Abstract
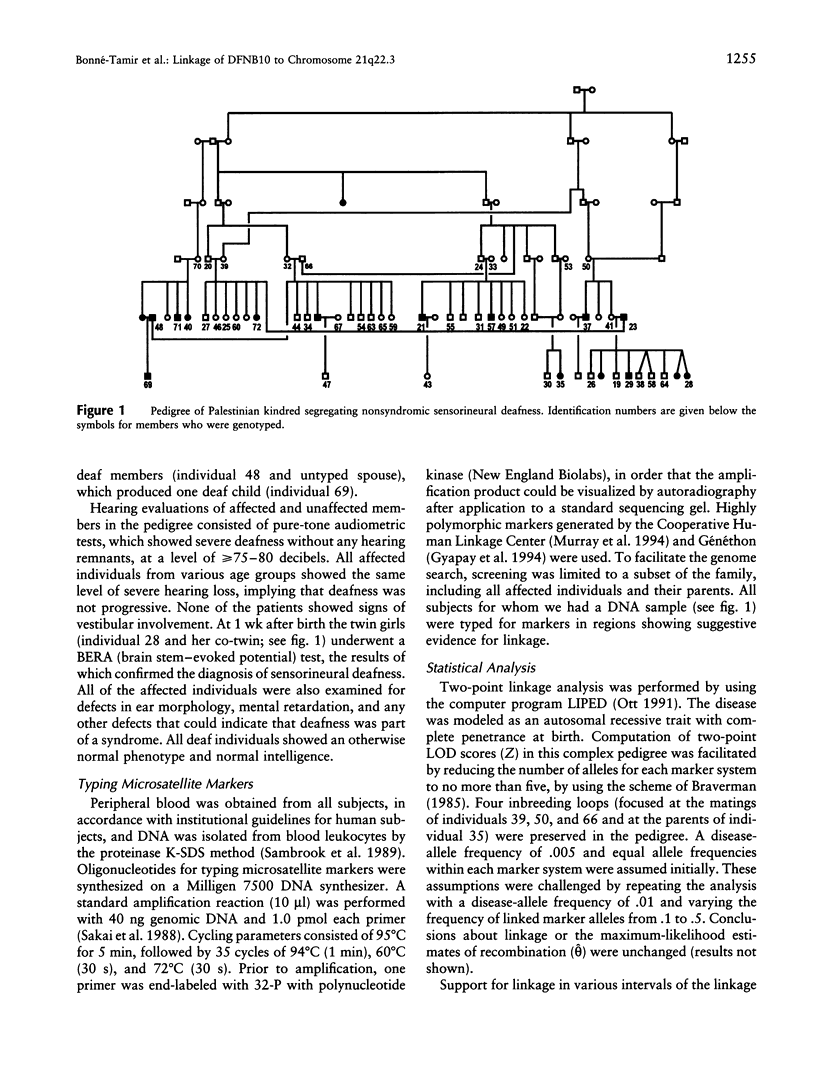
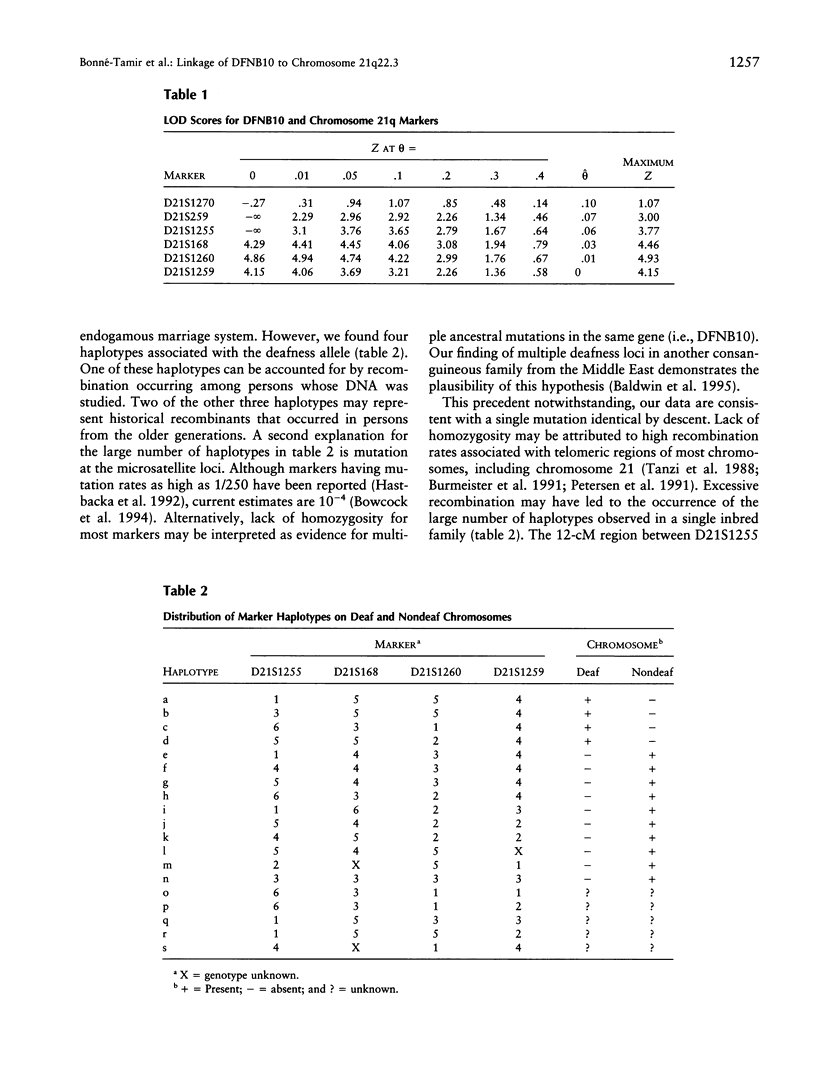
Deafness is a heterogeneous trait affecting approximately 1/1,000 newborns. Genetic linkage studies have already implicated more than a dozen distinct loci causing deafness. We conducted a genome search for linkage in a large Palestinian family segregating an autosomal recessive form of nonsyndromic deafness. Our results indicate that in this family the defective gene, DFNB10, is located in a 12-cM region near the telomere of chromosome 21. This genetic distance corresponds to <2.4 Mbp. Five marker loci typed from this region gave maximum LOD scores > or = to 3. Homozygosity of marker alleles was evident for only the most telomeric marker, D21S1259, suggesting that DFNB10 is closest to this locus. To our knowledge, this is the first evidence, at this location, for a gene that is involved in the development or maintenance of hearing. As candidate genes at these and other deafness loci are isolated and characterized, their roles in hearing will be revealed and may lead to development of mechanisms to prevent deafness.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnos K. S., Israel J., Wilson M. P., Devlin L. Genetics of hearing disorders. Clin Commun Disord. 1992 Fall;2(4):20–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arslan E., Trevisi P., Genovese E., Lupi G., Prosser S. Hearing loss etiology in a group of 996 children. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:315–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Hoth C. F., Amos J. A., da-Silva E. O., Milunsky A. An exonic mutation in the HuP2 paired domain gene causes Waardenburg's syndrome. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):637–638. doi: 10.1038/355637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Weiss S., Farrer L. A., De Stefano A. L., Adair R., Franklyn B., Kidd K. K., Korostishevsky M., Bonné-Tamir B. Linkage of congenital, recessive deafness (DFNB4) to chromosome 7q31 and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in the Middle Eastern Druze population. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Sep;4(9):1637–1642. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.9.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. F., Hostikka S. L., Zhou J., Chow L. T., Oliphant A. R., Gerken S. C., Gregory M. C., Skolnick M. H., Atkin C. L., Tryggvason K. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1224–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.2349482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beighton P., Viljoen D., Winship I., Beighton G., Sellars S. Profound childhood deafness in southern Africa. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:290–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Farrer L. A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Hebert J. M., Kidd K. K., Frydman M., Bonne-Tamir B. Mapping the Wilson disease locus to a cluster of linked polymorphic markers on chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;41(1):27–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Tomfohrde J., Weissenbach J., Bonne-Tamir B., St George-Hyslop P., Giagheddu M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Farrer L. A. Refining the position of Wilson disease by linkage disequilibrium with polymorphic microsatellites. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;54(1):79–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman M. S. An algorithm to improve the computational efficiency of genetic linkage analysis. Comput Biomed Res. 1985 Feb;18(1):24–36. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(85)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. G., Smeets B., Smeets D., Nelen M., Cremers C. W., Ropers H. H. Molecular genetics of X-linked hearing impairment. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:176–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Duyk G. M., Sheffield V. C., Wang Z., Murray J. C. Integrated human genome-wide maps constructed using the CEPH reference panel. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):391–393. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers C. W., Marres H. A., van Rijn P. M. Nonsyndromal profound genetic deafness in childhood. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:191–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman T. B., Liang Y., Weber J. L., Hinnant J. T., Barber T. D., Winata S., Arhya I. N., Asher J. H., Jr A gene for congenital, recessive deafness DFNB3 maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):86–91. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Ramesh A., Srisailapathy C. R., Ni L., Chen A., O'Neill M., Van Camp G., Coucke P., Smith S. D., Kenyon J. B. Consanguineous nuclear families used to identify a new locus for recessive non-syndromic hearing loss on 14q. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Sep;4(9):1643–1648. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.9.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M., Rapin I. Non-Mendelian mitochondrial inheritance as a cause of progressive genetic sensorineural hearing loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1994 Aug;30(2):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundfast K. M., Lalwani A. K. Practical approach to diagnosis and management of hereditary hearing impairment (HHI). Ear Nose Throat J. 1992 Oct;71(10):479-84, 487-93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilford P., Ayadi H., Blanchard S., Chaib H., Le Paslier D., Weissenbach J., Drira M., Petit C. A human gene responsible for neurosensory, non-syndromic recessive deafness is a candidate homologue of the mouse sh-1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):989–993. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilford P., Ben Arab S., Blanchard S., Levilliers J., Weissenbach J., Belkahia A., Petit C. A non-syndrome form of neurosensory, recessive deafness maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 13q. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):24–28. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain P. K., Fukushima K., Deshmukh D., Ramesh A., Thomas E., Lalwani A. K., Kumar S., Plopis B., Skarka H., Srisailapathy C. R. A human recessive neurosensory nonsyndromic hearing impairment locus is potential homologue of murine deafness (dn) locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2391–2394. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marazita M. L., Ploughman L. M., Rawlings B., Remington E., Arnos K. S., Nance W. E. Genetic epidemiological studies of early-onset deafness in the U.S. school-age population. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jun 15;46(5):486–491. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E. Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:16–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Manion F., Quillen J., Sheffield V. C., Sunden S., Duyk G. M. A comprehensive human linkage map with centimorgan density. Cooperative Human Linkage Center (CHLC). Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2049–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8091227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 27 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W. Genetic deafness. J Med Genet. 1992 Aug;29(8):521–526. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.8.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillmann T. Genetic diseases of hearing. Curr Opin Neurol. 1994 Feb;7(1):81–87. doi: 10.1097/00019052-199402000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Newton V. E., Liu X. Z., Brady A., Donnai D., Krajewska-Walasek M., Murday V., Norman A., Obersztyn E., Reardon W. The mutational spectrum in Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Nov;4(11):2131–2137. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.11.2131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veske A., Oehlmann R., Younus F., Mohyuddin A., Müller-Myhsok B., Mehdi S. Q., Gal A. Autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness locus (DFNB8) maps on chromosome 21q22 in a large consanguineous kindred from Pakistan. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jan;5(1):165–168. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Smith C. L. Large-scale structure conservation along the entire long arm of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):441–451. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


