Abstract
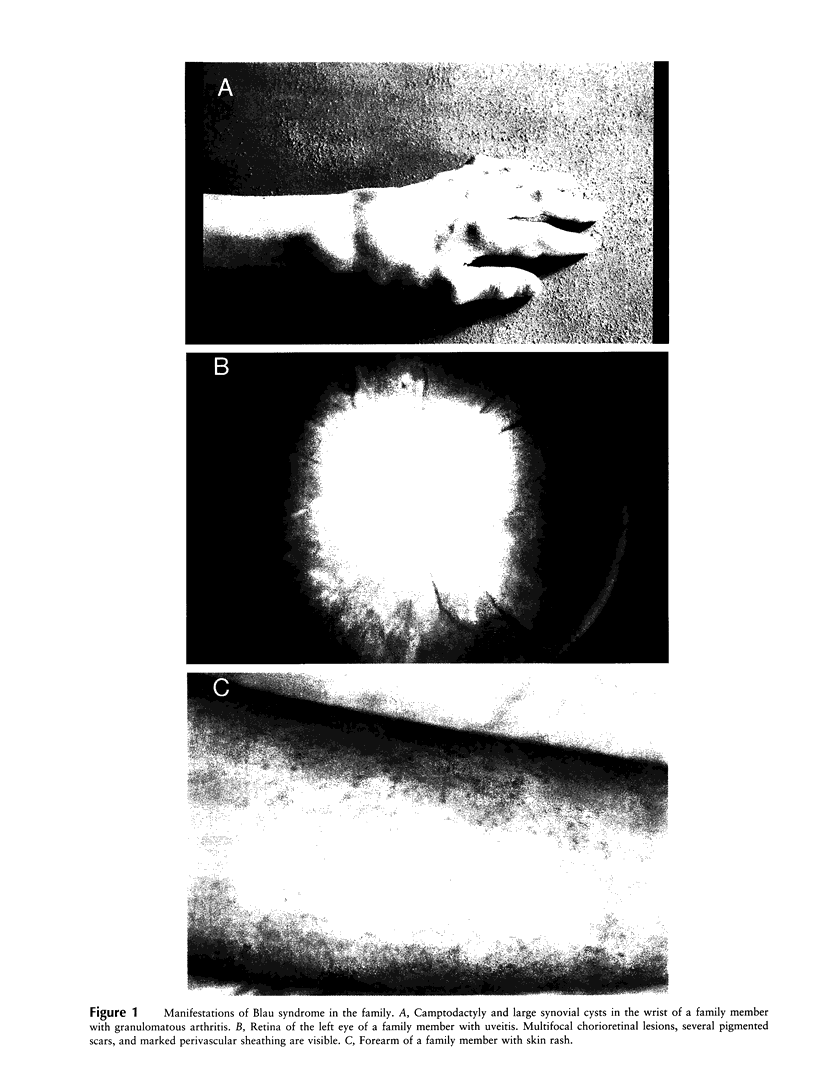
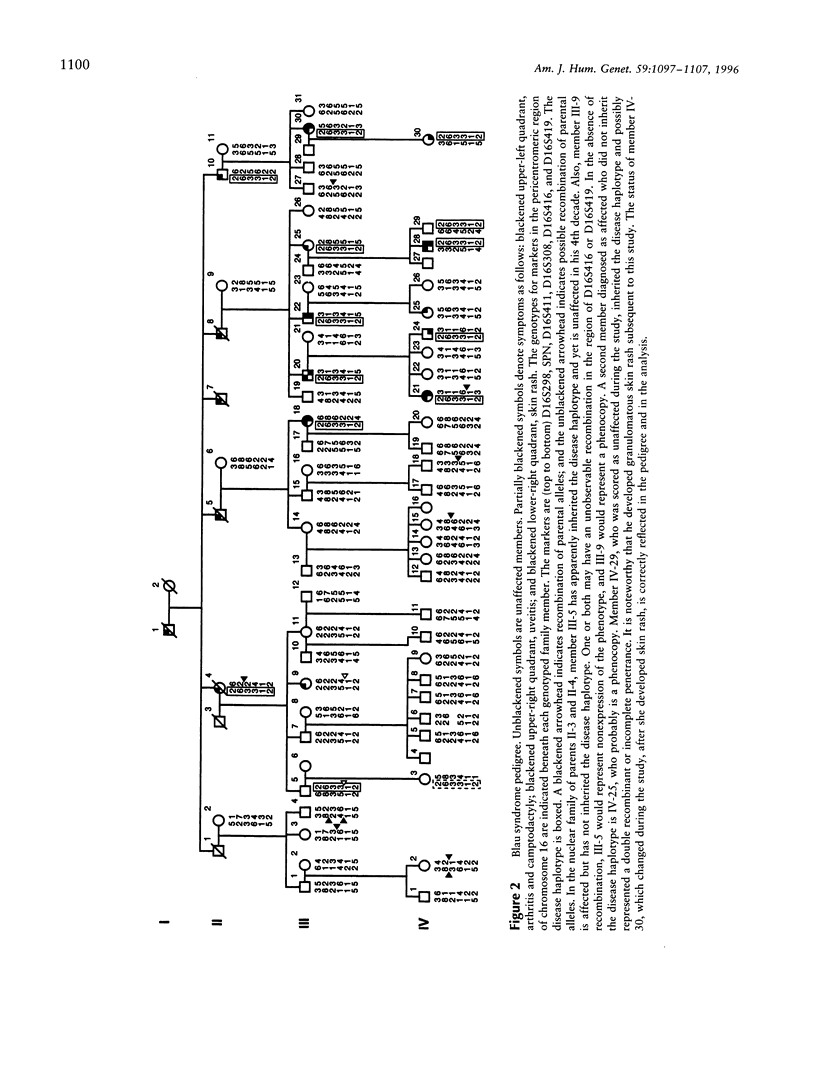
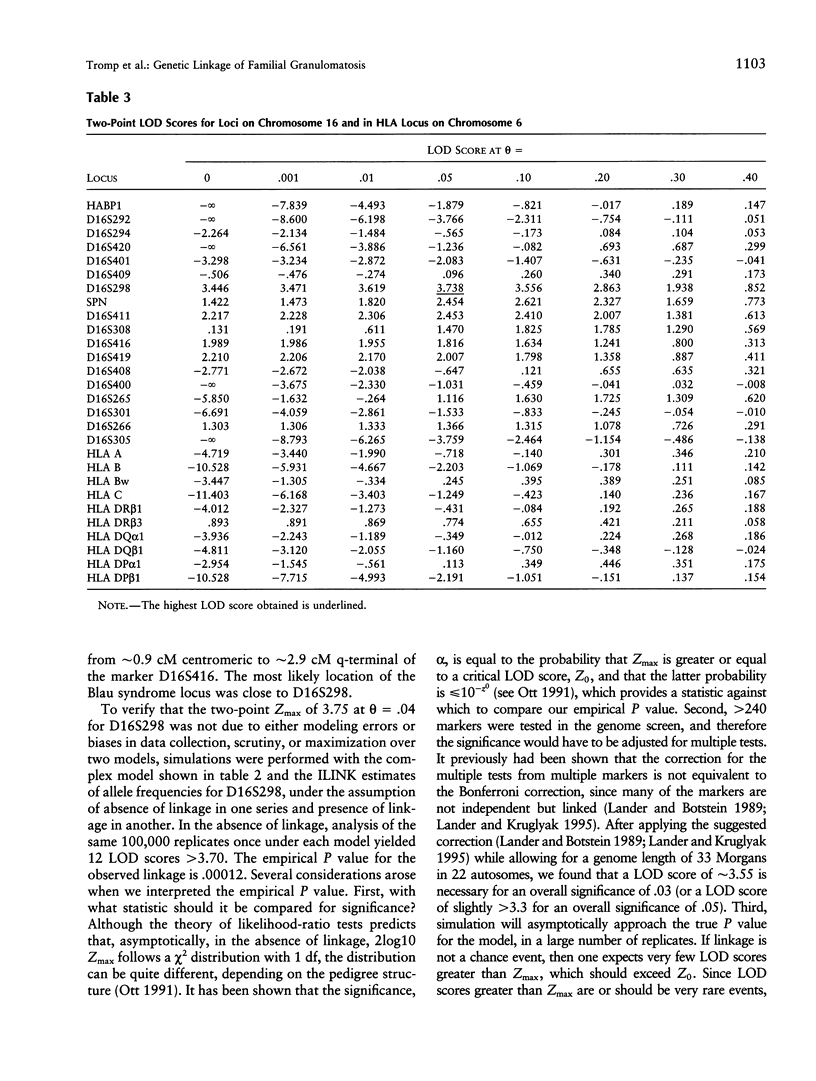
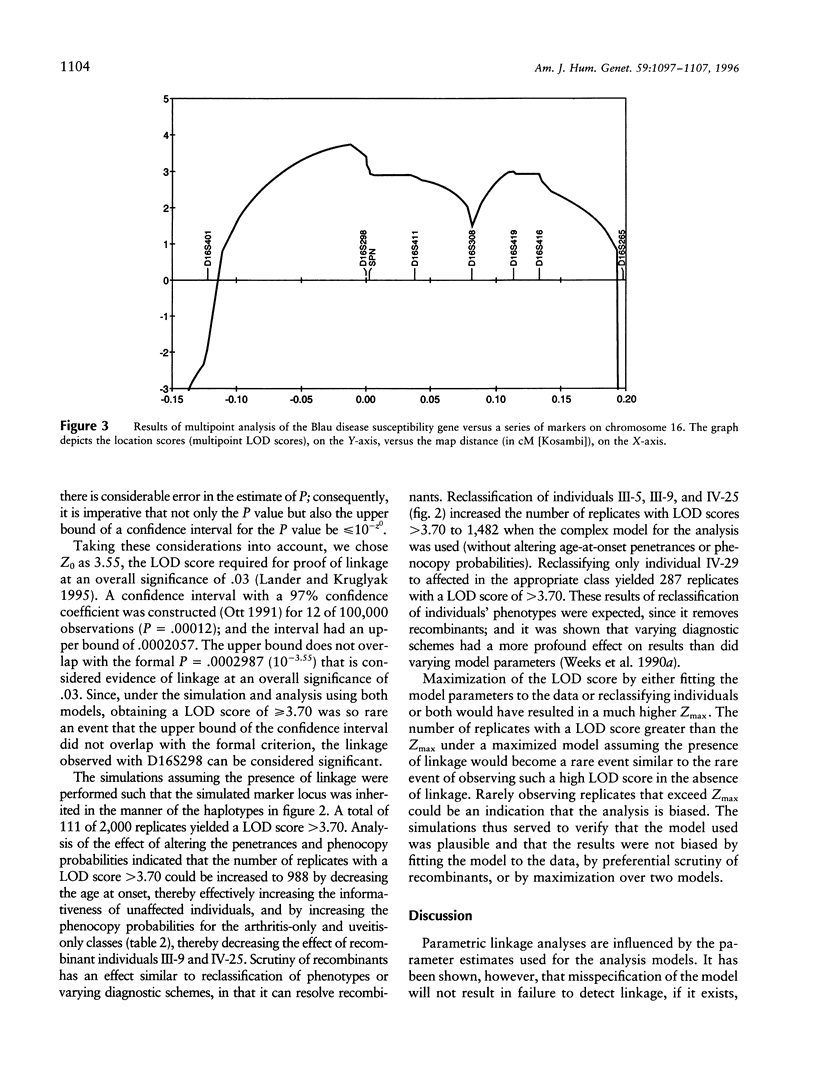
Blau syndrome (MIM 186580), first described in a large, three-generation kindred, is an autosomal, dominantly inherited disease characterized by multiorgan, tissue-specific inflammation. Its clinical phenotype includes granulomatous arthritis, skin rash, and uveitis and probably represents a subtype of a group of clinical entities referred to as "familial granulomatosis." It is the sole human model with recognizably Mendelian inheritance for a variety of multisystem inflammatory diseases affecting a significant percentage of the population. A genomewide search for the Blau susceptibility locus was undertaken after karyotypic analysis revealed no abnormalities. Sixty-two of the 74-member pedigree were genotyped with dinucleotide-repeat markers. Linkage analysis was performed under a dominant model of inheritance with reduced penetrance. The marker D16S298 gave a maximum LOD score of 3.75 at theta = .04, with two-point analysis. LOD scores for flanking markers were consistent and placed the Blau susceptibility locus within the 16p12-q21 interval.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Heliövaara M., Sievers K., Maatela J., Isomäki H. Clinical arthritis associated with positive radiological and serological findings in Finnish adults. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(1):7–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00270283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baarsma G. S. The epidemiology and genetics of endogenous uveitis: a review. Curr Eye Res. 1992;11 (Suppl):1–9. doi: 10.3109/02713689208999505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann M. P., Cosman D., Fanslow W., Maliszewski C. R., Lyman S. D. The interleukin-4 receptor: structure, function, and signal transduction. Chem Immunol. 1992;51:107–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E. B. Familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and rash. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):689–693. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. W., Felson D. T., Yood R. A., Walker A. M. Incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in central Massachusetts. