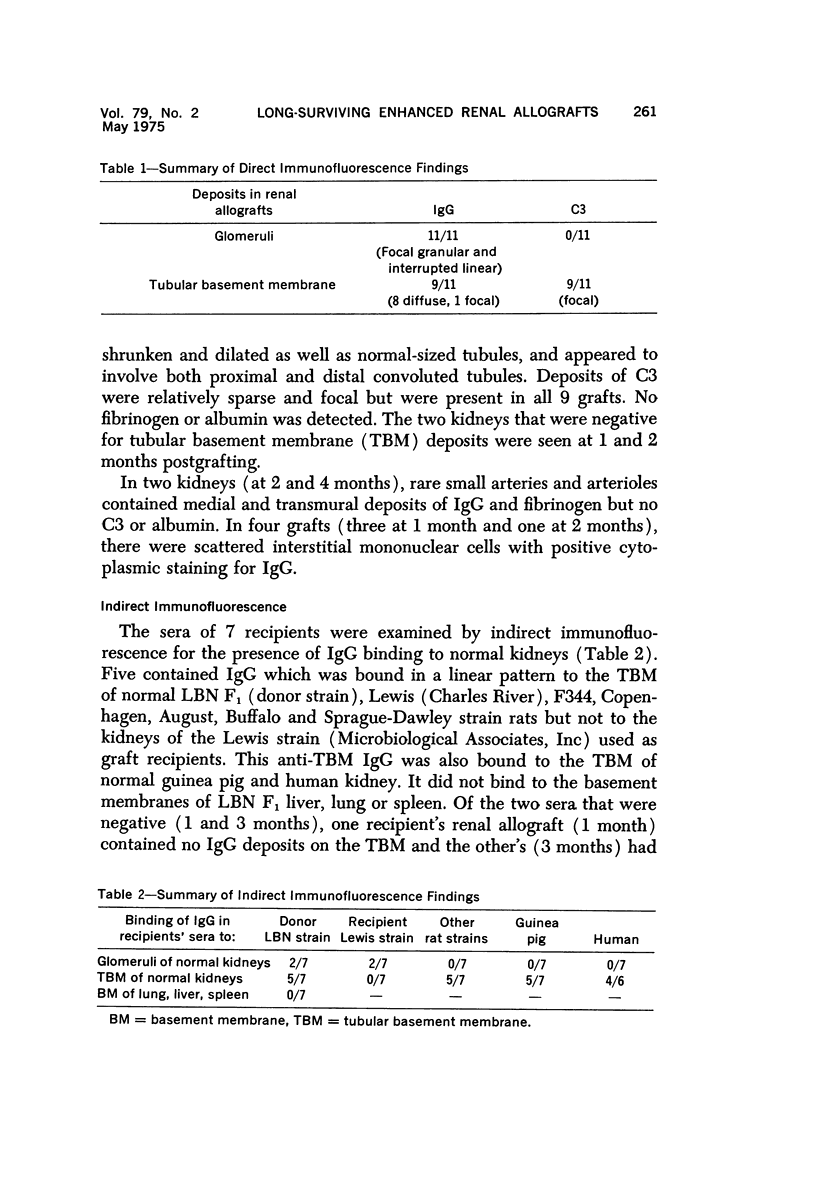
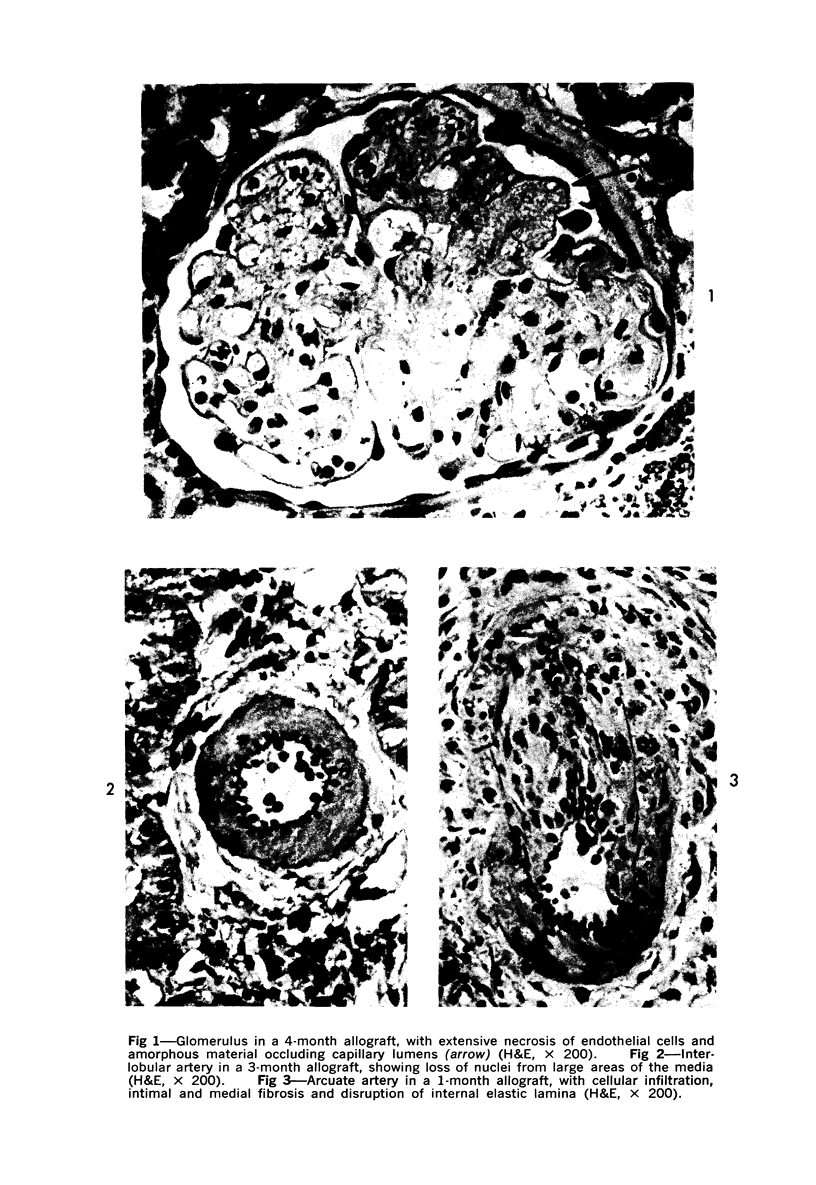
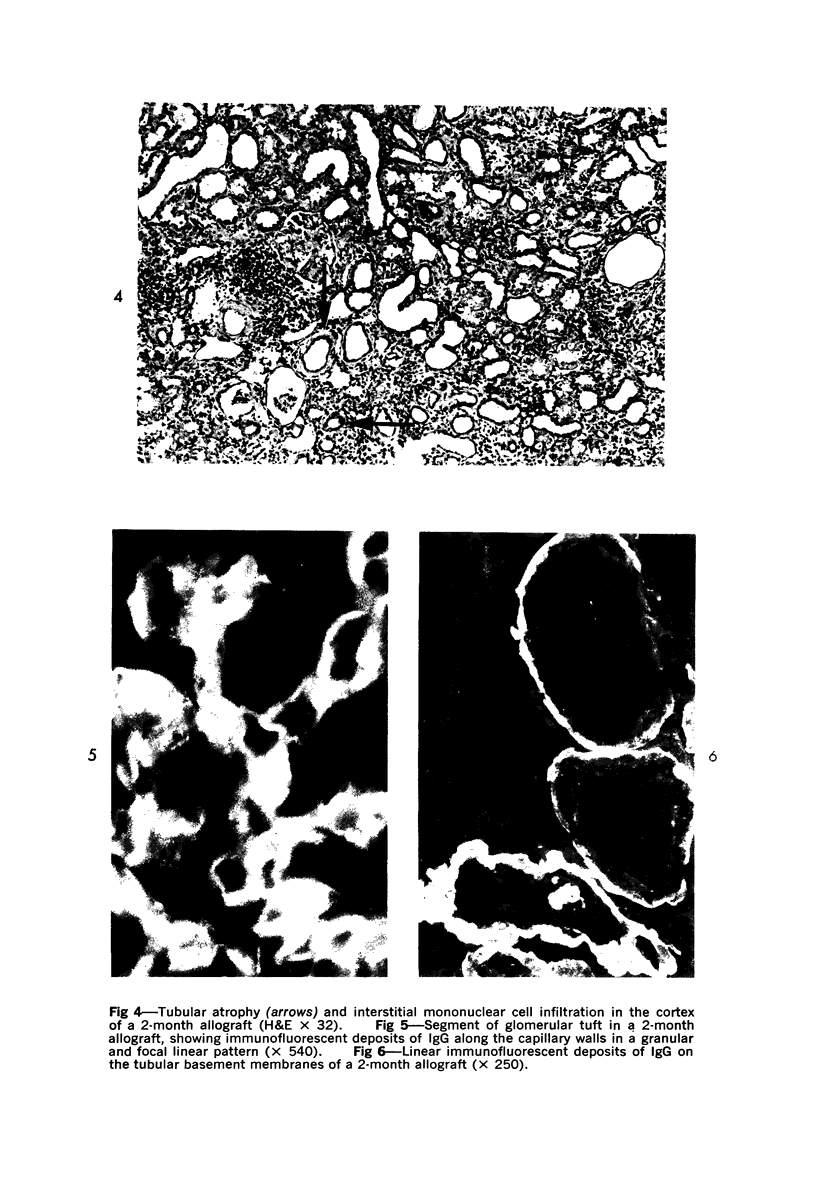
Immunologic enhancement of renal allografts from (Lewis times Brown Norway) F1 to Lewis rats was achieved by administering a single dose of antidonor serum at the time of transplantation. A series of grafts functioning for 1 to 4 months after transplantation were examined by light and immunofluorescence microscopy to evaluate the long-term protective effects of the enhancing serum and to determine if previously unobserved lesions appeared in long survivors. Despite the absence of detectable circulating cytotoxic alloantibody, long-term allografts showed necrotizing glomerular and arterial lesions which resembled those seen in acutely rejecting grafts and were compatible with humoral rejection. Thus, in this model, there is a late decline in the ability of passive enhancement to inhibit humoral rejection. Long-term grafts also developed tubular lesions with deposition of immunoglobulin and complement on the tubular basement membranes (TBM). Anti-TBM antibodies were demonstrated in recipients' sera and found to be organ specific but not major histocompatibility antigen or species specific. This tubular lesion is therefore a unique form of allograft injury in which the immune response is directed against tissue antigen(s) which are distinct from the major histocompatibility antigens that induce rejection.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K., Corson J. M., Carpenter C. B., Galvanek E. G., Merrill J. P., Dammin G. J. Immunologic enhancement of rat renal allografts. I. Comparative morphology of acutely rejecting and passively enhanced grafts. Am J Pathol. 1974 May;75(2):255–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbas A. K., Corson J. M., Carpenter C. B., Galvanek E. G., Merrill J. P., Dammin G. J. Immunologic enhancement of rat renal allografts. II. Immunohistology of acutely rejecting and passively enhanced grafts. Am J Pathol. 1974 May;75(2):271–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres G. A., Accinni L., Hsu K. C., Penn I., Porter K. A., Rendall J. M., Seegal B. C., Starzl T. E. Human renal transplants. 3. Immunopathologic studies. Lab Invest. 1970 Jun;22(6):588–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker J. L., Fitch F. W., Rowley D. A., Stuart F. P. Cellular and humoral immunity after allogeneic transplantation in the rat. 3. The effect of passive antibody on cellular and humoral immunity after allogeneic renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1973 Nov;16(5):432–440. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197311000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G. J., Reynolds E. S., Galvanek E. G., Braun W. E., Dammin G. J. Human renal allografts. The role of vascular injury in early graft failure. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Jan;50(1):29–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. E., Batchelor J. R. Immunological enhancement of rat kidney grafts. Lancet. 1969 Nov 22;2(7630):1103–1106. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90705-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garovoy M. R., Phillips S. M., Carpenter C. B., Merrill J. P. Antibody modulation of cellular reactivity post renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. P., Shaipanich T., Sells R. A., Maggs P., Lukl P., Wilson R. E. Active enhancement of rat renal allografts with soluble splenic antigen. Transplantation. 1972 Mar;13(3):322–329. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197203000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klassen J., Kano K., Milgrom F., Menno A. B., Anthone S., Anthone R., Sepulveda M., Elwood C. M., Andres G. A. Tubular lesions produced by autoantibodies to tubular basement membrane in human renal allografts. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(5):675–689. doi: 10.1159/000231067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klassen J., McCluskey R. T., Milgrom F. Nonglomerular renal disease produced in rabbits by immunization with homologous kidney. Am J Pathol. 1971 May;63(2):333–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman D. H., Lee S., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Induction of antitubular basement membrane antibodies in rats by renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1974 Apr;17(4):429–431. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197404000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman D. H., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Interstitial nephritis in rats immunized with heterologous tubular basement membrane. Kidney Int. 1974 Mar;5(3):187–195. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. R., Guttmann R. D., Merrill J. P. Renal transplantation in the inbred rat. II. An immunohistochemical study of acute allograft rejection. Am J Pathol. 1968 Mar;52(3):531–545. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas Z. J., Markley J., Travis M. Immunologic enhancement of renal allografts in the rat. I. Dissociation of graft survival and antibody response. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):2041–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R., Lucas Z. J. Immunologic enhancement of rat kidney grafts: evidence for peripheral action of homologous antiserum. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):697–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen Y., Takasugi M., Hildemann W. H. The immunologic status of rats with long-surviving (enhanced) kidney allografts. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner S. A., Guttmann R. D., Lindquist R. R. Renal transplantation in the inbred rat. 13. Modification of rejection by active immunization with bone marrow cells. Transplantation. 1970 Jan;9(1):30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palm J., Black G. Interrelationships of inbred rat strains with respect to Ag-B and non-Ag-B antigens. Transplantation. 1971 Feb;11(2):184–189. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197102000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quadracci L. J., Tremann J. A., Marchioro T. L., Striker G. E. Serum blocking factors in human recipients of renal allografts. Transplantation. 1974 Apr;17(4):361–370. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197404000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W., Rudofsky U. Renal tubular disease and autoantibodies against tubular basement membrane induced in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1971 Aug;107(2):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart F. P., Saitoh T., Fitch F. W. Rejection of renal allografts: specific immunologic suppression. Science. 1968 Jun 28;160(3835):1463–1465. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3835.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki T., Klassen J., Milgrom F., Andres G. A., McCluskey R. T. Immunopathologic study of an autoimmune tubular and interstitial renal disease in brown Norway rats. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):658–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Lehman D. H., McCoy R. C., Gunnells J. C., Jr, Stickel D. L. Antitubular basement membrane antibodies after renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1974 Nov;18(5):447–452. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197411000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]