Abstract
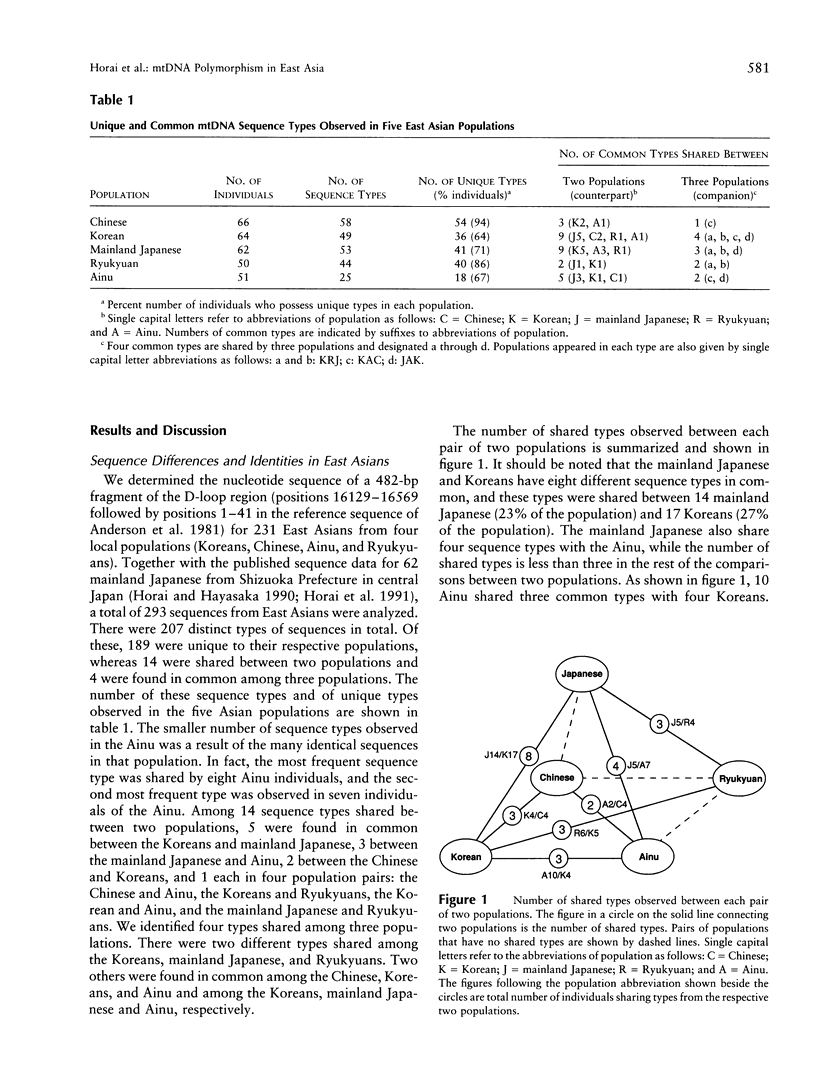
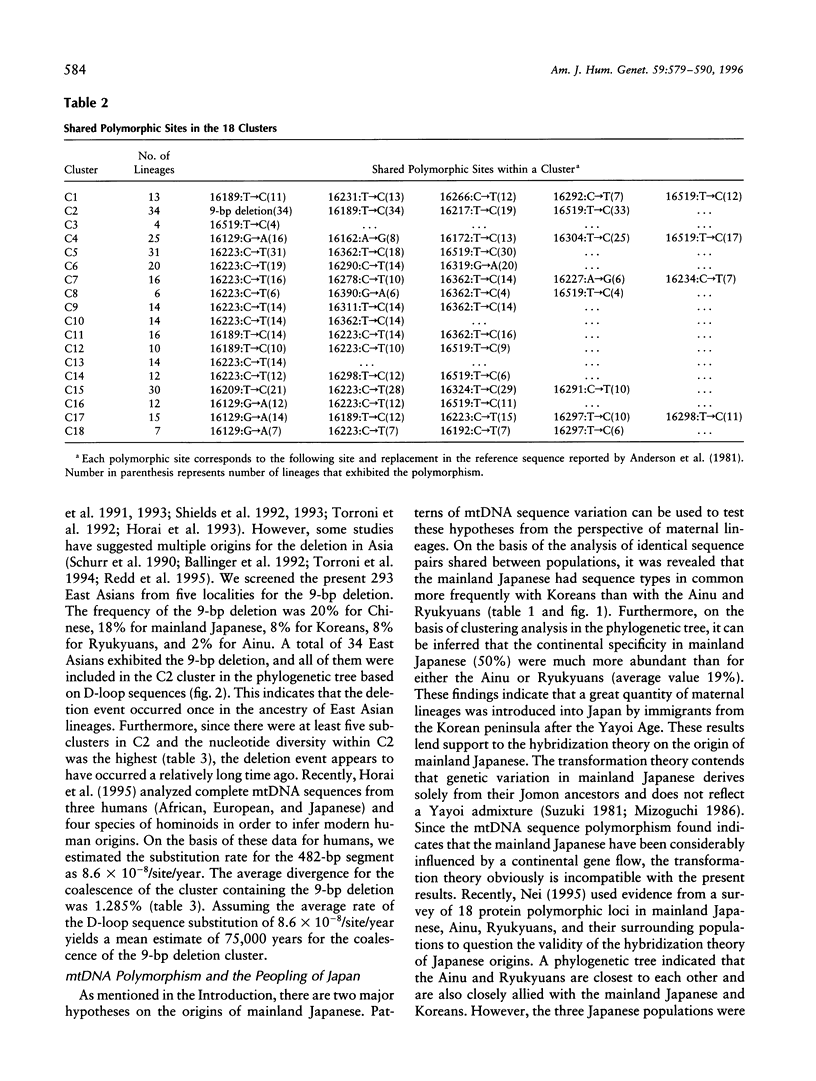
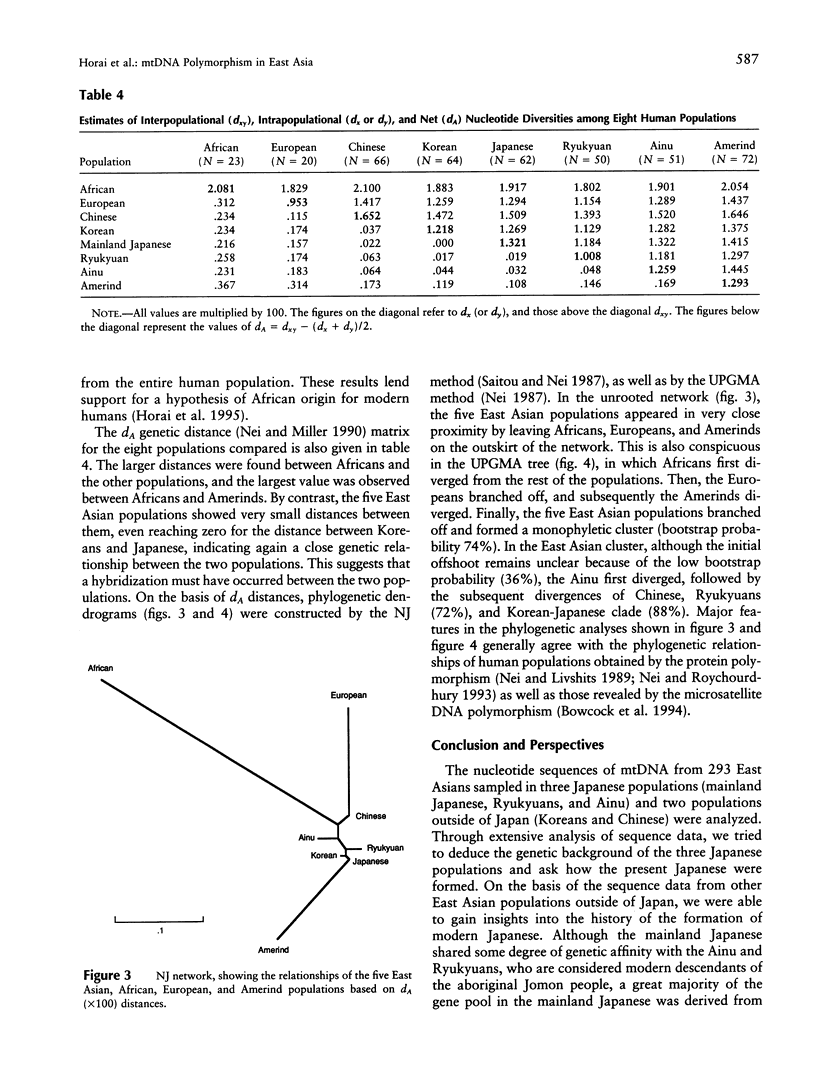
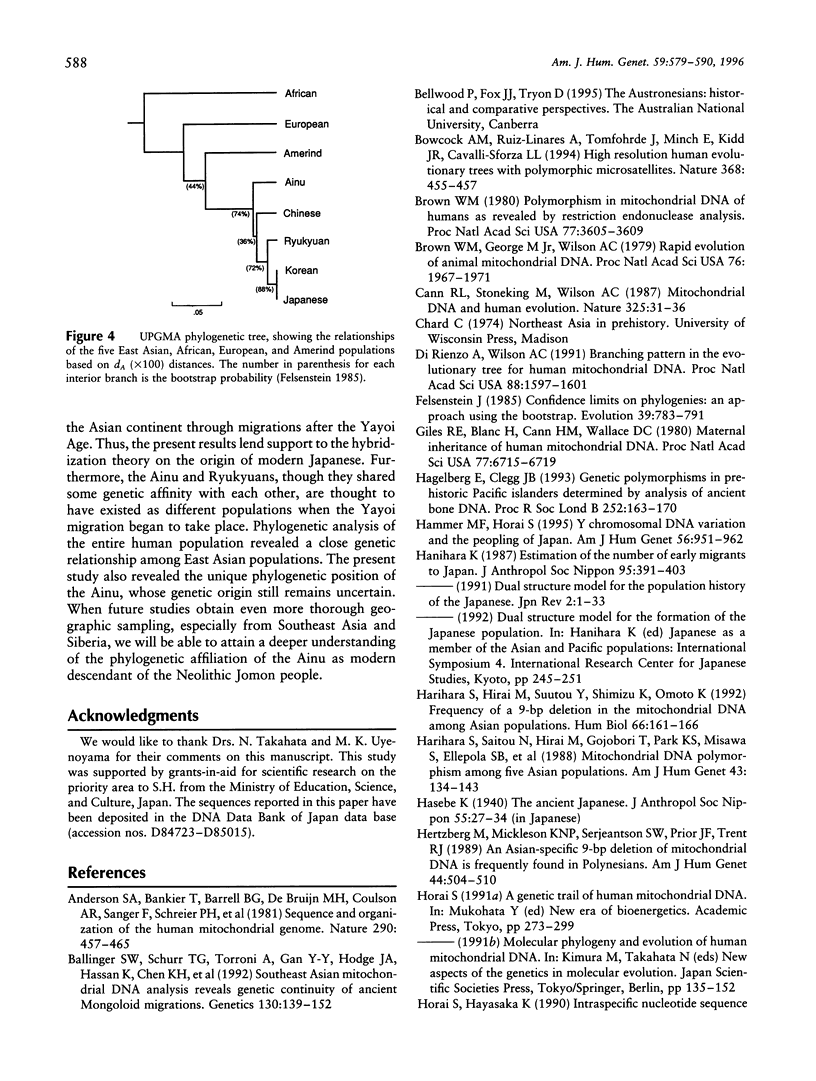
Nucleotide sequences of the major noncoding (D-loop) region of human mtDNA from five East Asian populations including mainland Japanese, Ainu, Ryukyuans, Koreans, and Chinese were analyzed. On the basis of a comparison of 482-bp sequences in 293 East Asians, 207 different sequence types were observed. Of these, 189 were unique to their respective populations, whereas 18 were shared between two or three populations. Among the shared types, eight were found in common between the mainland Japanese and Koreans, which is the largest number in the comparison. The intergenic COII/tRNA(Lys) 9-bp deletion was observed in every East Asian population with varying frequencies. The D-loop sequence variation suggests that the deletion event occurred only once in the ancestry of East Asians. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that East Asian lineages were classified into at least 18 monophyletic clusters, though lineages from the five populations were completely intermingled in the phylogenetic tree. However, we assigned 14 of the 18 clusters for their specificity on the basis of the population from which the maximum number of individuals in each cluster was derived. Of note is the finding that 50% of the mainland Japanese had continental specificity in which Chinese or Koreans were dominant, while < 20% of either Ryukyuans or Ainu possessed continental specificity. Phylogenetic analysis of the entire human population revealed the closest genetic affinity between the mainland Japanese and Koreans. Thus, the results of this study are compatible with the hybridization model on the origin of modern Japanese. It is suggested that approximately 65% of the gene pool in mainland Japanese was derived from the continental gene flow after the Yayoi Age.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger S. W., Schurr T. G., Torroni A., Gan Y. Y., Hodge J. A., Hassan K., Chen K. H., Wallace D. C. Southeast Asian mitochondrial DNA analysis reveals genetic continuity of ancient mongoloid migrations. Genetics. 