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;36(12):1691–1696. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Hochez J. Effects of misspecifying genetic parameters in lod score analysis. Biometrics. 1986 Jun;42(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbi A. L., Larson R. S., Kishimoto T. K., Springer T. A., Morton C. C. Chromosomal location of the genes encoding the leukocyte adhesion receptors LFA-1, Mac-1 and p150,95. Identification of a gene cluster involved in cell adhesion. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1597–1607. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwarkadas S., Schäffer A. A., Cottingham R. W., Jr, Cox A. L., Keleher P., Zwaenepoel W. Parallelization of general-linkage analysis problems. Hum Hered. 1994 May-Jun;44(3):127–141. doi: 10.1159/000154205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. J., Olsen N. J., Pincus T., Stastny P. HLA-DR alleles with naturally occurring amino acid substitutions and risk for development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jul;33(7):939–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A. Linkage analysis of "necessary" disease loci versus "susceptibility" loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;52(1):135–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henke C. E., Henke G., Elveback L. R., Beard C. M., Ballard D. J., Kurland L. T. The epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Rochester, Minnesota: a population-based study of incidence and survival. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 May;123(5):840–845. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs D. A., Houk J. L., Bias W. B., Arnett F. C. Familial granulomatous synovitis, uveitis, and cranial neuropathies. Am J Med. 1985 May;78(5):801–804. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):185–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. C., Hochberg M. C., Kelsey J. L., McDuffie F. C., Medsger T. A., Jr, Felts W. R., Shulman L. E. Estimates of the prevalence of selected arthritic and musculoskeletal diseases in the United States. J Rheumatol. 