Abstract
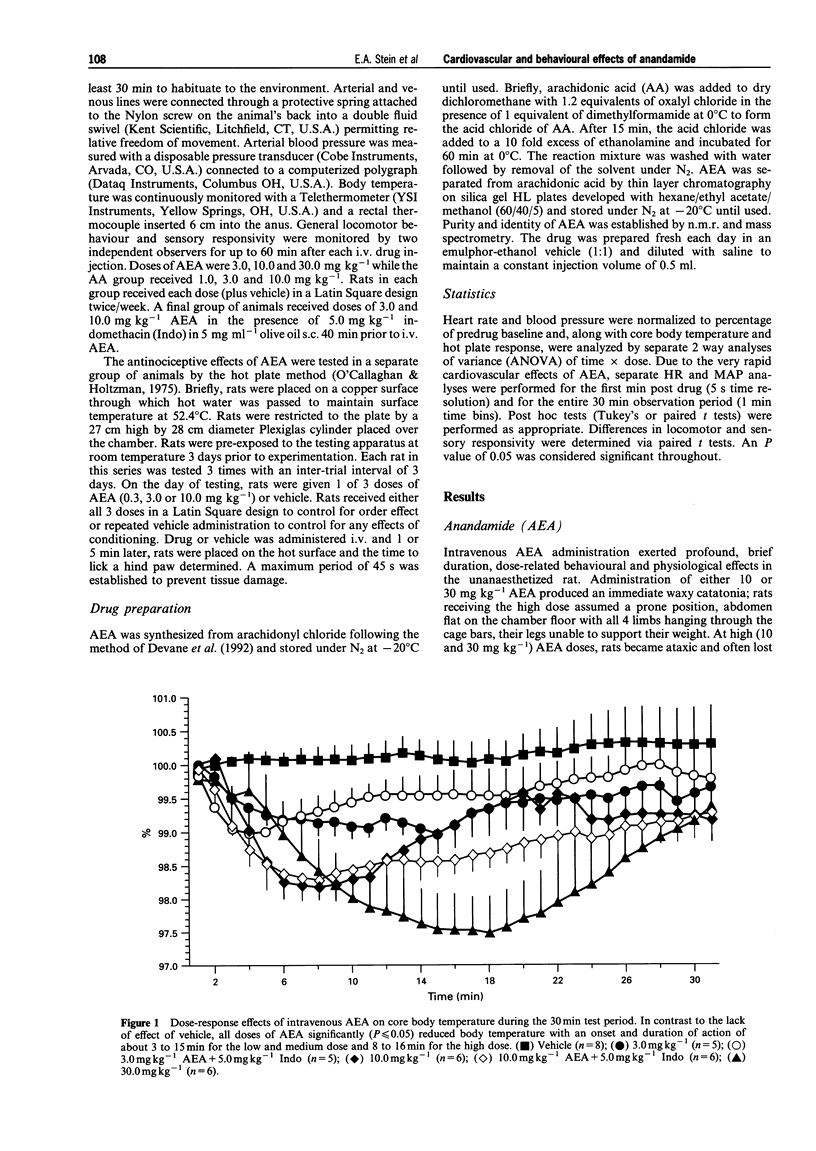
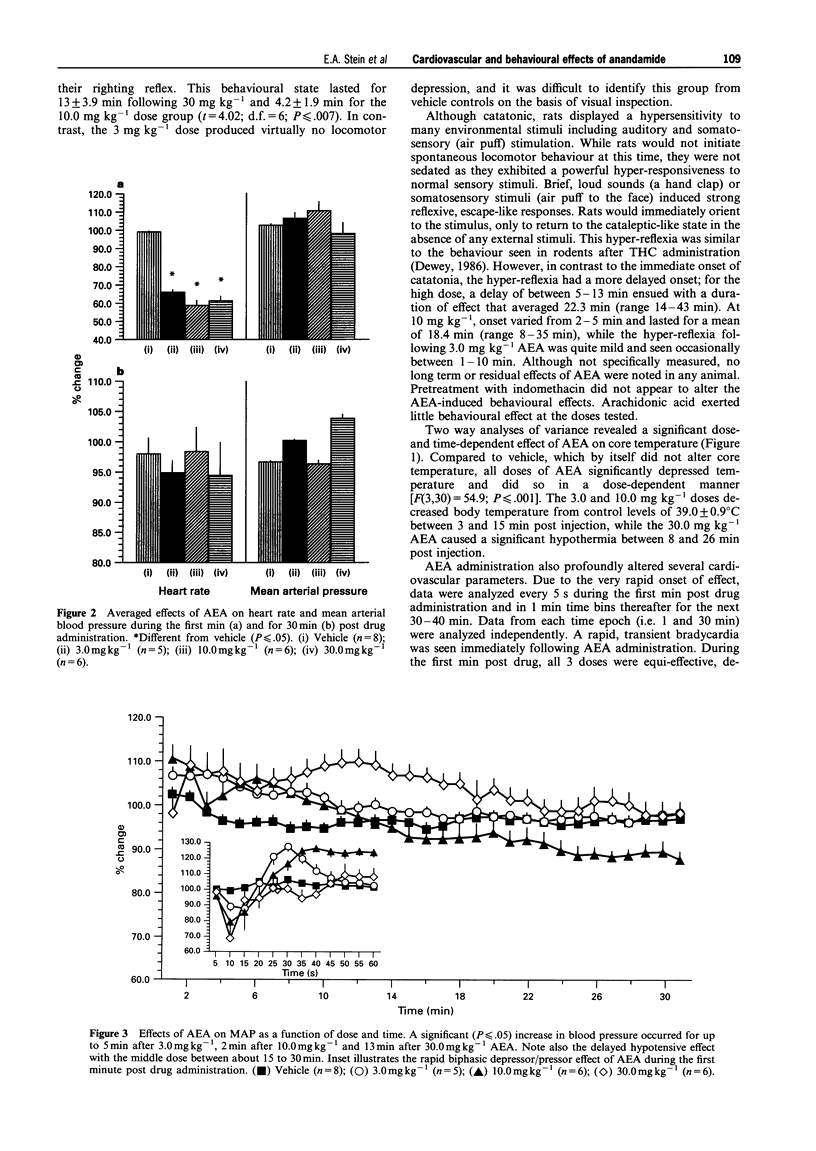
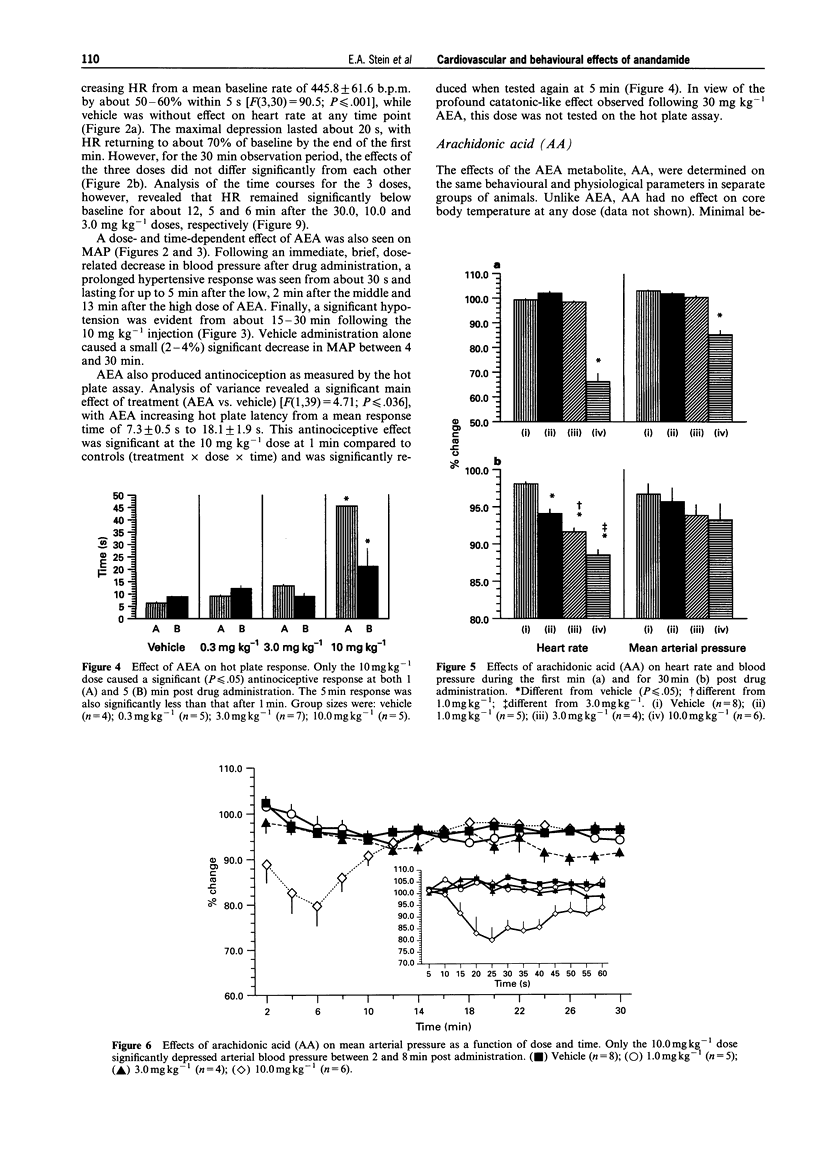
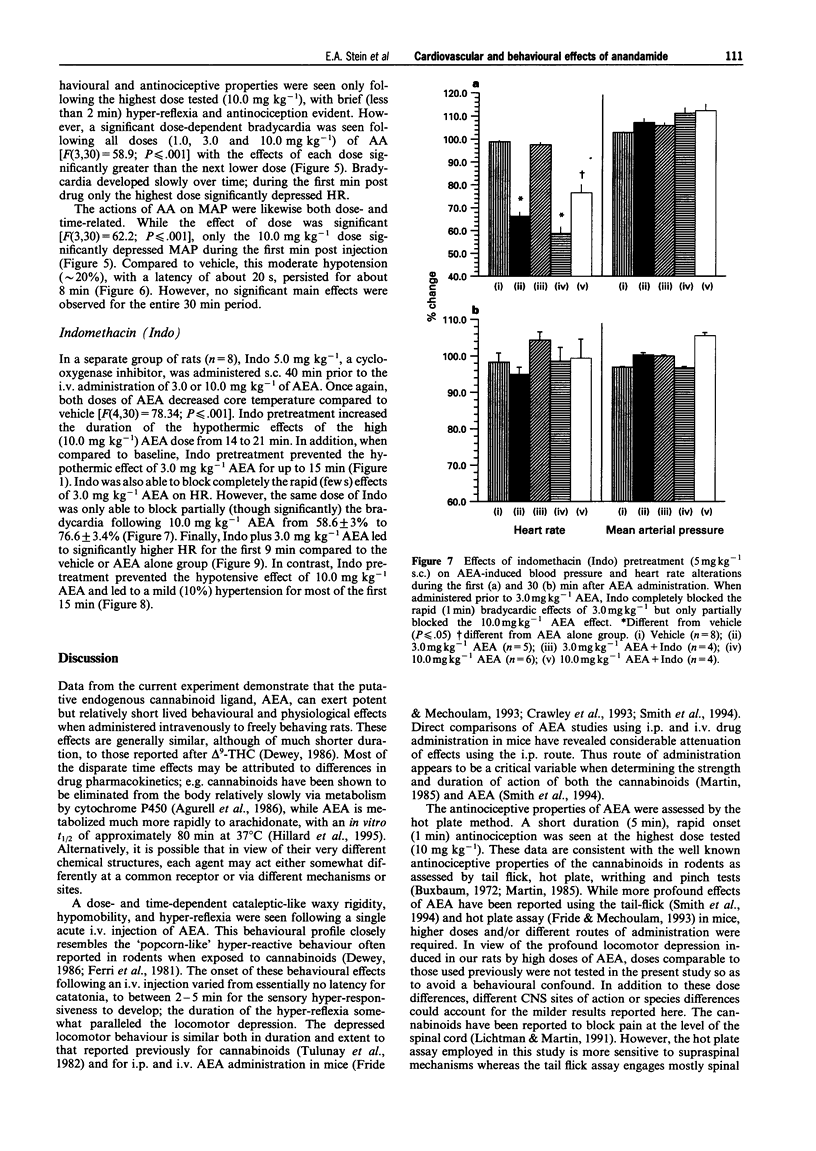
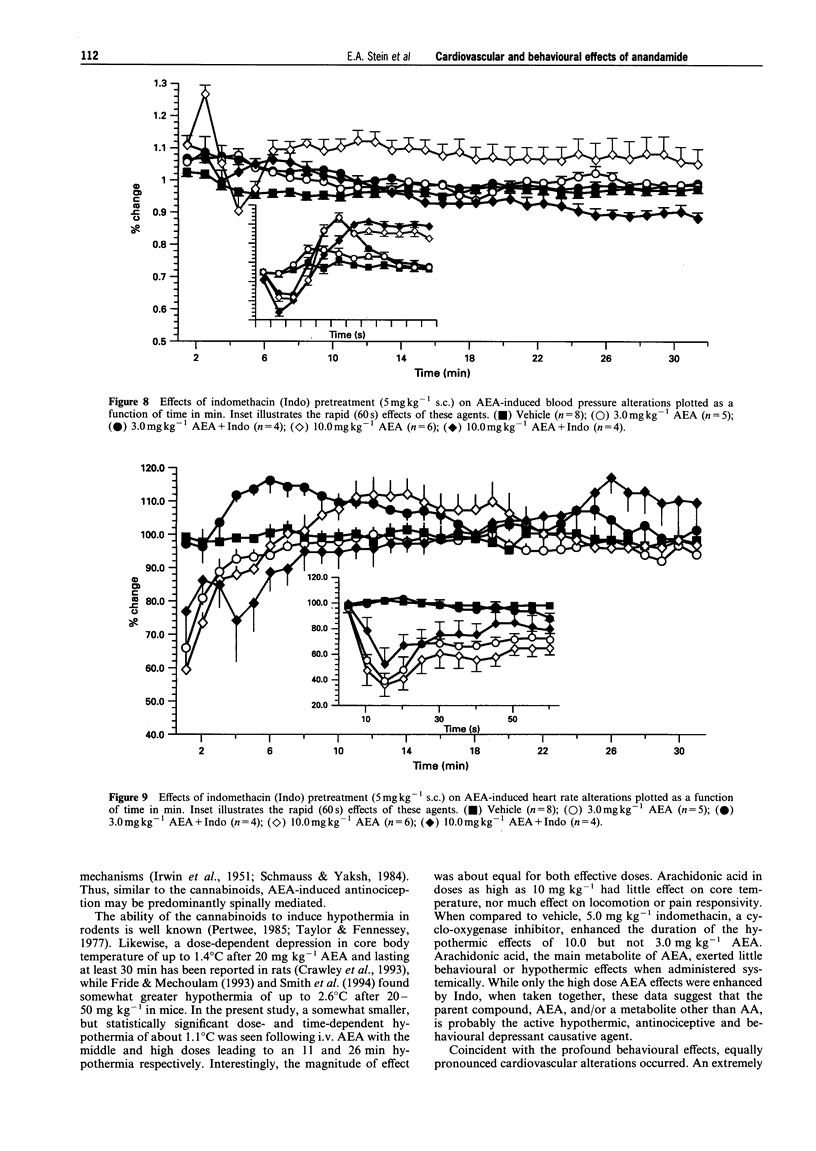
1. Arachidonylethanolamide (AEA; anandamide) has been isolated from mammalian brain and found to bind to, and is thought to be, an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptor. In order to understand better its behavioural and physiological properties, we have examined its acute effects in unanaesthetized freely behaving rats. 2. Intravenous AEA caused dose-related decreases in locomotor behaviour, a pronounced hyperreflexia, and a moderate antinociceptive state. At doses between 3 and 30 mg kg-1, a dose-dependent hypothermia and profound, time-dependent cardiovascular changes were also observed. 3. An immediate bradycardia exceeding 50% was seen within 10-15 s of administration and lasted up to 11 min following the highest dose of the drug. In contrast, the change in mean arterial pressure was biphasic: an immediate 20% decrease in mean arterial pressure followed by a significant increase in blood pressure that lasted about 13 min after the highest dose. 4. These data demonstrate that AEA in the unanaesthetized rat exerts behavioural and physiological effects generally similar to those seen following natural cannabinoids and synthetic cannabimimetic agents and suggests a role for AEA in regulation of various physiological processes.