1992 Jan;130(1):139–152. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Ruiz-Linares A., Tomfohrde J., Minch E., Kidd J. R., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. High resolution of human evolutionary trees with polymorphic microsatellites. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):455–457. doi: 10.1038/368455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., George M., Jr, Wilson A. C. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M. Polymorphism in mitochondrial DNA of humans as revealed by restriction endonuclease analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3605–3609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):31–36. doi: 10.1038/325031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles R. E., Blanc H., Cann H. M., Wallace D. C. Maternal inheritance of human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6715–6719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagelberg E., Clegg J. B. Genetic polymorphisms in prehistoric Pacific islanders determined by analysis of ancient bone DNA. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 May 22;252(1334):163–170. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M. F., Horai S. Y chromosomal DNA variation and the peopling of Japan. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Apr;56(4):951–962. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harihara S., Hirai M., Suutou Y., Shimizu K., Omoto K. Frequency of a 9-bp deletion in the mitochondrial DNA among Asian populations. Hum Biol. 1992 Apr;64(2):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harihara S., Saitou N., Hirai M., Gojobori T., Park K. S., Misawa S., Ellepola S. B., Ishida T., Omoto K. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism among five Asian populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;43(2):134–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg M., Mickleson K. N., Serjeantson S. W., Prior J. F., Trent R. J. An Asian-specific 9-bp deletion of mitochondrial DNA is frequently found in Polynesians. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):504–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Hayasaka K. Intraspecific nucleotide sequence differences in the major noncoding region of human mitochondrial DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):828–842. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Hayasaka K., Kondo R., Tsugane K., Takahata N. Recent African origin of modern humans revealed by complete sequences of hominoid mitochondrial DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):532–536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Kondo R., Murayama K., Hayashi S., Koike H., Nakai N. Phylogenetic affiliation of ancient and contemporary humans inferred from mitochondrial DNA. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1991 Sep 30;333(1268):409–417. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1991.0091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Kondo R., Nakagawa-Hattori Y., Hayashi S., Sonoda S., Tajima K. Peopling of the Americas, founded by four major lineages of mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):23–47. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Matsunaga E. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Japanese. II. Analysis with restriction enzymes of four or five base pair recognition. Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;72(2):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00283927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Newbold J. E., Potter S. S., Edgell M. H. Maternal inheritance of mammalian mitochondrial DNA. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):536–538. doi: 10.1038/251536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher T. D., Thomas W. K., Meyer A., Edwards S. V., Päbo S., Villablanca F. X., Wilson A. C. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum J. K., Rickards O., Ching C., Cann R. L. Polynesian mitochondrial DNAs reveal three deep maternal lineage clusters. Hum Biol. 1994 Aug;66(4):567–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Livshits G. Genetic relationships of Europeans, Asians and Africans and the origin of modern Homo sapiens. Hum Hered. 