Abstract
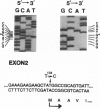
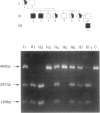
X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a congenital humoral immunodeficiency caused by a defect in a B-cell-specific signaling molecule, Btk. There has been little concordance of phenotype with genotype in this disorder, and defects in Btk cause immunodeficiencies that range from mild impairment to complete inability to produce antibodies. The factors modifying the phenotype of XLA are not understood. The current study is the first description of two male siblings with identical T134 --> C mutations in the translation initiation ATG of Btk who have different clinical phenotypes. The proband lacks immunoglobulins and B cells and has recurrent infections, while the elder, affected brother has normal levels of IgG and IgM and very few infections. Both have undetectable levels of Btk kinase activity in circulating mononuclear cells. Complete sequencing of Btk gene transcripts in both brothers revealed no additional mutations to account for the discordant phenotypes. This description provides unequivocal evidence that the phenotype of XLA is influenced by factors additional to the Btk gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki Y., Isselbacher K. J., Pillai S. Bruton tyrosine kinase is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated in pre-B lymphocytes and receptor-ligated B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10606–10609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUTON O. C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley L. A., Sweatman A. K., Lovering R. C., Jones A. M., Morgan G., Levinsky R. J., Kinnon C. Mutation detection in the X-linked agammaglobulinemia gene, BTK, using single strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):79–83. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Sidbury J. B., Jr Hereditary alterations in the immune response: coexistence of "agammaglobulinemia", acquired hypogammaglobulinemia and selective immunoglobulin deficiency in a sibship. Pediatr Res. 1968 Mar;2(2):72–84. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196803000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G., Ye Z. S., Baltimore D. Binding of Bruton's tyrosine kinase to Fyn, Lyn, or Hck through a Src homology 3 domain-mediated interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8152–8155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Fitch-Hilgenberg M. E., Cleveland J. L., Parolini O., Rohrer J. Screening of genomic DNA to identify mutations in the gene for Bruton's tyrosine kinase. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Oct;3(10):1751–1756. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.10.1751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Santis G. Heterogeneity in the severity of cystic fibrosis and the role of CFTR gene mutations. Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;93(4):364–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00201659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum R. M., Lord R. A., Cooper M. D., Gathings W. E., Goldman A. S. X-linked B lymphocyte deficiency. I. Panhypo-gamma-globulinemia and dys-gamma-globulinemia in siblings. J Pediatr. 1974 Aug;85(2):188–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Rabellino E., Pirofsky B. Immunoglobulins on the surface of lymphocytes. IV. Distribution in hypogammaglobulinemia, cellular immune deficiency, and chronic lymphatic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2368–2375. doi: 10.1172/JCI106735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guioli S., Arveiler B., Bardoni B., Notarangelo L. D., Panina P., Duse M., Ugazio A., Oberlé I., de Saint Basile G., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of probe p212 (DXS178) to X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;84(1):19–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00210664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haire R. N., Ohta Y., Lewis J. E., Fu S. M., Kroisel P., Litman G. W. TXK, a novel human tyrosine kinase expressed in T cells shares sequence identity with Tec family kinases and maps to 4p12. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):897–901. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Li X., Scott A. F., Meyers G., Chen W., Eccles M., Mao J. I., Charnas L. R., Jackson C. E., Jaye M. Jackson-Weiss and Crouzon syndromes are allelic with mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):275–279. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Good R. A., Litman G. W. Atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Oct 6;331(14):949–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Kratz J., Haire R. N., Litman G. W., Good R. A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia presenting as transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Apr;95(4):915–917. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Wedgwood R. J., Latt S., Rosen F. S. Mapping of the X-linked agammaglobulinemia locus by use of restriction fragment-length polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):649–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI112351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman H. M., Winkelstein J. A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: an analysis of 96 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 May;64(3):145–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leickley F. E., Buckley R. Variability in B cell maturation and differentiation in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):90–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensink E. J., Schuurman R. K., Schot J. D., Thompson A., Alt F. W. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangements in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):963–967. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenke M., Schell U., Hehr A., Robin N. H., Losken H. W., Schinzel A., Pulleyn L. J., Rutland P., Reardon W., Malcolm S. A common mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 gene in Pfeiffer syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Nov;8(3):269–274. doi: 10.1038/ng1194-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Rice P., Thompson J., Saraste M. The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Haire R. N., Litman R. T., Fu S. M., Nelson R. P., Kratz J., Kornfeld S. J., de la Morena M., Good R. A., Litman G. W. Genomic organization and structure of Bruton agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase: localization of mutations associated with varied clinical presentations and course in X chromosome-linked agammaglobulinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9062–9066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park W. J., Meyers G. A., Li X., Theda C., Day D., Orlow S. J., Jones M. C., Jabs E. W. Novel FGFR2 mutations in Crouzon and Jackson-Weiss syndromes show allelic heterogeneity and phenotypic variability. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jul;4(7):1229–1233. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.7.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl E. R., Vogler L. B., Okos A. J., Crist W. M., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. B lymphocyte precursors in human bone marrow: an analysis of normal individuals and patients with antibody-deficiency states. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1169–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Levin S. D., Appleby M. W., Anderson S. J., Alberola-Ila J. Regulation of lymphocyte function by protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:451–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo G., McKusick V. A. Phenotypic diversity, allelic series and modifier genes. Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):451–453. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutland P., Pulleyn L. J., Reardon W., Baraitser M., Hayward R., Jones B., Malcolm S., Winter R. M., Oldridge M., Slaney S. F. Identical mutations in the FGFR2 gene cause both Pfeiffer and Crouzon syndrome phenotypes. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):173–176. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffran D. C., Parolini O., Fitch-Hilgenberg M. E., Rawlings D. J., Afar D. E., Witte O. N., Conley M. E. Brief report: a point mutation in the SH2 domain of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 26;330(21):1488–1491. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405263302104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. J., Walters J. A., Fu S. M. Stimulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha production in human monocytes by inhibitors of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):897–901. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. The immunosuppressive activity of L-leucyl-L-leucine methyl ester: selective ablation of cytotoxic lymphocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1038–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Saffran D. C., Rawlings D. J., Parolini O., Allen R. C., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Kubagawa H., Mohandas T., Quan S. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90667-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetrie D., Vorechovský I., Sideras P., Holland J., Davies A., Flinter F., Hammarström L., Kinnon C., Levinsky R., Bobrow M. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):226–233. doi: 10.1038/361226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihinen M., Cooper M. D., de Saint Basile G., Fischer A., Good R. A., Hendriks R. W., Kinnon C., Kwan S. P., Litman G. W., Notarangelo L. D. BTKbase: a database of XLA-causing mutations. International Study Group. Immunol Today. 1995 Oct;16(10):460–465. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfert C. M., Buckley R. H., Mohanakumar T., Griffith J. F., Katz S. L., Whisnant J. K., Eggleston P. A., Moore M., Treadwell E., Oxman M. N. Persistent and fatal central-nervous-system ECHOvirus infections in patients with agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 30;296(26):1485–1489. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706302962601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Slaney S. F., Oldridge M., Poole M. D., Ashworth G. J., Hockley A. D., Hayward R. D., David D. J., Pulleyn L. J., Rutland P. Apert syndrome results from localized mutations of FGFR2 and is allelic with Crouzon syndrome. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):165–172. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weers M., Brouns G. S., Hinshelwood S., Kinnon C., Schuurman R. K., Hendriks R. W., Borst J. B-cell antigen receptor stimulation activates the human Bruton's tyrosine kinase, which is deficient in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):23857–23860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weers M., Mensink R. G., Kraakman M. E., Schuurman R. K., Hendriks R. W. Mutation analysis of the Bruton's tyrosine kinase gene in X-linked agammaglobulinemia: identification of a mutation which affects the same codon as is altered in immunodeficient xid mice. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):161–166. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]