Abstract
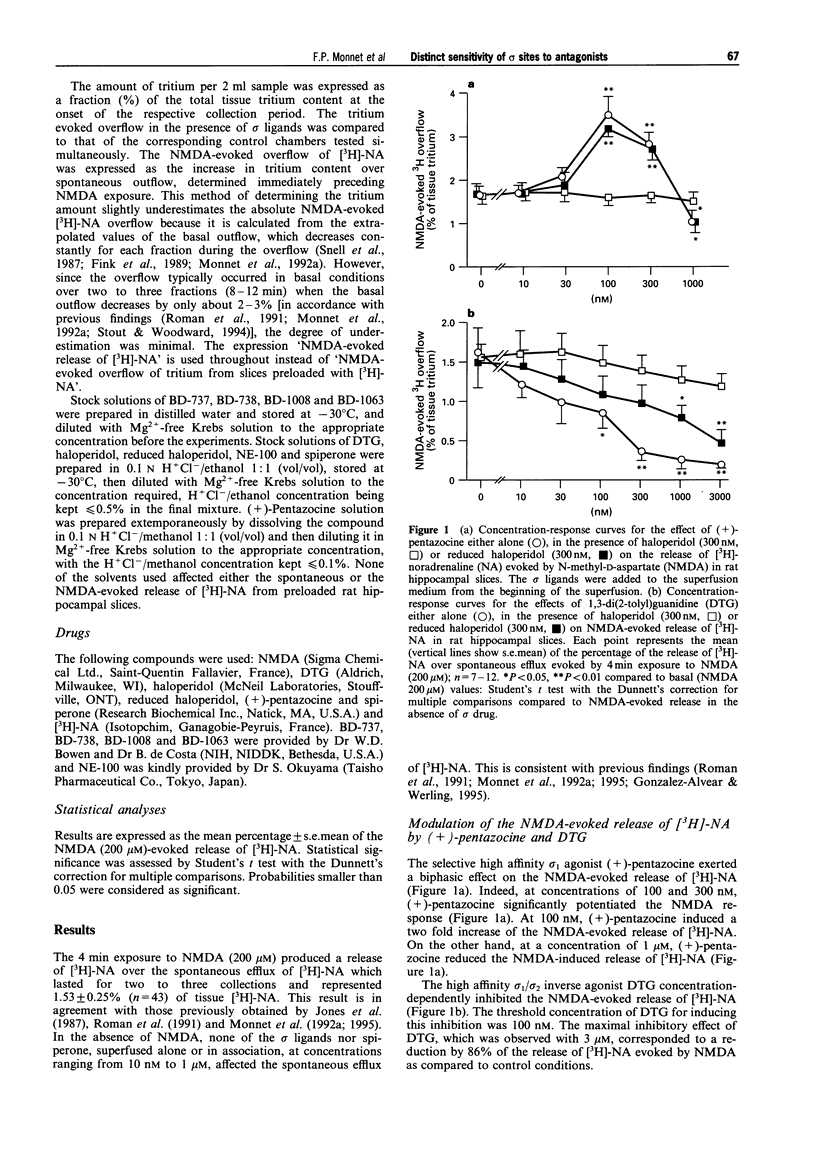
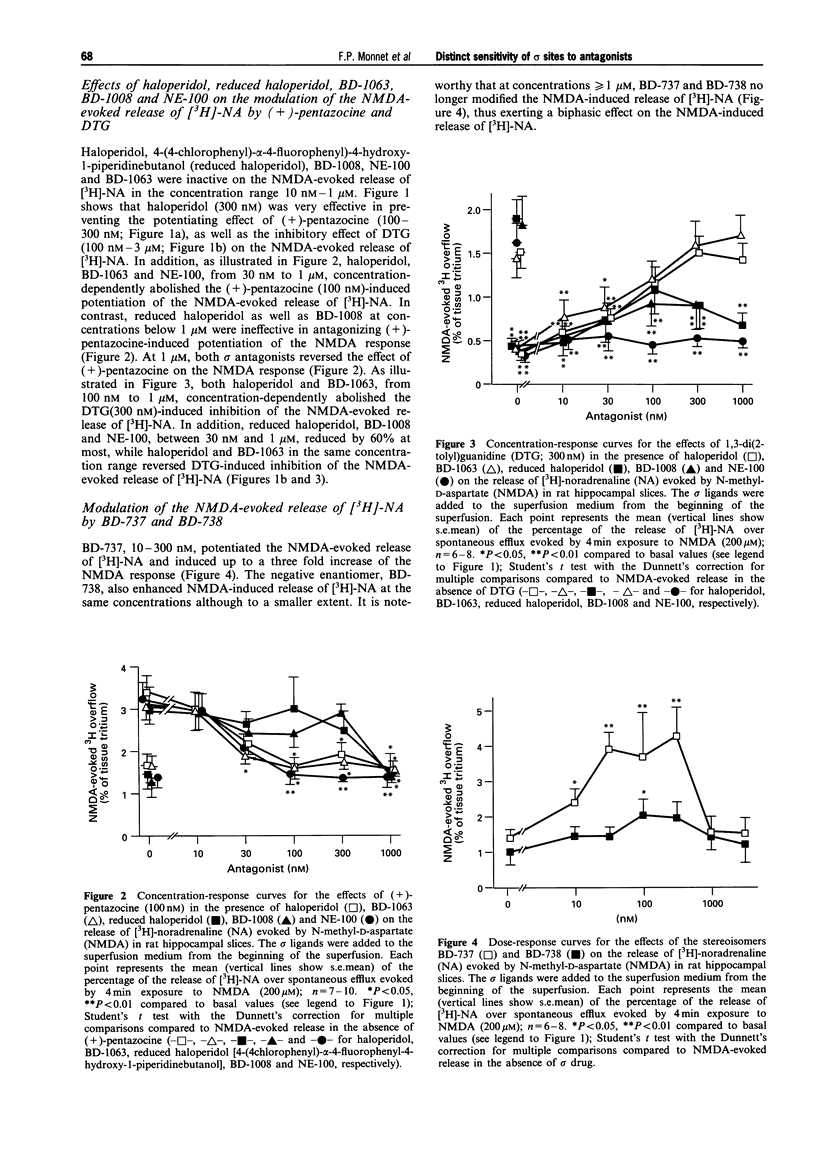
1. It is now widely accepted that there are two classes of sigma (sigma) binding sites, denoted sigma(1) and sigma(2), and recently sigma(3) subtype has been proposed. Selective sigma(1) and sigma(2) receptor agonists are known to modulate the neuronal response to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) in vivo and in vitro. To identify the site of action of a series of recently synthesised high affinity sigma ligands, the present in vitro series of experiments was carried out on NMDA-evoked [3H]-noradrenaline ([3H]-NA) overflow from preloaded hippocampal slices of the rat. 2. The ligands (+)-cis-N-methyl-N-[2,(3,4-dichlorophenyl) ethyl]-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl) cyclohexylamine (BD-737) and (+)-pentazocine, considered as the prototypic sigma(1) agonists, potentiated the NMDA response from 10 nM to 100 nM. This potentiation faded between 100 nM and 1 microM ligand concentrations. On the other hand, 1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine (DTG), a mixed sigma(1)/sigma(2) agonist, at concentrations greater than 100 nM inhibited the NMDA-evoked [3H]-NA release. Spiperone, considered as active on putative sigma(3) receptors, was without effect on the NMDA response, or on the potentiating effect of BD-737. 