Abstract
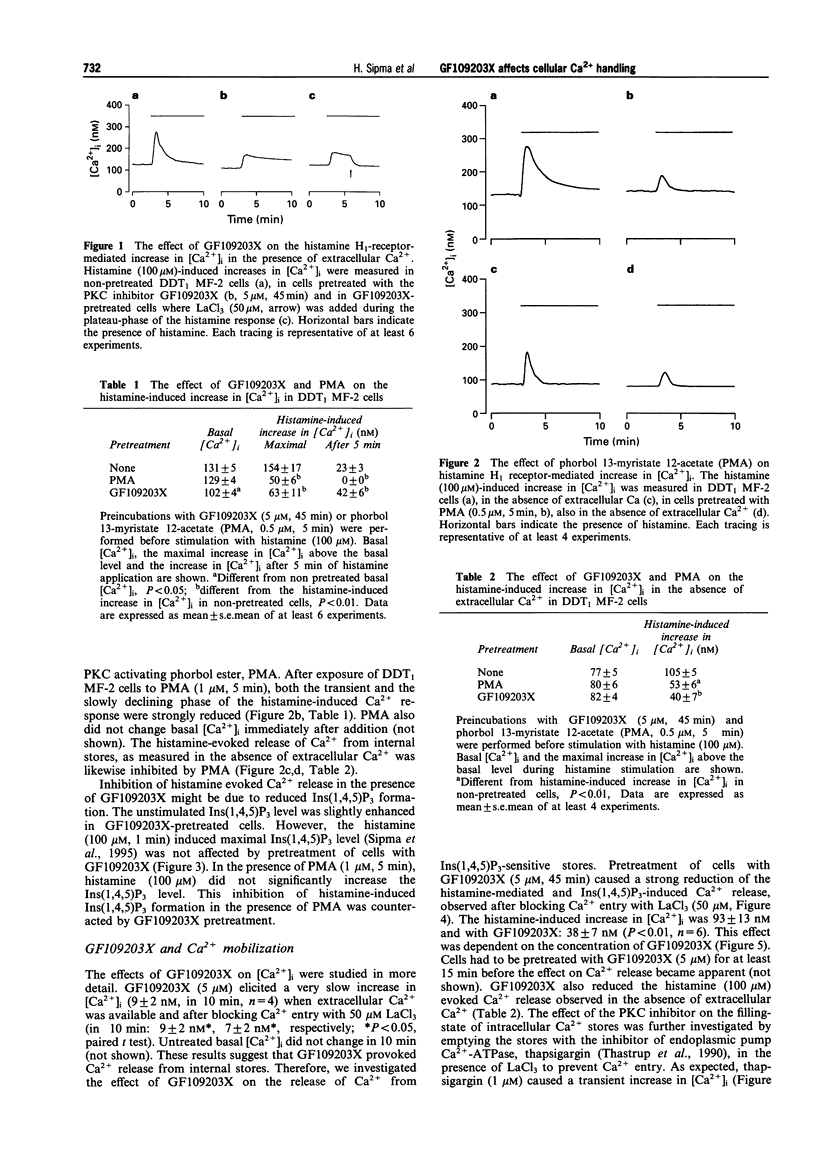
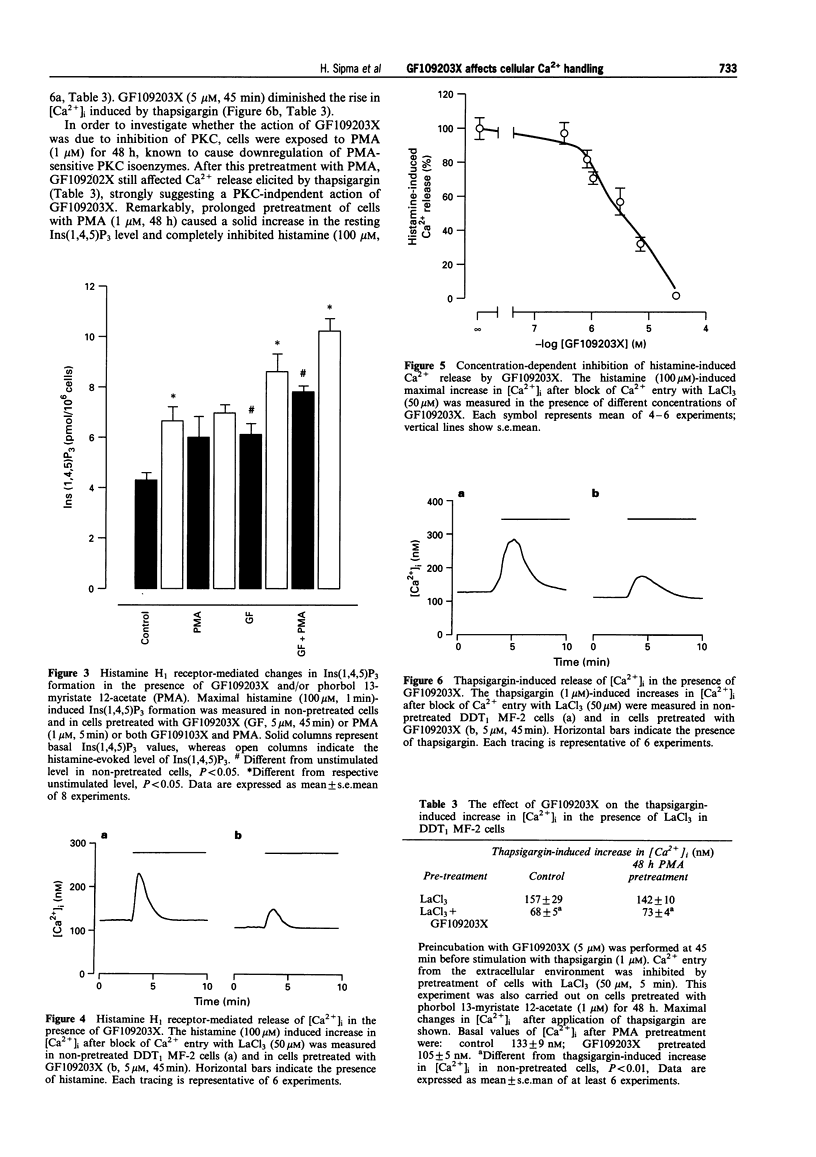
1. The effects of the specific protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, GF109203X, were measured on the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), and on histamine H1 receptor- and thapsigargin-mediated increases in [Ca2+]i in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. 2. After pretreatment of cells with GF109203X (5 microM, 45 min), the histamine (100 microM)-induced initial rise in [Ca2+]i, representing Ca2+ mobilization from internal stores, was inhibited (by 59 +/- 7%). The slowly declining phase of the histamine induced Ca2+ response, reflecting Ca2+ entry, was enhanced (83 +/- 26%) in the presence of the PKC inhibitor. 3. The histamine induced release of Ca2+ from internal stores, measured after blocking Ca2+ entry with LaCl3 was inhibited by GF109203X in a concentration-dependent manner (IC50: 3.1 +/- 1.1 microM). 4. Histamine-induced formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) was not changed in the presence of GF109203X. 5. The PKC activating phorbol ester, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, 1 microM), strongly reduced histamine-induced Ins(1,4,5)P3 formation (58 +/- 16%). This effect was reversed by GF109203X (5 microM). Furthermore, PMA diminished histamine evoked Ca2+ release (50 +/- 6%) and blocked Ca2+ entry completely. 6. The rise in [Ca2+]i caused by blocking endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase with thapsigargin (1 microM), was strongly reduced (57 +/- 3%) after pretreatment of cells with GF109203X. Downregulation of PKC by long-term pretreatment of cells with PMA (1 microM, 48 h) did not abolish this effect of GF109203X (48 +/- 3% inhibition). 7. In permeabilized DDT, MF-2 cells preloaded with 45Ca2+ in the presence of GF109203X, the amount of 45Ca2+ released by Ins(1,4,5)P3 (10 microM) was markedly reduced (42 +/- 9%). GF109203X did not release Ca2+ itself and did not impair Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptor function. 8. Uptake of 45Ca2+ by intact cells, representing Ca2+ entry, was enhanced by GF109203X (65 +/- 11%), by histamine (24 +/- 6%) and also by thapsigargin (121 +/- 10%). The GF109203X- and the thapsigargin-induced uptake of 45Ca2+ were not additive. 9. These data suggest that GF109203X reduces the filling-state of intracellular Ins(1,4,5)P3 sensitive Ca2+ stores by inhibiting the Ca2+ uptake into these stores, thereby promoting store-dependent (capacitive) Ca2+ entry.