1989 Apr;16(4):427–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxer R. M., Cameron B. J., Chaisson D., Smith C. R., Stein L. D. The camptodactyly-arthropathy-pericarditis syndrome: case report and literature review. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):439–444. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linos A., Worthington J. W., O'Fallon W. M., Kurland L. T. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Rochester, Minnesota: a study of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Jan;111(1):87–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney M. D., Lingwood C. A. CD19 has a potential CD77 (globotriaosyl ceramide)-binding site with sequence similarity to verotoxin B-subunits: implications of molecular mimicry for B cell adhesion and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli pathogenesis. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):191–201. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Erlich H. MHC class-II molecules and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:493–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. F., Jr, Fink C. W., Gibson W. M., Levinson J. E., Schuchter S. L., Howard W. K., Johnson N. H., Harris C. Sarcoid arthritis in children. Am J Med. 1970 Apr;48(4):449–455. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J. B., Cathcart E. S. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis. Follow-up evaluation of the effect of criteria on rates in Sudbury, Massachusetts. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):573–577. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Computer-simulation methods in human linkage analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4175–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastores G. M., Michels V. V., Stickler G. B., Su W. P., Nelson A. M., Bovenmyer D. A. Autosomal dominant granulomatous arthritis, uveitis, skin rash, and synovial cysts. J Pediatr. 1990 Sep;117(3):403–408. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. A., Baker E., Whitmore S. A., Sutherland G. R., Idzerda R. L., Park L. S., Cosman D., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G. The interleukin-4 receptor gene (IL4R) maps to 16p11.2-16p12.1 in human and to the distal region of mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90466-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raphael S. A., Blau E. B., Zhang W. H., Hsu S. H. Analysis of a large kindred with Blau syndrome for HLA, autoimmunity, and sarcoidosis. Am J Dis Child. 