Abstract
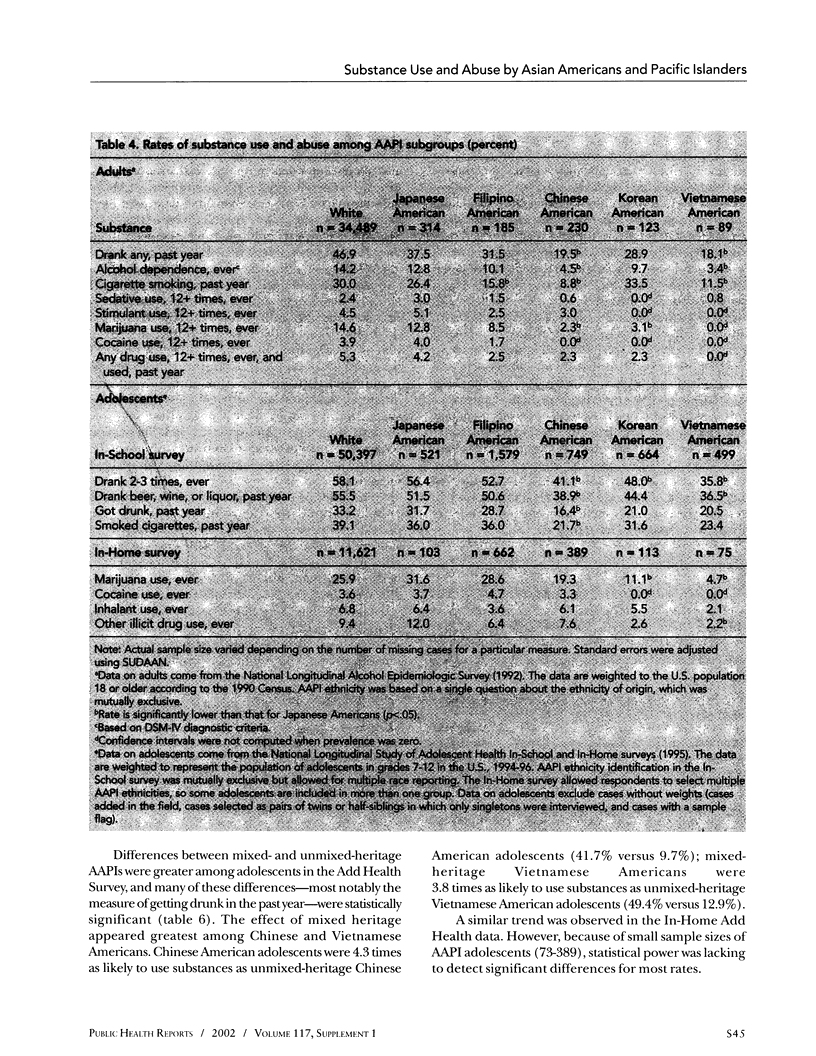
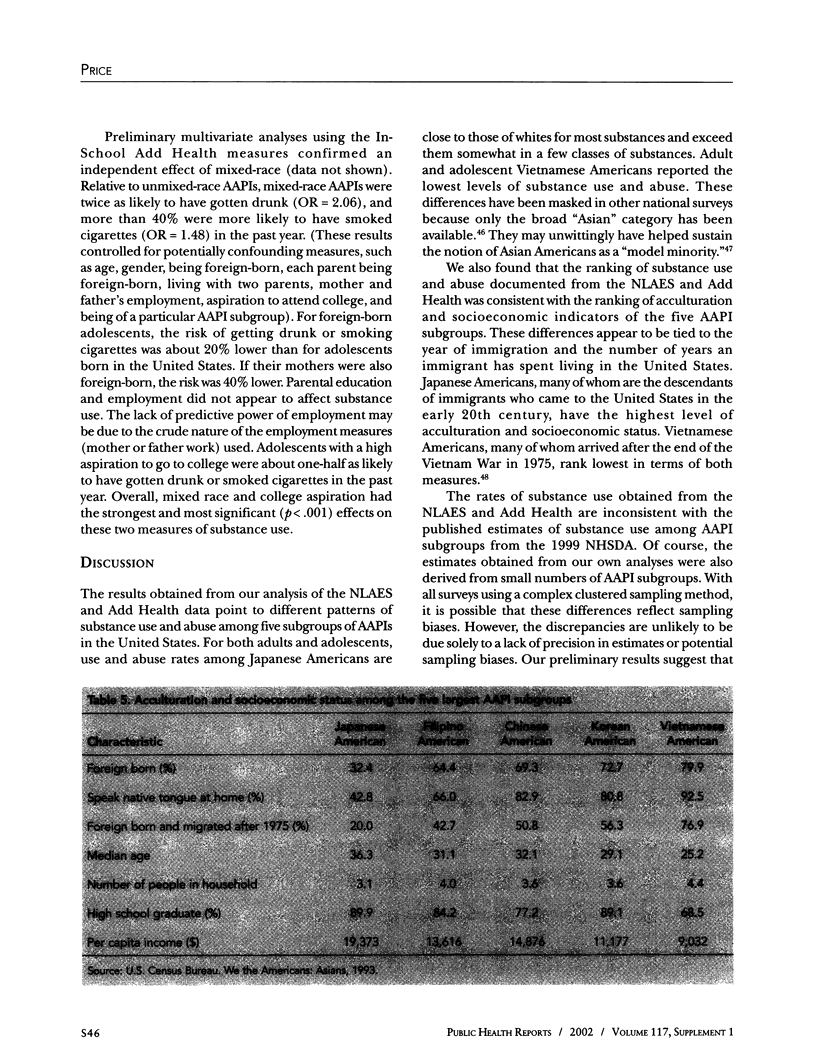
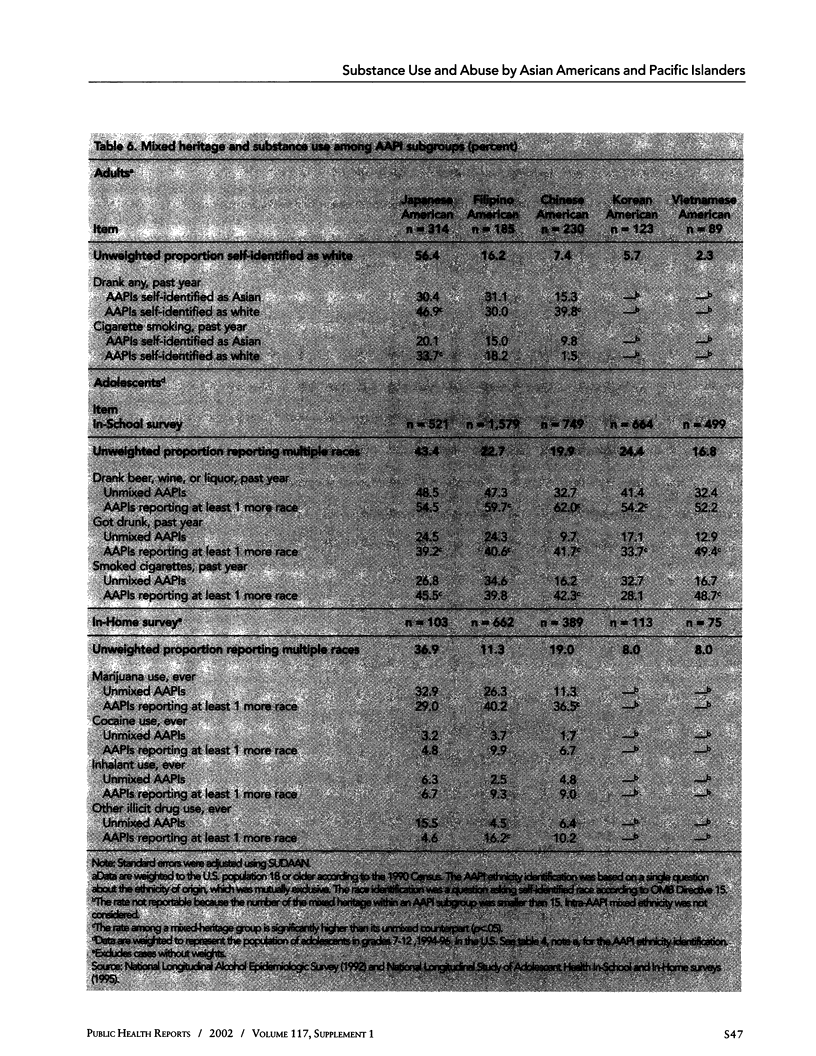
OBJECTIVE: The authors analyzed four recent large national surveys to assess the degree of use and abuse of a wide range of psychoactive substances across subgroups of Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders (AAPIs) and in comparison with whites. METHOD: The surveys analyzed were the 1999 National Household Survey on Drug Abuse, the 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey, and the 1995 National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health In-School and In-Home surveys. The AAPI sample sizes varied from 900 to more than 4,500 across the four surveys. RESULTS: Among major racial groups, use of major substances is lowest for AAPIs. Among disaggregated AAPI groups, Japanese Americans have the highest substance use rates. Mixed-heritage AAPIs are at high risk for substance use, even after controlling for cultural protective factors and socioeconomic measures. Differential rates correspond to the ranking of several acculturation and socioeconomic indices. CONCLUSION: The results, while preliminary, point to the importance of rethinking ethnic and racial classifications for estimating substance use and abuse, for studying substance abuse problems in mixed-heritage adolescents, and for studying socioenvironmental and potentially genetic protective factors.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachman J. G., Wallace J. M., Jr, O'Malley P. M., Johnston L. D., Kurth C. L., Neighbors H. W. Racial/Ethnic differences in smoking, drinking, and illicit drug use among American high school seniors, 1976-89. Am J Public Health. 