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assender J. W., Kontny E., Fredholm B. B. Expression of protein kinase C isoforms in smooth muscle cells in various states of differentiation. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 28;342(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80588-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
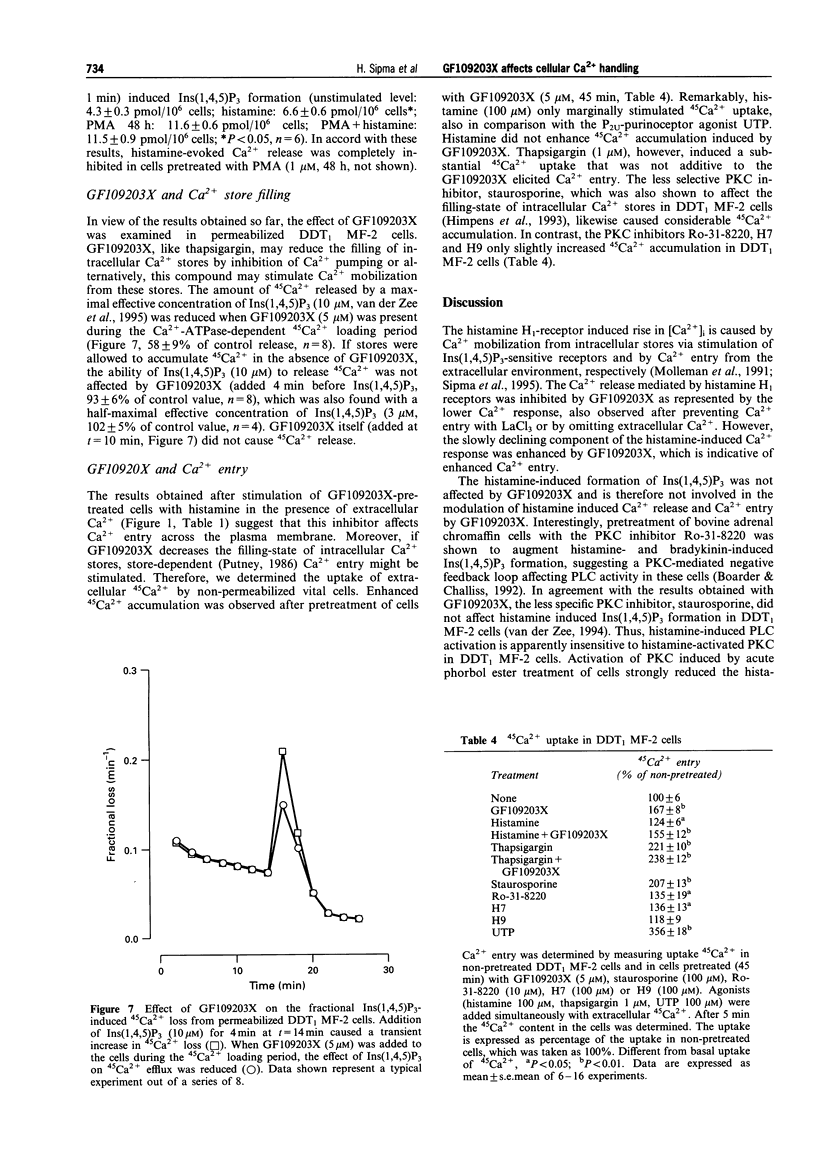
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bian J. H., Ghosh T. K., Wang J. C., Gill D. L. Identification of intracellular calcium pools. Selective modification by thapsigargin. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8801–8806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., Challiss R. A. Role of protein kinase C in the regulation of histamine and bradykinin stimulated inositol polyphosphate turnover in adrenal chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1140–1145. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Challiss R. A., Barnes P. J., Nahorski S. R. Mass changes of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in trachealis muscle following agonist stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog A. Calcium and the alpha-action of catecholamines on guinea-pig taenia caeci. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:109–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog A., Hoiting B., Molleman A., Van den Akker J., Duin M., Nelemans A. Calcium release from separate receptor-specific intracellular stores induced by histamine and ATP in a hamster cell line. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:591–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Hill S. J. Homologous and heterologous desensitization of histamine H1- and ATP-receptors in the smooth muscle cell line, DDT1MF-2: the role of protein kinase C. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1449–1456. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunteski-Hamblin A. M., Greeb J., Shull G. E. A novel Ca2+ pump expressed in brain, kidney, and stomach is encoded by an alternative transcript of the slow-twitch muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase gene. Identification of cDNAs encoding Ca2+ and other cation-transporting ATPases using an oligonucleotide probe derived from the ATP-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15032–15040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., De Smedt H., Casteels R. Staurosporine induced Ca2+ increase in DDT1MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C544–C551. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. A., Owen P. J., Boarder M. R. Influence of phorbol esters, and diacylglycerol kinase and lipase inhibitors on noradrenaline release and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Lukyanetz E. A., Ter-Markosyan A. S. Parathyroid hormone enhances calcium current in snail neurones--simulation of the effect by phorbol esters. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Feb;420(2):146–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00374983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. W., Severson D. L. Signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: diacylglycerol second messengers and PKC action. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):C659–C678. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.3.C659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny-Baron G., Kazanietz M. G., Mischak H., Blumberg P. M., Kochs G., Hug H., Marmé D., Schächtele C. Selective inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by the indolocarbazole Gö 6976. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9194–9197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., Declerck I., Droogmans G., Plessers L., De Smedt H., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Agonist-dependent Ca2+ and Mn2+ entry dependent on state of filling of Ca2+ stores in aortic smooth muscle cells of the rat. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:171–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molleman A., Hoiting B., Duin M., van den Akker J., Nelemans A., Den Hertog A. Potassium channels regulated by inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and internal calcium in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5658–5663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S., Müller S., Walzog B. Effect of staurosporine on fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated human neutrophils: dissociated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, diacylglycerol and intracellular calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 29;1135(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane S. G., Dunlap K. Kinase C activator 1,2-oleoylacetylglycerol attenuates voltage-dependent calcium current in sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipma H., Duin M., Hoiting B., den Hertog A., Nelemans A. Regulation of histamine- and UTP-induced increases in Ins(1,4,5)P3, Ins (1,3,4,5)P4 and Ca2+ by cyclic AMP in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(2):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M. J., Bloemers S. M., Leurs R., Tertoolen L. G., Bast A., de Laat S. W., Timmerman H. Short-term desensitization of the histamine H1 receptor in human HeLa cells: involvement of protein kinase C dependent and independent pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):448–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornquist K., Tashjian A. H., Jr 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate decreases influx of extracellular Ca2+ induced by depolarization in GH4C1 cells: effects of pretreatment with 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):2068–2078. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-2068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toullec D., Pianetti P., Coste H., Bellevergue P., Grand-Perret T., Ajakane M., Baudet V., Boissin P., Boursier E., Loriolle F. The bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15771–15781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkson J., Li X. B., Wong K. Staurosporine induces hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 18;343(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80602-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Zee L., Sipma H., Nelemans A., Den Hertog A. The role of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in internal Ca2+ mobilization following histamine H1 receptor stimulation in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 May 26;289(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. E., Parker P. J., Nixon J. S. Isoenzyme specificity of bisindolylmaleimides, selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):335–337. doi: 10.1042/bj2940335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K., Kwan-Yeung L., Turkson J. Staurosporine clamps cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations of human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):499–505. doi: 10.1042/bj2830499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., Nakashima S., Nozawa Y. Coupling of polyphosphoinositide breakdown with calcium efflux in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated rabbit neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


