Abstract
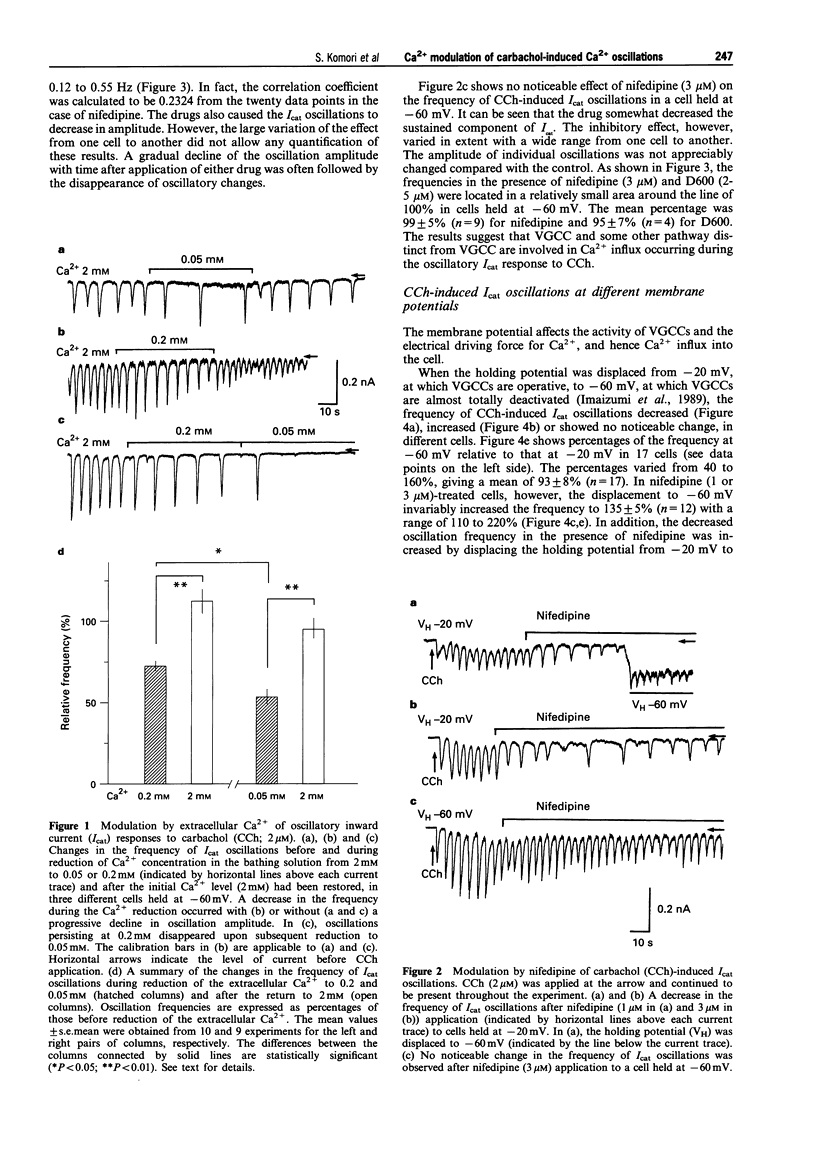
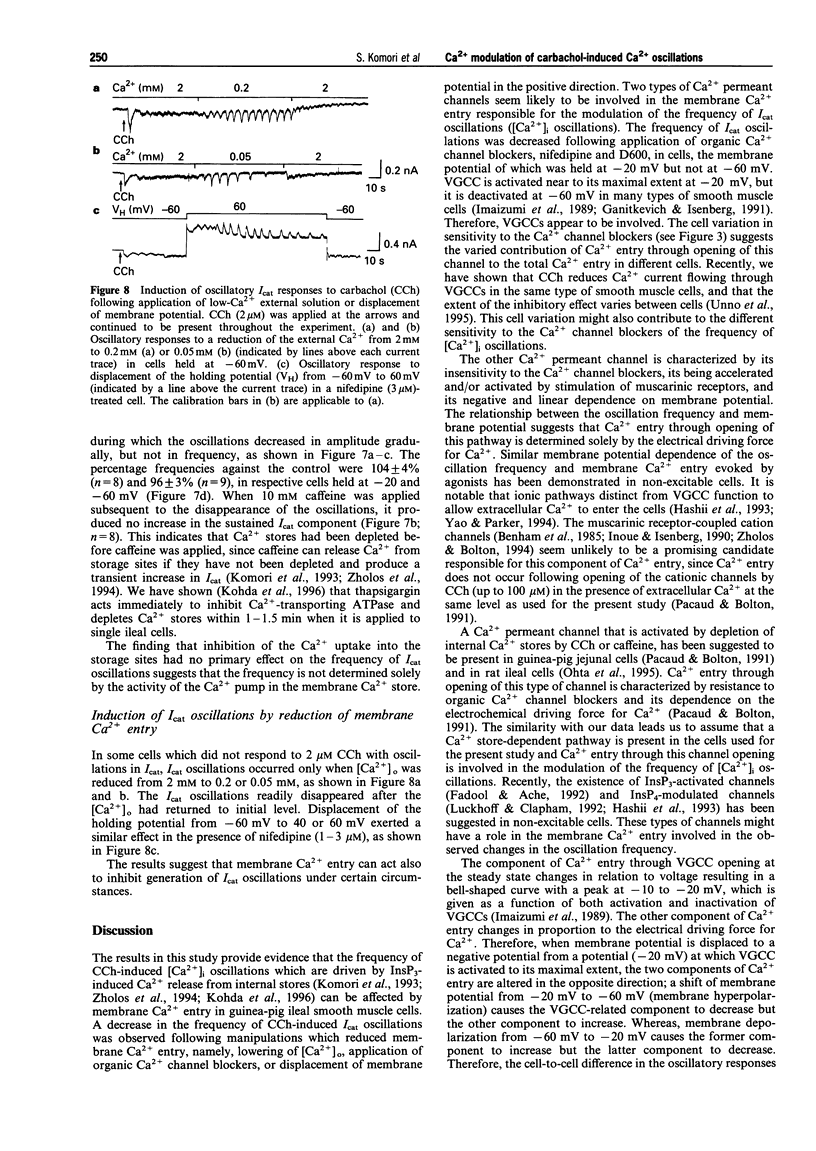
1. Oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) evoked by carbachol (CCh; 2 microM), a muscarinic agonist, were detected as oscillatory changes of muscarinic receptor-coupled cationic current (Icat) in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle cells by the whole cell patch-clamp technique. 2. Reduction of extracellular Ca2+ from 2 mM to 0.2 or 0.05 mM, during CCh-induced Icat oscillations, caused them to disappear or to decrease markedly in frequency. A return to 2 mM Ca2+ concentration restored the initial Icat oscillations. 3. Application of nifedipine (1-3 microM) or D600 (2-5 microM) to block the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel (VGCC) decreased the frequency of the ongoing Icat oscillations in the cells held at -20 mV, but it was without effect in cells held at -60 mV. 4. Displacement of the holding potential of -20 mV to -60 mV to deactivate VGCC produced a decrease, an increase or no noticeable change in the frequency of the Icat oscillations in different cells. Displacement to 20 mV to inactivate VGCC invariably produced a decrease in the frequency. In nifedipine-treated cells, the Icat oscillations varied in frequency voltage-dependently in a reverse and linear way within the range -80 to 40 mV. 5. Application of thapsigargin (1 or 2 microM), an inhibitor of Ca(2+)-ATPase in the membrane of internal Ca2+ stores, caused CCh-induced Icat oscillations to disappear with a progressing phase during which their amplitude, but not frequency, declined. 6. The results suggest that membrane Ca2+ entry has a crucial role to play in regulation of the frequency of CCh-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations in addition to persistence of their generation, and that the effect is brought about by a potential mechanism independent of Ca2+ store replenishment. They also provide evidence that two types of Ca2+ permeant channels, VGCC and an as yet unidentified channel, are involved in the Ca2+ entry responsible for modulation of [Ca2+]i oscillations.