1991 Mar;81(3):372–377. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.3.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Avanzo C. E., Frye B., Froman R. Culture, stress and substance use in Cambodian refugee women. J Stud Alcohol. 1994 Jul;55(4):420–426. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1994.55.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant B. F. Prevalence and correlates of alcohol use and DSM-IV alcohol dependence in the United States: results of the National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. J Stud Alcohol. 1997 Sep;58(5):464–473. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1997.58.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ja D. Y., Aoki B. Substance abuse treatment: cultural barriers in the Asian-American community. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1993 Jan-Mar;25(1):61–71. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1993.10472592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Nagoshi C. T. Asians, Asian-Americans and alcohol. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1990 Jan-Mar;22(1):45–52. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1990.10472196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. M., Fernandez M. Trends in Asian American racial/ethnic intermarriage: a comparison of 1980 and 1990 census data. Sociol Perspect. 1998;41(2):323–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oscarson M., McLellan R. A., Gullstén H., Yue Q. Y., Lang M. A., Bernal M. L., Sinues B., Hirvonen A., Raunio H., Pelkonen O. Characterisation and PCR-based detection of a CYP2A6 gene deletion found at a high frequency in a Chinese population. FEBS Lett. 1999 Apr 1;448(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pianezza M. L., Sellers E. M., Tyndale R. F. Nicotine metabolism defect reduces smoking. Nature. 1998 Jun 25;393(6687):750–750. doi: 10.1038/31623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. D., Bearman P. S., Blum R. W., Bauman K. E., Harris K. M., Jones J., Tabor J., Beuhring T., Sieving R. E., Shew M. Protecting adolescents from harm. Findings from the National Longitudinal Study on Adolescent Health. JAMA. 1997 Sep 10;278(10):823–832. doi: 10.1001/jama.278.10.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall T. L., Shea S. H., Chan K. K., Carr L. G. A genetic association with the development of alcohol and other substance use behavior in Asian Americans. J Abnorm Psychol. 2001 Feb;110(1):173–178. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.110.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellington C. Genetics and substance abuse. Clin Genet. 1998 Oct;54(4):266–266. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.1998.5440402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff P. H. Vasomotor sensitivity to alcohol in diverse Mongoloid populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Mar;25(2):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff D. A. Methamphetamine abuse: an overview for health care professionals. Hawaii Med J. 1997 Feb;56(2):34-6, 44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi T., Kamataki T. Genetic polymorphism of drug metabolizing enzymes: new mutations in CYP2D6 and CYP2A6 genes in Japanese. Pharm Res. 1998 Apr;15(4):517–524. doi: 10.1023/a:1011913407147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