1993 Aug;147(8):842–848. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1993.02160320044017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharkoff T. Apropos of the present level of epidemiologic knowledge on sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis. 1987 Sep;4(2):152–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer A. A., Gupta S. K., Shriram K., Cottingham R. W., Jr Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jul-Aug;44(4):225–237. doi: 10.1159/000154222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y., Kozman H. M., Thompson A., Phillips H. A., Holman K., Nancarrow J., Lane S., Chen L. Z., Apostolou S., Doggett N. A. A PCR-based genetic linkage map of human chromosome 16. Genomics. 1994 Jul 1;22(1):68–76. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lehner T., Squires-Wheeler E., Kaufmann C., Ott J. Measuring the inflation of the lod score due to its maximization over model parameter values in human linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1990;7(4):237–243. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370070402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hicok K. C., Hunder G. G., Goronzy J. J. The HLA-DRB1 locus as a genetic component in giant cell arteritis. Mapping of a disease-linked sequence motif to the antigen binding site of the HLA-DR molecule. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2355–2361. doi: 10.1172/JCI116125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Xie C., Goronzy J. J. Homozygosity for the HLA-DRB1 allele selects for extraarticular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):2033–2039. doi: 10.1172/JCI115814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chadarévian J. P., Raphael S. A., Murphy G. F. Histologic, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical features of the granulomas seen in a child with the syndrome of familial granulomatous arthritis, uveitis, and rash. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993 Oct;117(10):1050–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