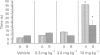
Full text
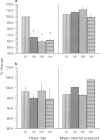
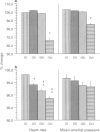
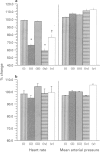
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Earnhardt J. T., Dewey W. L., Harris L. S. Vasoconstrictor actions of delta8- and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Mar;196(3):649–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agurell S., Halldin M., Lindgren J. E., Ohlsson A., Widman M., Gillespie H., Hollister L. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of delta 1-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids with emphasis on man. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Mar;38(1):21–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum D. M. Analgesic activity of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol in the rat and mouse. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;25(3):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00422507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Sexton T., Roy M. B. Effects of anandamide on cannabinoid receptors in rat brain membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 11;47(4):711–715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Corwin R. L., Robinson J. K., Felder C. C., Devane W. A., Axelrod J. Anandamide, an endogenous ligand of the cannabinoid receptor, induces hypomotility and hypothermia in vivo in rodents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993 Dec;46(4):967–972. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(93)90230-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Chin S. A. Enzymatic synthesis and degradation of anandamide, a cannabinoid receptor agonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 1;46(5):791–796. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90486-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devane W. A., Dysarz F. A., 3rd, Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Howlett A. C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):605–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devane W. A., Hanus L., Breuer A., Pertwee R. G., Stevenson L. A., Griffin G., Gibson D., Mandelbaum A., Etinger A., Mechoulam R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1946–1949. doi: 10.1126/science.1470919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey W. L. Cannabinoid pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Jun;38(2):151–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Johnson M. R., Howlett A. C. Ca(2+)-dependent release from rat brain of cannabinoid receptor binding activity. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):780–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Briley E. M., Axelrod J., Simpson J. T., Mackie K., Devane W. A. Anandamide, an endogenous cannabimimetic eicosanoid, binds to the cloned human cannabinoid receptor and stimulates receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7656–7660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri S., Costa G., Murari G., Panico A. M., Rapisarda E., Speroni E., Arrigo-Reina R. Investigations on behavioral effects of an extract of Cannabis sativa L. in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1981;75(2):144–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00432176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fride E., Mechoulam R. Pharmacological activity of the cannabinoid receptor agonist, anandamide, a brain constituent. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 9;231(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90468-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Groen B. G., Lynn A. B., De Costa B. R., Richfield E. K. Neuronal localization of cannabinoid receptors and second messengers in mutant mouse cerebellum. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 28;552(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90096-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Lynn A. B., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., de Costa B. R., Rice K. C. Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):563–583. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Lynn A. B., Little M. D., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., de Costa B. R., Rice K. C. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillard C. J., Edgemond W. S., Campbell W. B. Characterization of ligand binding to the cannabinoid receptor of rat brain membranes using a novel method: application to anandamide. J Neurochem. 1995 Feb;64(2):677–683. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64020677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. C., Bidaut-Russell M., Devane W. A., Melvin L. S., Johnson M. R., Herkenham M. The cannabinoid receptor: biochemical, anatomical and behavioral characterization. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Oct;13(10):420–423. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRWIN S., HOUDE R. W., BENNETT D. R., HENDERSHOT L. C., SEEVERS M. H. The effects of morphine methadone and meperidine on some reflex responses of spinal animals to nociceptive stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1951 Feb;101(2):132–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Martin B. R. Spinal and supraspinal components of cannabinoid-induced antinociception. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacsko P., Messina E. J., Kaley G. Reduced hypotensive action of arachidonic acid in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1980 Sep-Oct;2(5):657–663. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie K., Hille B. Cannabinoids inhibit N-type calcium channels in neuroblastoma-glioma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3825–3829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailleux P., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Distribution of neuronal cannabinoid receptor in the adult rat brain: a comparative receptor binding radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience. 1992;48(3):655–668. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90409-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R. Structural requirements for cannabinoid-induced antinociceptive activity in mice. Life Sci. 1985 Apr 22;36(16):1523–1530. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda L. A., Bonner T. I., Lolait S. J. Localization of cannabinoid receptor mRNA in rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jan 22;327(4):535–550. doi: 10.1002/cne.903270406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda L. A., Lolait S. J., Brownstein M. J., Young A. C., Bonner T. I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):561–564. doi: 10.1038/346561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan J. P., Holtzman S. G. Quantification of the analgesic activity of narcotic antagonists by a modified hot-plate procedure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):497–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmauss C., Yaksh T. L. In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. B., Compton D. R., Welch S. P., Razdan R. K., Mechoulam R., Martin B. R. The pharmacological activity of anandamide, a putative endogenous cannabinoid, in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jul;270(1):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Fennessy M. R. Biphasic nature of the effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on body temperature and brain amines of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 15;46(2):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulunay F. C., Ayhan I. H., Sparber S. B. The effects of morphine and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on motor activity in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1982;78(4):358–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00433741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga K., Lake K., Martin B. R., Kunos G. Novel antagonist implicates the CB1 cannabinoid receptor in the hypotensive action of anandamide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 May 24;278(3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00181-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Barg J., Levy R., Saya D., Heldman E., Mechoulam R. Anandamide, a brain endogenous compound, interacts specifically with cannabinoid receptors and inhibits adenylate cyclase. J Neurochem. 1993 Jul;61(1):352–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]