3. The high affinity sigma antagonists haloperidol and 1[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-4-methylpiperazine (BD-1063), inactive by themselves on the NMDA-induced response, at concentrations above 30 nM totally prevented the potentiating effect of (+)-pentazocine (100 nM) as well as the inhibitory effect of DTG (300 nM) on NMDA-evoked [3H]-NA release. Whereas haloperidol and BD-1063, at concentrations < 1 microM, were inactive on the potentiating effect of BD-737 (100 nM). 4. 4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-alpha-4-fluorophenyl-4-hydroxy-1-piperidinebutanol (reduced haloperidol), N-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-N-methyl-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethylamine (BD-1008), inactive by themselves on the NMDA-evoked [3H]-NA release, failed to reverse the effects of (+)-pentazocine and DTG, but at concentrations of 30 nM to 1 microM antagonised the BD-737-induced potentiation of the NMDA response. Conversely, N,N-dipropyl-2-[4-methoxy-3-(2-phenylethoxy)phenyl]-ethylamine monohydrochloride (NE-100) blocked the effects of (+)-pentazocine as well as those of BD-737, but not those of DTG. 5. The present results provide in vitro functional evidence for a sigma receptor type preferentially sensitive to BD-737, reduced haloperidol, BD-1008 and also to NE-100, that differs from the already identified sigma(1), sigma(2) and sigma(3) sites.
