Abstract
Autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss (ARNSHL) is the most common form of severe inherited childhood deafness. We present the linkage analysis of two inbred Bedouin kindreds from Israel that are affected with ARNSHL. A rapid genomewide screen for markers linked to the disease was performed by using pooled DNA samples. This screen revealed evidence for linkage with markers D9S922 and D9S301 on chromosome 9q. Genotyping of individuals from both kindreds confirmed linkage to chromosome 9q and a maximum combined LOD score of 26.2 (recombination fraction [theta] .025) with marker D9S927. The disease locus was mapped to a 1.6-cM region of chromosome 9ql3-q2l, between markers D9S15 and D9S927. The disease segregates with a common haplotype in the two kindreds, at markers D9S927, D9S175, and D9S284 in the linked interval, supporting the hypothesis that both kindreds inherited the deafness gene from a common ancestor. Although this nonsyndromic-hearing-loss (NSHL) locus maps to the same cytogenetic interval as DFNB7, it does not overlap the currently defined DFNB7 interval and may represent (1) a novel form of NSHL in close proximity to DFNB7 or (2) a relocalization of the DFNB7 interval to a region telomeric to its reported location. This study further demonstrates that DNA pooling is an effective means of quickly identifying regions of linkage in inbred families with heterogeneous autosomal recessive disorders.
Full text
PDF
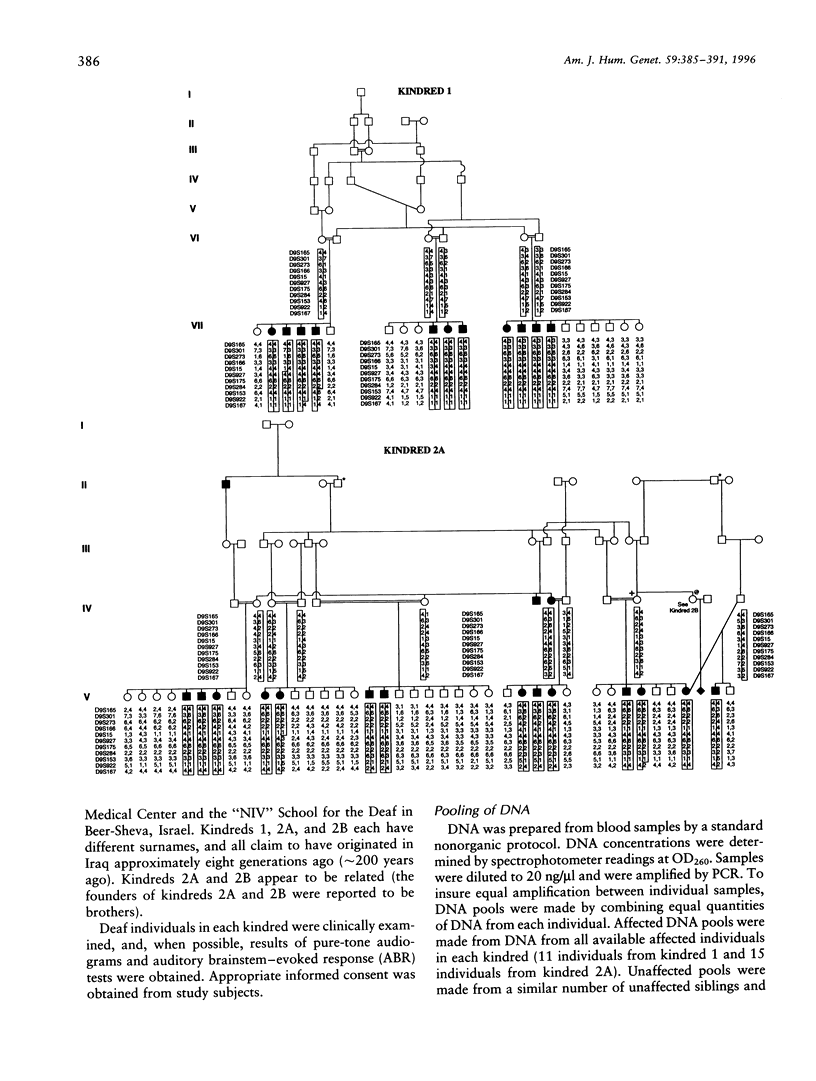
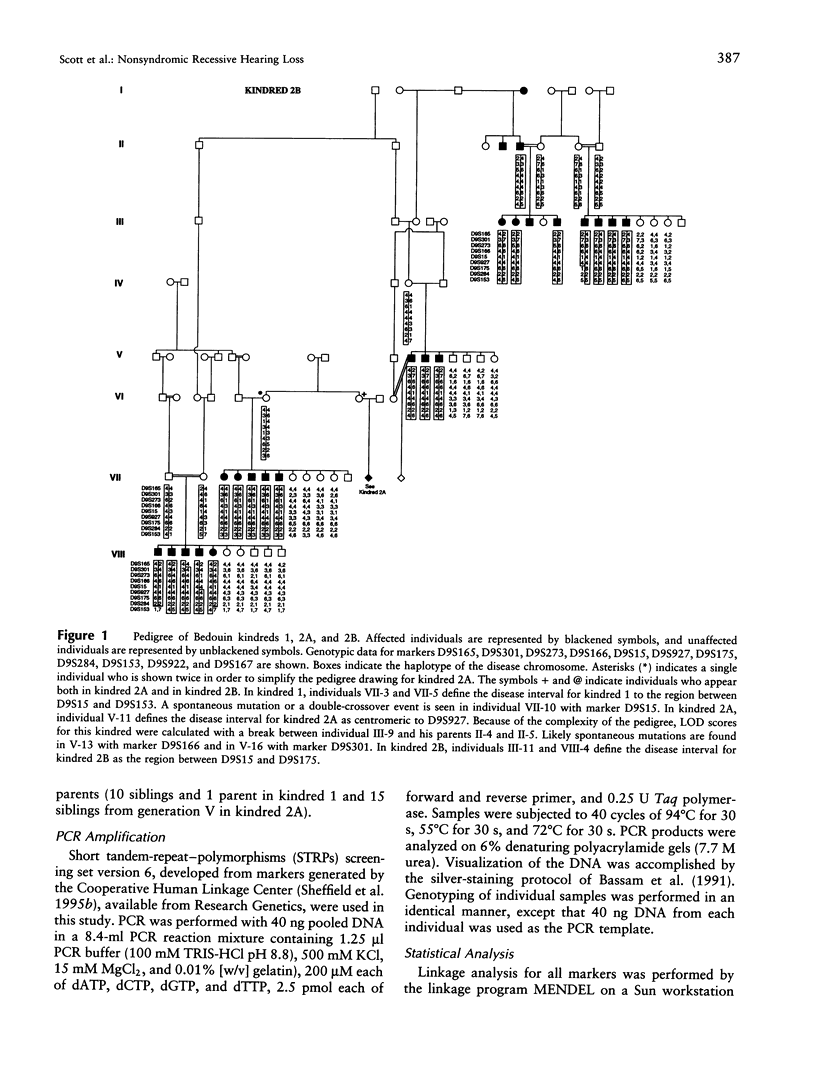

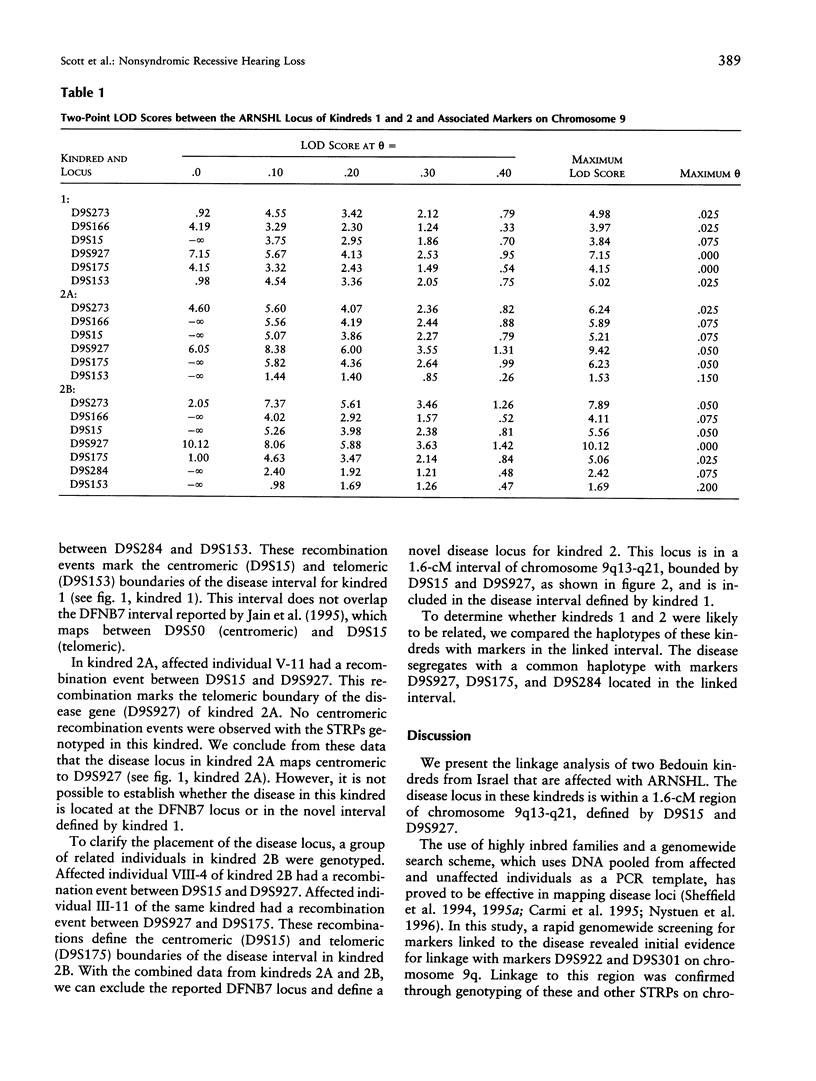
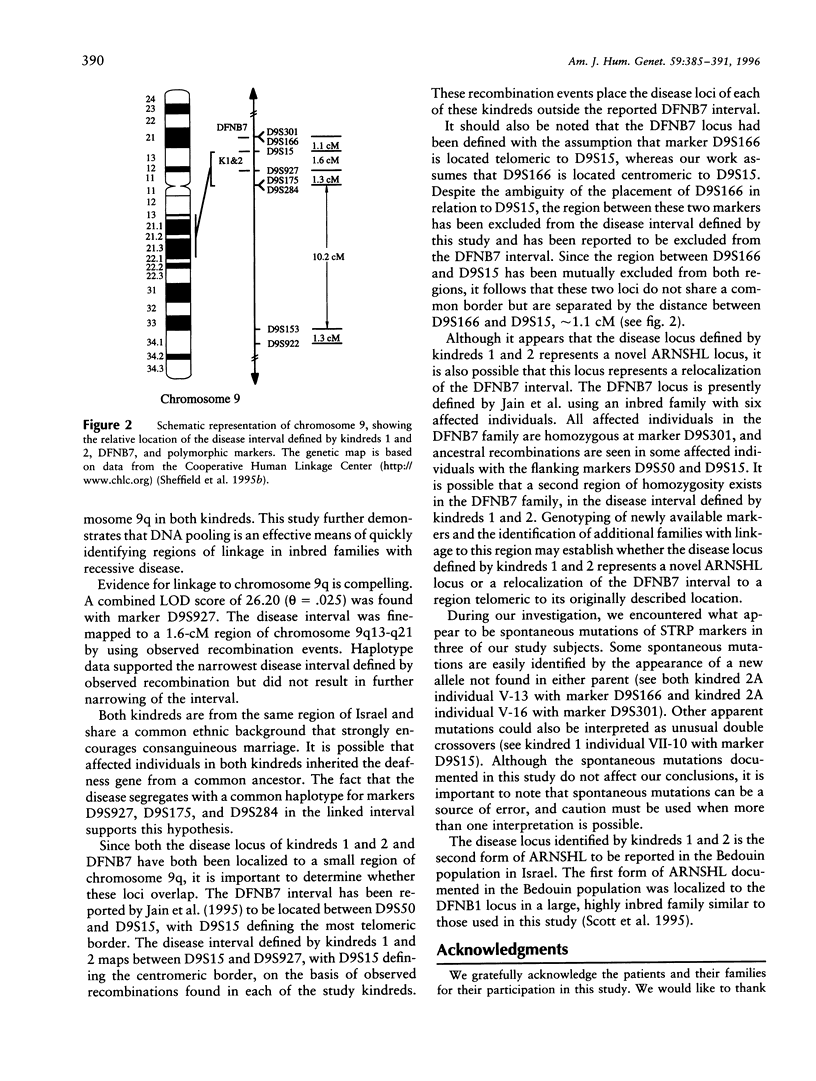

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin C. T., Weiss S., Farrer L. A., De Stefano A. L., Adair R., Franklyn B., Kidd K. K., Korostishevsky M., Bonné-Tamir B. Linkage of congenital, recessive deafness (DFNB4) to chromosome 7q31 and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in the Middle Eastern Druze population. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Sep;4(9):1637–1642. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.9.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassam B. J., Caetano-Anollés G., Gresshoff P. M. Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jul;196(1):80–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90120-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu X., Shohat M., Jaber L., Rotter J. I. A form of sensorineural deafness is determined by a mitochondrial and an autosomal locus: evidence from pedigree segregation analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(1):3–15. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmi R., Rokhlina T., Kwitek-Black A. E., Elbedour K., Nishimura D., Stone E. M., Sheffield V. C. Use of a DNA pooling strategy to identify a human obesity syndrome locus on chromosome 15. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jan;4(1):9–13. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaïb H., Lina-Granade G., Guilford P., Plauchu H., Levilliers J., Morgon A., Petit C. A gene responsible for a dominant form of neurosensory non-syndromic deafness maps to the NSRD1 recessive deafness gene interval. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Dec;3(12):2219–2222. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.12.2219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaïb H., Place C., Salem N., Chardenoux S., Vincent C., Weissenbach J., El-Zir E., Loiselet J., Petit C. A gene responsible for a sensorineural nonsyndromic recessive deafness maps to chromosome 2p22-23. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jan;5(1):155–158. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman T. B., Liang Y., Weber J. L., Hinnant J. T., Barber T. D., Winata S., Arhya I. N., Asher J. H., Jr A gene for congenital, recessive deafness DFNB3 maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):86–91. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Ramesh A., Srisailapathy C. R., Ni L., Chen A., O'Neill M., Van Camp G., Coucke P., Smith S. D., Kenyon J. B. Consanguineous nuclear families used to identify a new locus for recessive non-syndromic hearing loss on 14q. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Sep;4(9):1643–1648. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.9.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Ramesh A., Srisailapathy C. R., Ni L., Wayne S., O'Neill M. E., Van Camp G., Coucke P., Jain P., Wilcox E. R. An autosomal recessive nonsyndromic form of sensorineural hearing loss maps to 3p-DFNB6. Genome Res. 1995 Oct;5(3):305–308. doi: 10.1101/gr.5.