Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bormann J., Rundström N., Betz H., Langosch D. Residues within transmembrane segment M2 determine chloride conductance of glycine receptor homo- and hetero-oligomers. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3729–3737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter M. S., Cook S. A., Davisson M. T., White W. F., Camper S. A. A frameshift mutation in the mouse alpha 1 glycine receptor gene (Glra1) results in progressive neurological symptoms and juvenile death. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Nov;3(11):2025–2030. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.11.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Schmieden V., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H., Siddique T., Mohandas T. K., Becker C. M., Betz H. Alpha subunit variants of the human glycine receptor: primary structures, functional expression and chromosomal localization of the corresponding genes. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):771–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsmore S. F., Giros B., Suh D., Bieniarz M., Caron M. G., Seldin M. F. Glycine receptor beta-subunit gene mutation in spastic mouse associated with LINE-1 element insertion. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):136–141. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langosch D., Laube B., Rundström N., Schmieden V., Bormann J., Betz H. Decreased agonist affinity and chloride conductance of mutant glycine receptors associated with human hereditary hyperekplexia. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4223–4228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajendra S., Lynch J. W., Pierce K. D., French C. R., Barry P. H., Schofield P. R. Startle disease mutations reduce the agonist sensitivity of the human inhibitory glycine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18739–18742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees M. I., Andrew M., Jawad S., Owen M. J. Evidence for recessive as well as dominant forms of startle disease (hyperekplexia) caused by mutations in the alpha 1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Dec;3(12):2175–2179. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.12.2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. G., Buckwalter M. S., Lynch J. W., Handford C. A., Segura L., Shiang R., Wasmuth J. J., Camper S. A., Schofield P., O'Connell P. A missense mutation in the gene encoding the alpha 1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor in the spasmodic mouse. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):131–135. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. G., Dixon M. J., Nigro M. A., Kelts K. A., Markand O. N., Terry J. C., Shiang R., Wasmuth J. J., O'Connell P. Genetic and radiation hybrid mapping of the hyperekplexia region on chromosome 5q. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1334–1343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorderet D. F., Pescia G., Bernasconi A., Regli F. An additional family with Startle disease and a G1192A mutation at the alpha 1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jul;3(7):1201–1201. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.7.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
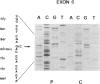
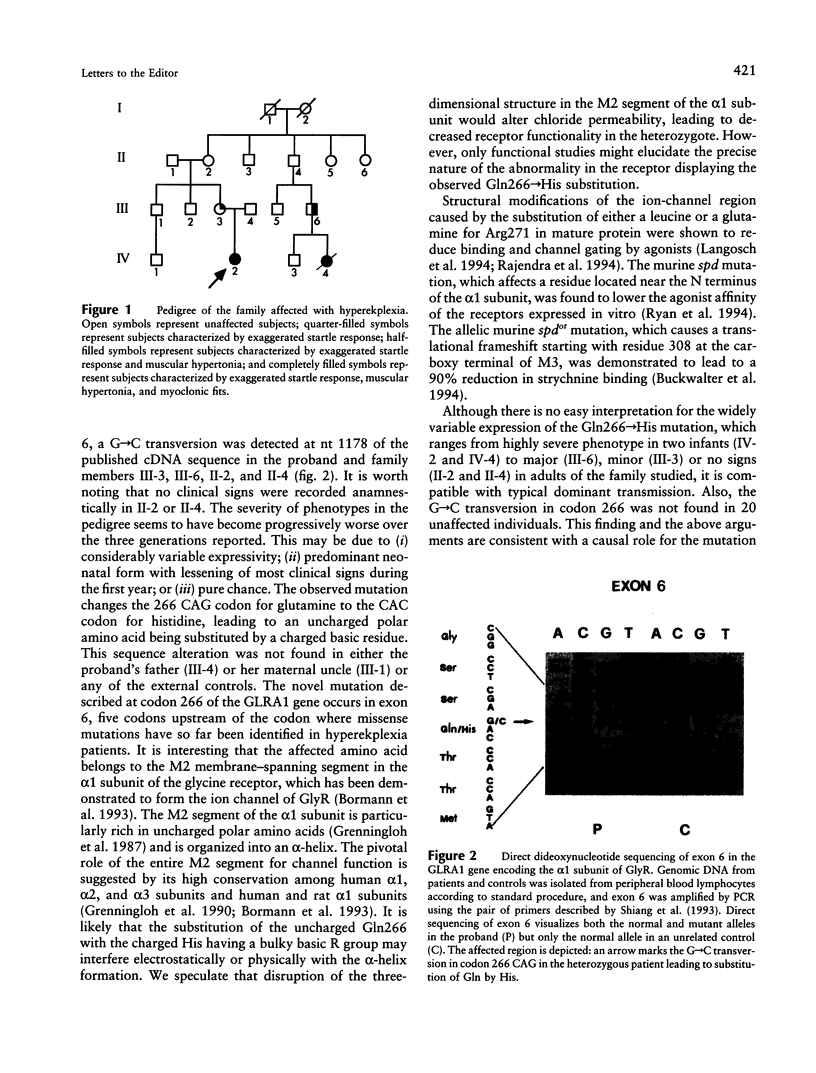
- Shiang R., Ryan S. G., Zhu Y. Z., Hahn A. F., O'Connell P., Wasmuth J. J. Mutations in the alpha 1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor cause the dominant neurologic disorder, hyperekplexia. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):351–358. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]