Full text
PDF

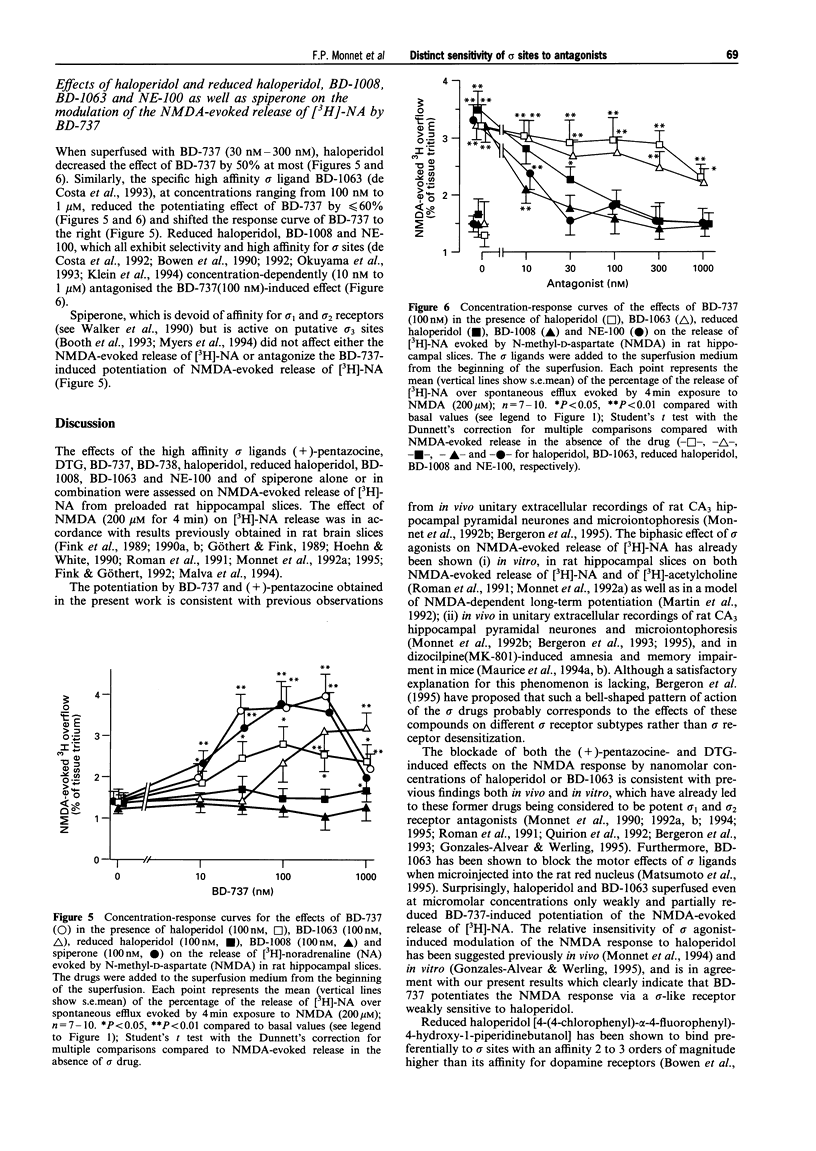



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergeron R., Debonnel G., De Montigny C. Modification of the N-methyl-D-aspartate response by antidepressant sigma receptor ligands. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 24;240(2-3):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90918-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron R., de Montigny C., Debonnel G. Biphasic effects of sigma ligands on the neuronal response to N-methyl-D-aspartate. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;351(3):252–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00233244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R. G., Wyrick S. D., Baldessarini R. J., Kula N. S., Myers A. M., Mailman R. B. New sigma-like receptor recognized by novel phenylaminotetralins: ligand binding and functional studies. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;44(6):1232–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. D., Moses E. L., Tolentino P. J., Walker J. M. Metabolites of haloperidol display preferential activity at sigma receptors compared to dopamine D-2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 27;177(3):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90260-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. D., Walker J. M., de Costa B. R., Wu R., Tolentino P. J., Finn D., Rothman R. B., Rice K. C. Characterization of the enantiomers of cis-N-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-N-methyl-2-(1- pyrrolidinyl)cyclohexylamine (BD737 and BD738): novel compounds with high affinity, selectivity and biological efficacy at sigma receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):32–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoster M. A., Klette K. L., Knight E. S., Tortella F. C. Sigma receptor-mediated neuroprotection against glutamate toxicity in primary rat neuronal cultures. Brain Res. 1995 Feb 6;671(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)01294-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Bönisch H., Göthert M. Presynaptic NMDA receptors stimulate noradrenaline release in the cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 21;185(1):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90219-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M. Ethanol inhibits the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced attenuation of the NMDA-evoked noradrenaline release in the rat brain cortex: interaction with NMDA-induced desensitization. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;344(2):167–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00167214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M., Molderings G., Schlicker E. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated stimulation of noradrenaline release, but not release of other neurotransmitters, in the rat brain cortex: receptor location, characterization and desensitization. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 May;339(5):514–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00167254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M. Presynaptic site of action underlying the ethanol-induced inhibition of norepinephrine release evoked by stimulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1992 Feb 14;572(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90446-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M., Schlicker E. Veratridine and other depolarizing agents counteract the inhibitory effect of Mg2+ ions on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced noradrenaline release in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;342(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00178972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Alvear G. M., Werling L. L. Regulation of [3H]dopamine release from rat striatal slices by sigma receptor ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Oct;271(1):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Alvear G. M., Werling L. L. Sigma receptor regulation of norepinephrine release from rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1995 Feb 27;673(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)01394-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Fink K. Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)- and L-glutamate-induced noradrenaline and acetylcholine release in the rat brain by ethanol. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):516–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00260606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. S., Bowen W. D., Lee K. S., Williams W., Weinberger D. R., de Costa B. R. Synthesis and binding characteristics of potential SPECT imaging agents for sigma-1 and sigma-2 binding sites. J Med Chem. 1993 Mar 5;36(5):566–571. doi: 10.1021/jm00057a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Bowen W. D. A sigma-like binding site in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: decreased affinity for (+)-benzomorphans and lower molecular weight suggest a different sigma receptor form from that of guinea pig brain. Brain Res. 1990 Sep 17;527(2):244–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn K., White T. D. N-methyl-D-aspartate, kainate and quisqualate release endogenous adenosine from rat cortical slices. Neuroscience. 1990;39(2):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90280-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaen J. C., Caprathe B. W., Pugsley T. A., Wise L. D., Akunne H. Evaluation of the effects of the enantiomers of reduced haloperidol, azaperol, and related 4-amino-1-arylbutanols on dopamine and sigma receptors. J Med Chem. 1993 Nov 26;36(24):3929–3936. doi: 10.1021/jm00076a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Snell L. D., Johnson K. M. Phencyclidine selectively inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced hippocampal [3H]norepinephrine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Feb;240(2):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Cooper T. B., Musacchio J. M. Effects of haloperidol and reduced haloperidol on binding to sigma sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar 21;254(3):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesage A. S., De Loore K. L., Peeters L., Leysen J. E. Neuroprotective sigma ligands interfere with the glutamate-activated NOS pathway in hippocampal cell culture. Synapse. 1995 Jun;20(2):156–164. doi: 10.1002/syn.890200210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart B. P., Soulard P., Benicourt C., Privat A., Junien J. L. Distinct neuroprotective profiles for sigma ligands against N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), and hypoxia-mediated neurotoxicity in neuronal culture toxicity studies. Brain Res. 1995 Mar 27;675(1-2):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00049-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malva J. O., Carvalho A. P., Carvalho C. M. Modulation of dopamine and noradrenaline release and of intracellular Ca2+ concentration by presynaptic glutamate receptors in hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1439–1447. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto R. R., Bowen W. D., Tom M. A., Vo V. N., Truong D. D., De Costa B. R. Characterization of two novel sigma receptor ligands: antidystonic effects in rats suggest sigma receptor antagonism. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul 14;280(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice T., Hiramatsu M., Itoh J., Kameyama T., Hasegawa T., Nabeshima T. Behavioral evidence for a modulating role of sigma ligands in memory processes. I. Attenuation of dizocilpine (MK-801)-induced amnesia. Brain Res. 1994 May 30;647(1):44–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice T., Su T. P., Parish D. W., Nabeshima T., Privat A. PRE-084, a sigma selective PCP derivative, attenuates MK-801-induced impairment of learning in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1994 Dec;49(4):859–869. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Blier P., Debonnel G., de Montigny C. Modulation by sigma ligands of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced [3H]noradrenaline release in the rat hippocampus: G-protein dependency. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;346(1):32–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00167567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., Bergeron R., Gronier B., de Montigny C. The effects of sigma ligands and of neuropeptide Y on N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation of CA3 dorsal hippocampus neurones are differentially affected by pertussin toxin. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):709–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., Junien J. L., De Montigny C. N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation is selectively modulated by sigma receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 25;179(3):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90186-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., de Montigny C. In vivo electrophysiological evidence for a selective modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation in rat CA3 dorsal hippocampus by sigma ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Apr;261(1):123–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Mahé V., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids, via sigma receptors, modulate the [3H]norepinephrine release evoked by N-methyl-D-aspartate in the rat hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3774–3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Charifson P. S., Owens C. E., Kula N. S., McPhail A. T., Baldessarini R. J., Booth R. G., Wyrick S. D. Conformational analysis, pharmacophore identification, and comparative molecular field analysis of ligands for the neuromodulatory sigma 3 receptor. J Med Chem. 1994 Nov 25;37(24):4109–4117. doi: 10.1021/jm00050a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama S., Imagawa Y., Ogawa S., Araki H., Ajima A., Tanaka M., Muramatsu M., Nakazato A., Yamaguchi K., Yoshida M. NE-100, a novel sigma receptor ligand: in vivo tests. Life Sci. 1993;53(18):PL285–PL290. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90588-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama S., Imagawa Y., Sakagawa T., Nakazato A., Yamaguchi K., Katoh M., Yamada S., Araki H., Otomo S. NE-100, a novel sigma receptor ligand: effect on phencyclidine-induced behaviors in rats, dogs and monkeys. Life Sci. 1994;55(7):PL133–PL138. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00749-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontecorvo M. J., Karbon E. W., Goode S., Clissold D. B., Borosky S. A., Patch R. J., Ferkany J. W. Possible cerebroprotective and in vivo NMDA antagonist activities of sigma agents. Brain Res Bull. 1991 Mar;26(3):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(91)90025-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Bowen W. D., Itzhak Y., Junien J. L., Musacchio J. M., Rothman R. B., Su T. P., Tam S. W., Taylor D. P. A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):85–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90030-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell L. D., Jones S. M., Johnson K. M. Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced hippocampal [3H]norepinephrine release by phencyclidine is dependent on potassium concentration. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 5;78(3):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout A. K., Woodward J. J. Differential effects of nitric oxide gas and nitric oxide donors on depolarization-induced release of [3H]norepinephrine from rat hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Nov;33(11):1367–1374. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Cook L. Sigma opiates and certain antipsychotic drugs mutually inhibit (+)-[3H] SKF 10,047 and [3H]haloperidol binding in guinea pig brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5618–5621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Bowen W. D., Walker F. O., Matsumoto R. R., De Costa B., Rice K. C. Sigma receptors: biology and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Dec;42(4):355–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Sonders M., Quarum M., McLean S., Pou S., Keana J. F. 1,3-Di(2-[5-3H]tolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8784–8788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Costa B. R., He X. S., Linders J. T., Dominguez C., Gu Z. Q., Williams W., Bowen W. D. Synthesis and evaluation of conformationally restricted N-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-N-methyl-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethylamines at sigma receptors. 2. Piperazines, bicyclic amines, bridged bicyclic amines, and miscellaneous compounds. J Med Chem. 1993 Aug 6;36(16):2311–2320. doi: 10.1021/jm00068a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Costa B. R., Radesca L., Di Paolo L., Bowen W. D. Synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of a novel class of N-(arylethyl)-N-alkyl-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethylamines: structural requirements and binding affinity at the sigma receptor. J Med Chem. 1992 Jan;35(1):38–47. doi: 10.1021/jm00079a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Costa B. R., Rice K. C., Bowen W. D., Thurkauf A., Rothman R. B., Band L., Jacobson A. E., Radesca L., Contreras P. C., Gray N. M. Synthesis and evaluation of N-substituted cis-N-methyl-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)cyclohexylamines as high affinity sigma receptor ligands. Identification of a new class of highly potent and selective sigma receptor probes. J Med Chem. 1990 Nov;33(11):3100–3110. doi: 10.1021/jm00173a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


