Abstract
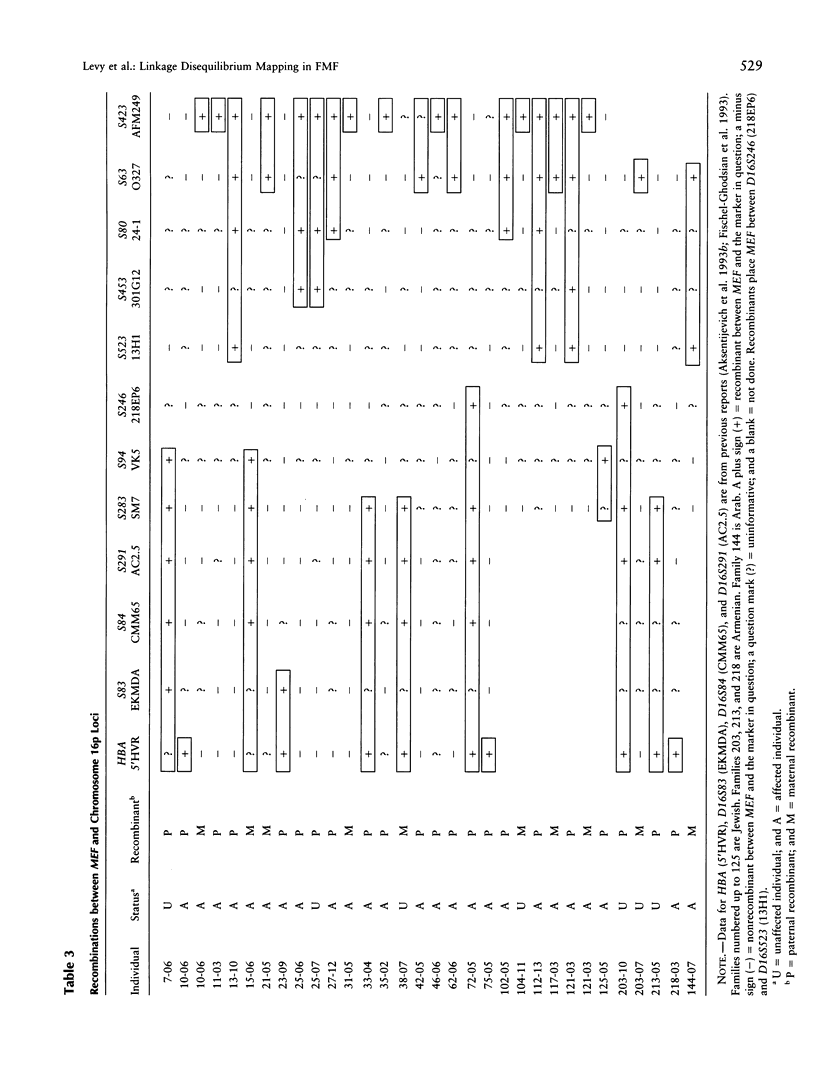
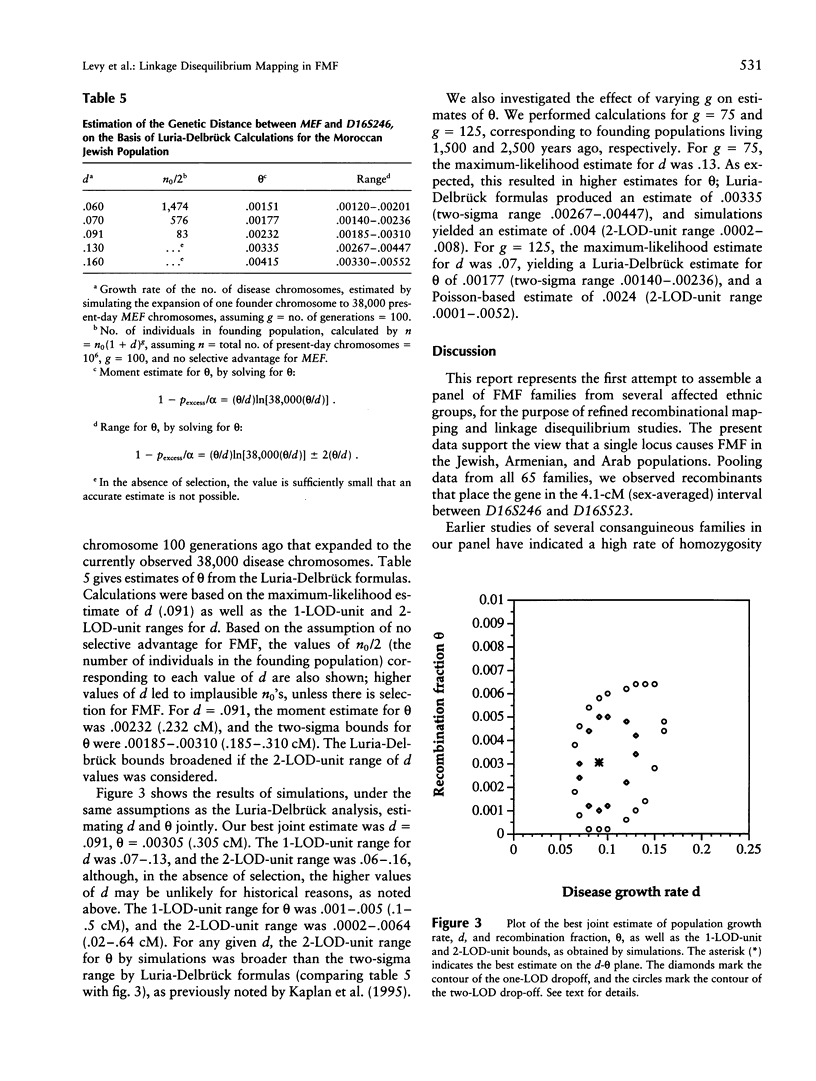
This report presents refined genetic mapping data for the gene causing familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), a recessively inherited disorder of inflammation. We sampled 65 Jewish, Armenian, and Arab families and typed them for eight markers from chromosome 16p. Using a new algorithm that permits multipoint calculations for a dense map of markers in consanguineous families, we obtained a maximal LOD score of 49.2 at a location 1.6 cM centromeric to D16S246. A specific haplotype at D16S283-D16S94-D16S246 was found in 76% of Moroccan and 32% of non-Moroccan Jewish carrier chromosomes, but this haplotype was not overrepresented in Armenian or Arab FMF carriers. Moreover, the 2.5-kb allele at D16S246 was significantly associated with FMF in Moroccan and non-Moroccan Jews but not in Armenians or Arabs. Since the Moroccan Jewish community represents a relatively recently established and genetically isolated founder population, we analyzed the Moroccan linkage-disequilibrium data by using Luria-Delbrück formulas and simulations based on a Poisson branching process. These methods place the FMF susceptibility gene within 0.305 cM of D16S246 (2-LOD-unit range 0.02-0.64 cM).
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen J., Björses P., Sandkuijl L., Perheentupa J., Peltonen L. An autosomal locus causing autoimmune disease: autoimmune polyglandular disease type I assigned to chromosome 21. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):83–87. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksentijevich I., Pras E., Gruberg L., Shen Y., Holman K., Helling S., Prosen L., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I., Dean M. Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) in Moroccan Jews: demonstration of a founder effect by extended haplotype analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;53(3):644–651. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barakat M. H., Karnik A. M., Majeed H. W., el-Sobki N. I., Fenech F. F. Familial Mediterranean fever (recurrent hereditary polyserositis) in Arabs--a study of 175 patients and review of the literature. Q J Med. 1986 Sep;60(233):837–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrall M. Homozygosity mapping: familiarity breeds debility. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):107–108. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischel-Ghodsian N., Bu X., Prezant T. R., Oeztas S., Huang Z. S., Bohlman M. C., Rotter J. I., Shohat M. Regional mapping of the gene for familial Mediterranean fever on human chromosome 16p13. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jul 1;46(6):689–693. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haataja L., Schleutker J., Laine A. P., Renlund M., Savontaus M. L., Dib C., Weissenbach J., Peltonen L., Aula P. The genetic locus for free sialic acid storage disease maps to the long arm of chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jun;54(6):1042–1049. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. C., Thomas S., Ratcliffe P. J., Breuning M. H., Coto E., Lopez-Larrea C. Rapid genetic analysis of families with polycystic kidney disease 1 by means of a microsatellite marker. Lancet. 1991 Dec 14;338(8781):1484–1487. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92300-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G. Linkage disequilibrium among multiple neutral alleles produced by mutation in finite population. Theor Popul Biol. 1975 Oct;8(2):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(75)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Mahtani M. M., Clines G., Reeve-Daly M. P., Daly M., Hamilton B. A., Kusumi K., Trivedi B., Weaver A. The diastrophic dysplasia gene encodes a novel sulfate transporter: positional cloning by fine-structure linkage disequilibrium mapping. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Likelihood methods for locating disease genes in nonequilibrium populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):18–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Weir B. S. Are moment bounds on the recombination fraction between a marker and a disease locus too good to be true? Allelic association mapping revisited for simple genetic diseases in the Finnish population. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1486–1498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestilä M., Männikkö M., Holmberg C., Gyapay G., Weissenbach J., Savolainen E. R., Peltonen L., Tryggvason K. Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type maps to the long arm of chromosome 19. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):757–764. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozman H. M., Keith T. P., Donis-Keller H., White R. L., Weissenbach J., Dean M., Vergnaud G., Kidd K., Gusella J., Royle N. J. The CEPH consortium linkage map of human chromosome 16. Genomics. 1995 Jan 1;25(1):44–58. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Lander E. S. Rapid multipoint linkage analysis of recessive traits in nuclear families, including homozygosity mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):519–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Homozygosity mapping: a way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2884728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Norio R., Tirrito S., Sistonen P., Lander E., de la Chapelle A. Localization of the EPM1 gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy on chromosome 21: linkage disequilibrium allows high resolution mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1229–1234. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison H. M., O'Rawe A. M., Taschner P. E., Sandkuijl L. A., Santavuori P., de Vos N., Breuning M. H., Mole S. E., Gardiner R. M., Järvelä I. E. Batten disease gene, CLN3: linkage disequilibrium mapping in the Finnish population, and analysis of European haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):654–662. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Proia R. L. Tay-Sachs disease in Moroccan Jews: deletion of a phenylalanine in the alpha-subunit of beta-hexosaminidase. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):412–419. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir A. I., Sokmen C. Familial Mediterranean fever among the Turkish people. Am J Gastroenterol. 1969 Apr;51(4):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigg M., Jagell S., Sillén A., Weissenbach J., Gustavson K. H., Wadelius C. The Sjögren-Larsson syndrome gene is close to D17S805 as determined by linkage analysis and allelic association. Nat Genet. 1994 Dec;8(4):361–364. doi: 10.1038/ng1294-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras E., Aksentijevich I., Gruberg L., Balow J. E., Jr, Prosen L., Dean M., Steinberg A. D., Pras M., Kastner D. L. Mapping of a gene causing familial Mediterranean fever to the short arm of chromosome 16. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 4;326(23):1509–1513. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206043262301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras E., Aksentijevich I., Levy E., Gruberg L., Prosen L., Dean M., Pras M., Kastner D. L. The gene causing familial Mediterranean fever maps to the short arm of chromosome 16 in Druze and Moslem Arab families. Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;94(5):576–577. doi: 10.1007/BF00211032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe A. D., Peters R. S. Familial Mediterranean Fever in Armenians. Analysis of 100 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Nov;53(6):453–462. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197411000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y., Holman K., Doggett N. A., Callen D. F., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Four dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms on human chromosome 16. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1745–1745. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shohat M., Bu X., Shohat T., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Magal N., Nakamura Y., Schwabe A. D., Schlezinger M., Danon Y., Rotter J. I. The gene for familial Mediterranean fever in both Armenians and non-Ashkenazi Jews is linked to the alpha-globin complex on 16p: evidence for locus homogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1349–1354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohar E., Gafni J., Pras M., Heller H. Familial Mediterranean fever. A survey of 470 cases and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1967 Aug;43(2):227–253. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulisalo T., Klockars J., Mäkitie O., Francomano C. A., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P. High-resolution linkage-disequilibrium mapping of the cartilage-hair hypoplasia gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;55(5):937–945. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S., Cockerham C. C. Testing Hypotheses about Linkage Disequilibrium with Multiple Alleles. Genetics. 1978 Mar;88(3):633–642. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