1989;39(5):276–281. doi: 10.1159/000153872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Miller J. C. A simple method for estimating average number of nucleotide substitutions within and between populations from restriction data. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):873–879. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Roychoudhury A. K. Evolutionary relationships of human populations on a global scale. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Sep;10(5):927–943. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarino G., Semino O., Modiano G., Santachiara-Benerecetti A. S. COII/tRNA(Lys) intergenic 9-bp deletion and other mtDNA markers clearly reveal that the Tharus (southern Nepal) have Oriental affinities. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;53(3):609–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redd A. J., Takezaki N., Sherry S. T., McGarvey S. T., Sofro A. S., Stoneking M. Evolutionary history of the COII/tRNALys intergenic 9 base pair deletion in human mitochondrial DNAs from the Pacific. Mol Biol Evol. 1995 Jul;12(4):604–615. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed T. E. Caucasian genes in American Negroes. Science. 1969 Aug 22;165(3895):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3895.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr T. G., Ballinger S. W., Gan Y. Y., Hodge J. A., Merriwether D. A., Lawrence D. N., Knowler W. C., Weiss K. M., Wallace D. C. Amerindian mitochondrial DNAs have rare Asian mutations at high frequencies, suggesting they derived from four primary maternal lineages. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):613–623. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields G. F., Hecker K., Voevoda M. I., Reed J. K. Absence of the Asian-specific region V mitochondrial marker in Native Beringians. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):758–765. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields G. F., Schmiechen A. M., Frazier B. L., Redd A., Voevoda M. I., Reed J. K., Ward R. H. mtDNA sequences suggest a recent evolutionary divergence for Beringian and northern North American populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;53(3):549–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torroni A., Chen Y. S., Semino O., Santachiara-Beneceretti A. S., Scott C. R., Lott M. T., Winter M., Wallace D. C. mtDNA and Y-chromosome polymorphisms in four Native American populations from southern Mexico. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Feb;54(2):303–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torroni A., Schurr T. G., Yang C. C., Szathmary E. J., Williams R. C., Schanfield M. S., Troup G. A., Knowler W. C., Lawrence D. N., Weiss K. M. Native American mitochondrial DNA analysis indicates that the Amerind and the Nadene populations were founded by two independent migrations. Genetics. 1992 Jan;130(1):153–162. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuner C. G., 2nd Dental evidence on the origins of the Ainu and Japanese. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):911–913. doi: 10.1126/science.781841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigilant L., Pennington R., Harpending H., Kocher T. D., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA sequences in single hairs from a southern African population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9350–9354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigilant L., Stoneking M., Harpending H., Hawkes K., Wilson A. C. African populations and the evolution of human mitochondrial DNA. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1503–1507. doi: 10.1126/science.1840702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. 1994 William Allan Award Address. Mitochondrial DNA variation in human evolution, degenerative disease, and aging. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):201–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. H., Frazier B. L., Dew-Jager K., Päbo S. Extensive mitochondrial diversity within a single Amerindian tribe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8720–8724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. H., Redd A., Valencia D., Frazier B., Päbo S. Genetic and linguistic differentiation in the Americas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10663–10667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