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilford P., Ayadi H., Blanchard S., Chaib H., Le Paslier D., Weissenbach J., Drira M., Petit C. A human gene responsible for neurosensory, non-syndromic recessive deafness is a candidate homologue of the mouse sh-1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):989–993. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilford P., Ben Arab S., Blanchard S., Levilliers J., Weissenbach J., Belkahia A., Petit C. A non-syndrome form of neurosensory, recessive deafness maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 13q. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):24–28. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain P. K., Fukushima K., Deshmukh D., Ramesh A., Thomas E., Lalwani A. K., Kumar S., Plopis B., Skarka H., Srisailapathy C. R. A human recessive neurosensory nonsyndromic hearing impairment locus is potential homologue of murine deafness (dn) locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2391–2394. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Weeks D., Boehnke M. Programs for Pedigree Analysis: MENDEL, FISHER, and dGENE. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5(6):471–472. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370050611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marazita M. L., Ploughman L. M., Rawlings B., Remington E., Arnos K. S., Nance W. E. Genetic epidemiological studies of early-onset deafness in the U.S. school-age population. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jun 15;46(5):486–491. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moatti L., Garabedian E. N., Lacombe H., Spir-Jacob C. Surdités de perception congénitales et syndromes associés. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 1990;107(3):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nystuen A., Benke P. J., Merren J., Stone E. M., Sheffield V. C. A cerebellar ataxia locus identified by DNA pooling to search for linkage disequilibrium in an isolated population from the Cayman Islands. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Apr;5(4):525–531. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prezant T. R., Agapian J. V., Bohlman M. C., Bu X., Oztas S., Qiu W. Q., Arnos K. S., Cortopassi G. A., Jaber L., Rotter J. I. Mitochondrial ribosomal RNA mutation associated with both antibiotic-induced and non-syndromic deafness. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):289–294. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W. Genetic deafness. J Med Genet. 1992 Aug;29(8):521–526. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.8.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. A., Carmi R., Elbedour K., Duyk G. M., Stone E. M., Sheffield V. C. Nonsyndromic autosomal recessive deafness is linked to the DFNB1 locus in a large inbred Bedouin family from Israel. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Oct;57(4):965–968. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Carmi R., Kwitek-Black A., Rokhlina T., Nishimura D., Duyk G. M., Elbedour K., Sunden S. L., Stone E. M. Identification of a Bardet-Biedl syndrome locus on chromosome 3 and evaluation of an efficient approach to homozygosity mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1331–1335. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Nishimura D. Y., Stone E. M. Novel approaches to linkage mapping. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Jun;5(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Weber J. L., Buetow K. H., Murray J. C., Even D. A., Wiles K., Gastier J. M., Pulido J. C., Yandava C., Sunden S. L. A collection of tri- and tetranucleotide repeat markers used to generate high quality, high resolution human genome-wide linkage maps. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Oct;4(10):1837–1844. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.10.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veske A., Oehlmann R., Younus F., Mohyuddin A., Müller-Myhsok B., Mehdi S. Q., Gal A. Autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness locus (DFNB8) maps on chromosome 21q22 in a large consanguineous kindred from Pakistan. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jan;5(1):165–168. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