Full text
PDF

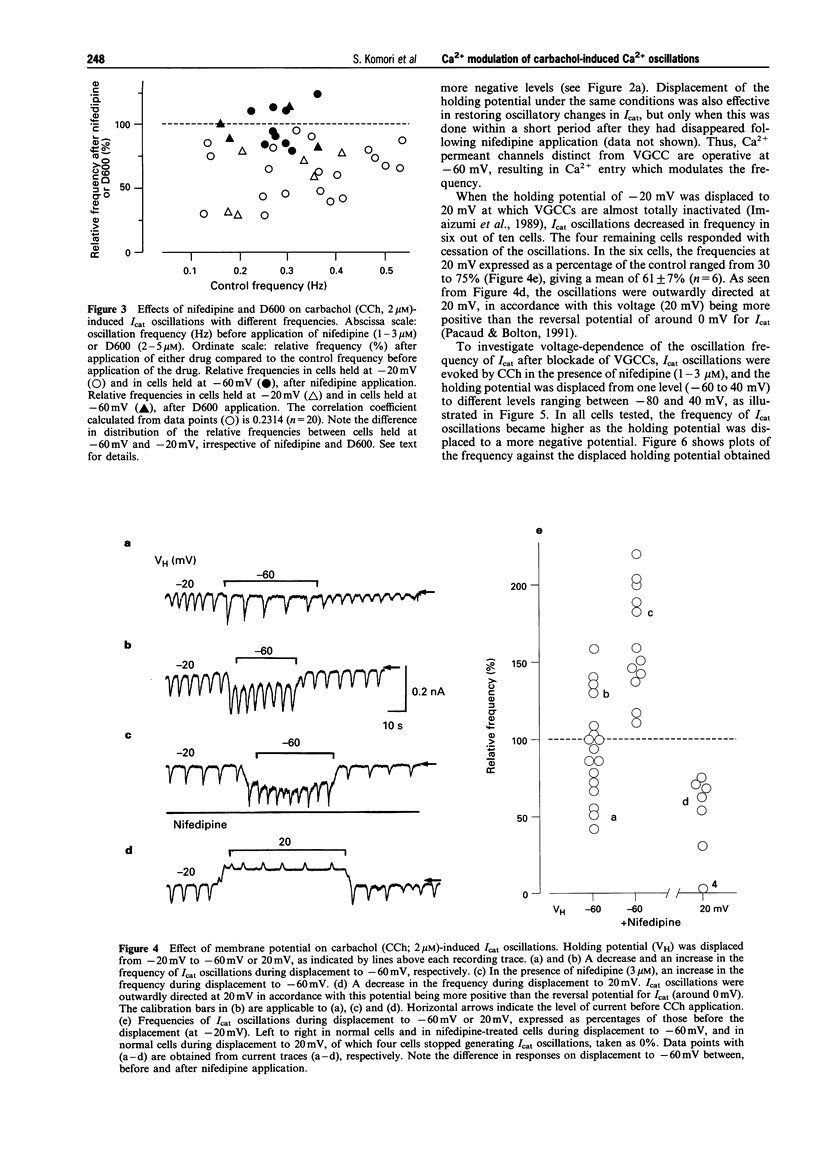
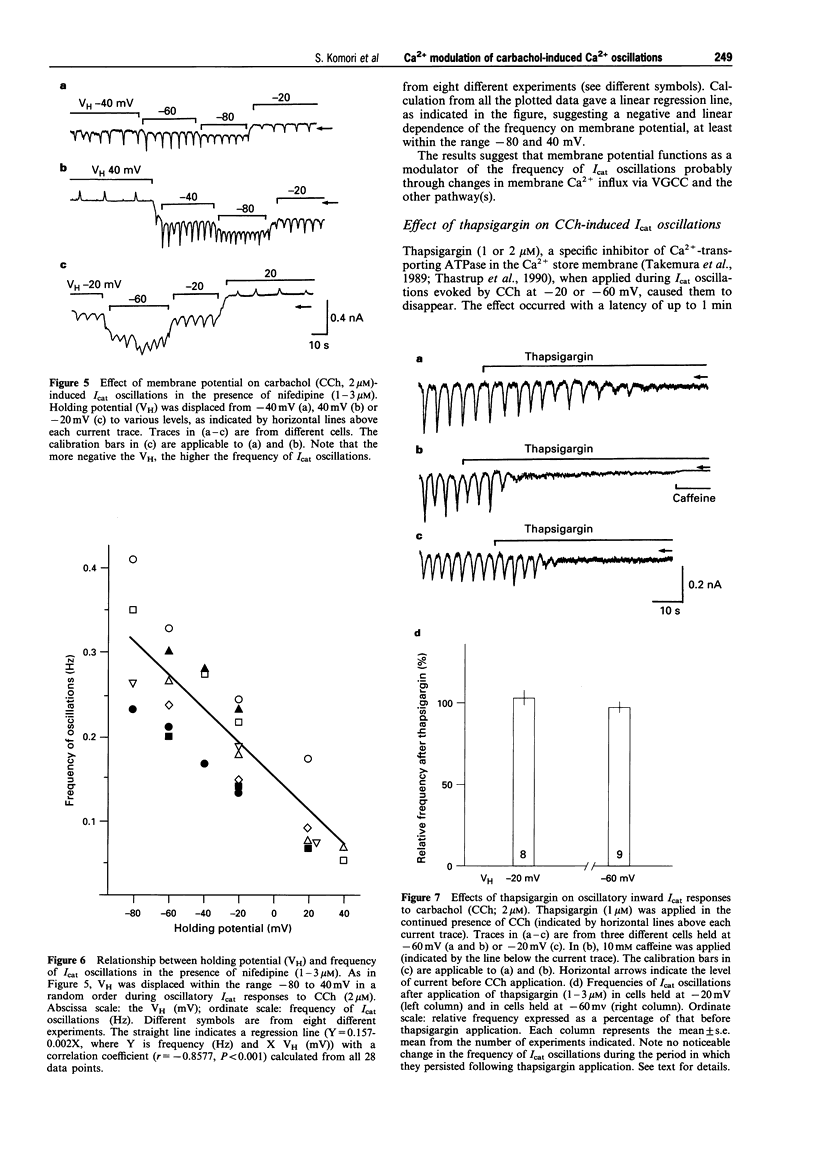


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F., Sneddon P. Evidence for multiple sources of calcium for activation of the contractile mechanism of guinea-pig taenia coli on stimulation with carbachol. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;70(2):229–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young G. W., Keizer J. A single-pool inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-receptor-based model for agonist-stimulated oscillations in Ca2+ concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9895–9899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadool D. A., Ache B. W. Plasma membrane inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated channels mediate signal transduction in lobster olfactory receptor neurons. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):907–918. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90243-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich V Y. a., Isenberg G. Depolarization-mediated intracellular calcium transients in isolated smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:187–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Dupont G., Berridge M. J. Minimal model for signal-induced Ca2+ oscillations and for their frequency encoding through protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar R. J., Bonventre J. V. Oscillations of intracellular calcium induced by vasopressin in individual fura-2-loaded mesangial cells. Frequency dependence on basal calcium concentration, agonist concentration, and temperature. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21589–21594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Paranjape S., Tsien R. Y. Generation of calcium oscillations in fibroblasts by positive feedback between calcium and IP3. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1986413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashii M., Nozawa Y., Higashida H. Bradykinin-induced cytosolic Ca2+ oscillations and inositol tetrakisphosphate-induced Ca2+ influx in voltage-clamped ras-transformed NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19403–19410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Biphasic Ca2+ dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca release in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jun;95(6):1103–1122. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Muraki K., Takeda M., Watanabe M. Measurement and simulation of noninactivating Ca current in smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C880–C885. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Repetitive spikes in cytoplasmic calcium evoked by histamine in human endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):40–45. doi: 10.1038/335040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi T., Blank L. M., Harootunian A. T., Smith M. T., Tsien R. Y. Ca2+ oscillations induced by hormonal stimulation of individual fura-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12859–12866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer J., De Young G. Effect of voltage-gated plasma membrane Ca2+ fluxes on IP3-linked Ca2+ oscillations. Cell Calcium. 1993 May;14(5):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda M., Komori S., Unno T., Ohashi H. Carbachol-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations in single smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 15;492(Pt 2):315–328. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Pacaud P., Ohashi H., Bolton T. B. Oscillations of receptor-operated cationic current and internal calcium in single guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Sep;424(5-6):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00374905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Takewaki T., Ohashi H. GTP-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:105–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. X., Keizer J., Stojilković S. S., Rinzel J. Ca2+ excitability of the ER membrane: an explanation for IP3-induced Ca2+ oscillations. Am J Physiol. 1995 Nov;269(5 Pt 1):C1079–C1092. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.5.C1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Clapham D. E. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates an endothelial Ca(2+)-permeable channel. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):356–358. doi: 10.1038/355356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Kawai K., Ito S., Nakazato Y. Ca2+ entry activated by emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores in ileal smooth muscle of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;114(6):1165–1170. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Ivorra I. Inhibition by Ca2+ of inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ liberation: a possible mechanism for oscillatory release of Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojilković S. S., Kukuljan M., Tomić M., Rojas E., Catt K. J. Mechanism of agonist-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations in pituitary gonadotrophs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7713–7720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Dawson A. P., Scharff O., Foder B., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Bjerrum P. J., Christensen S. B., Hanley M. R. Thapsigargin, a novel molecular probe for studying intracellular calcium release and storage. Agents Actions. 1989 Apr;27(1-2):17–23. doi: 10.1007/BF02222186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unno T., Komori S., Ohashi H. Inhibitory effect of muscarinic receptor activation on Ca2+ channel current in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1995 May 1;484(Pt 3):567–581. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Parker I. Ca2+ influx modulation of temporal and spatial patterns of inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ liberation in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1994 Apr 1;476(1):17–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Bolton T. B. G-protein control of voltage dependence as well as gating of muscarinic metabotropic channels in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 15;478(Pt 2):195–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Komori S., Ohashi H., Bolton T. B. Ca2+ inhibition of inositol trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in single smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 15;481(Pt 1):97–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweifach A., Lewis R. S. Mitogen-regulated Ca2+ current of T lymphocytes is activated by depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6295–6299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


