Abstract
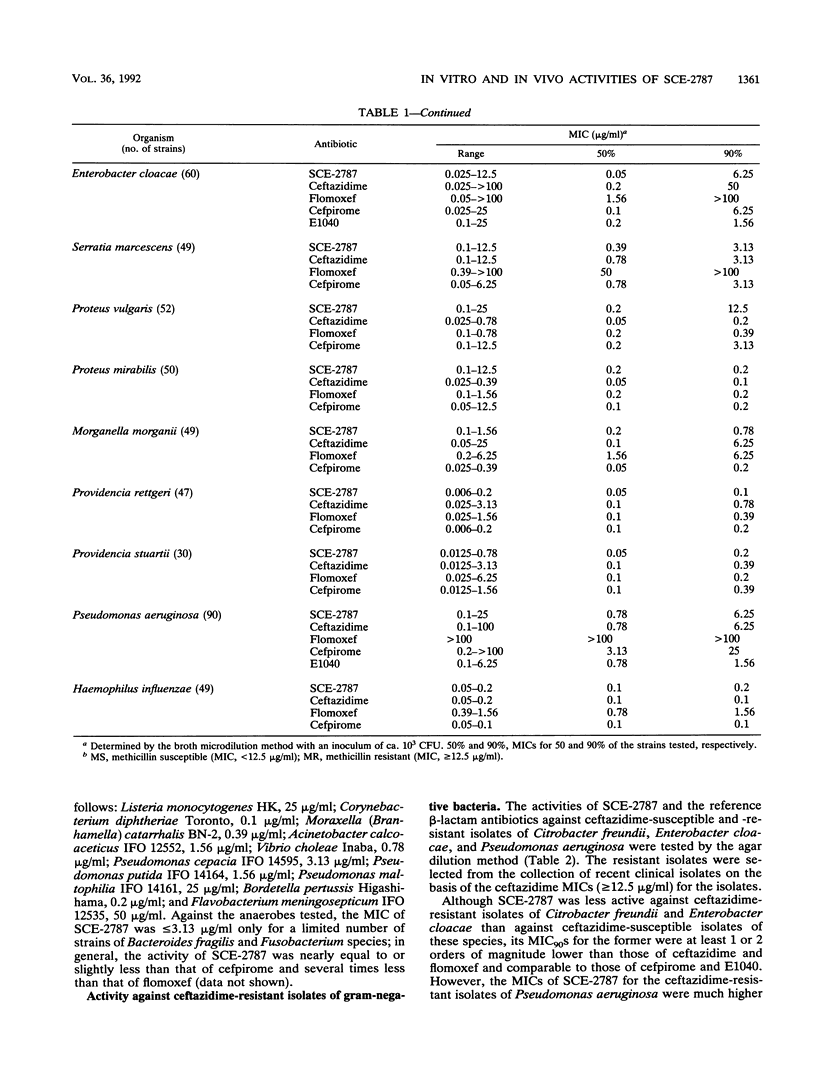
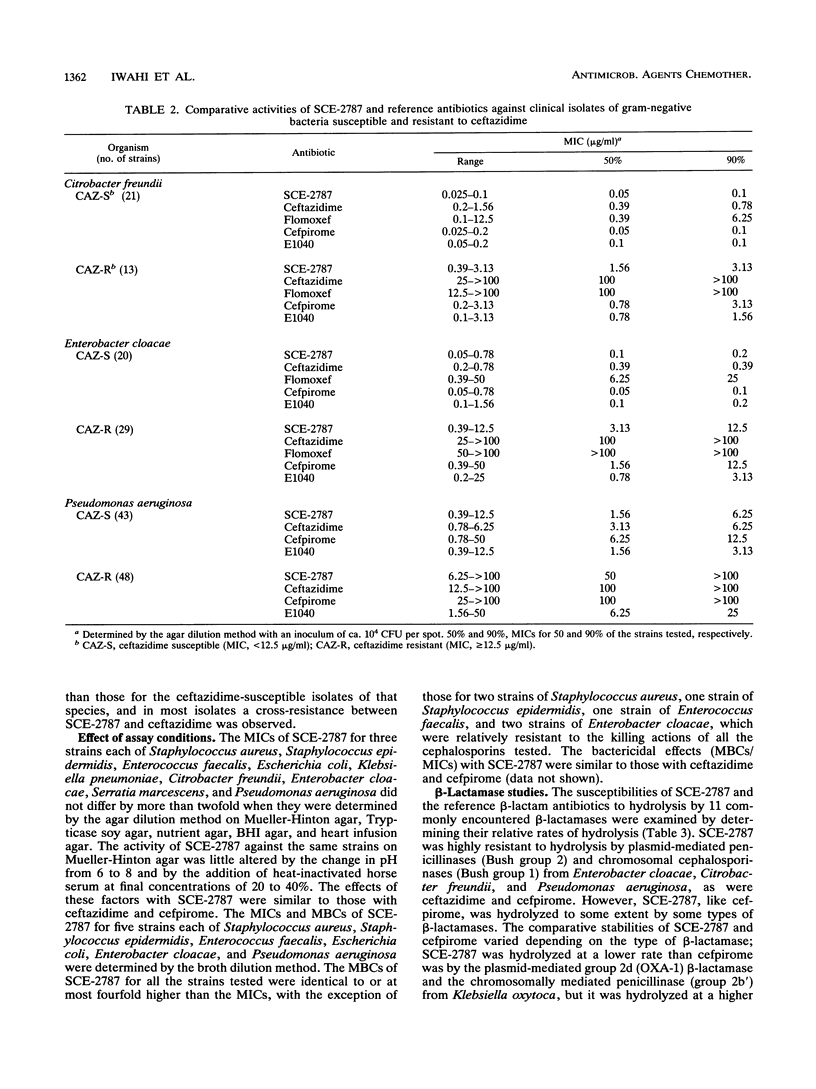
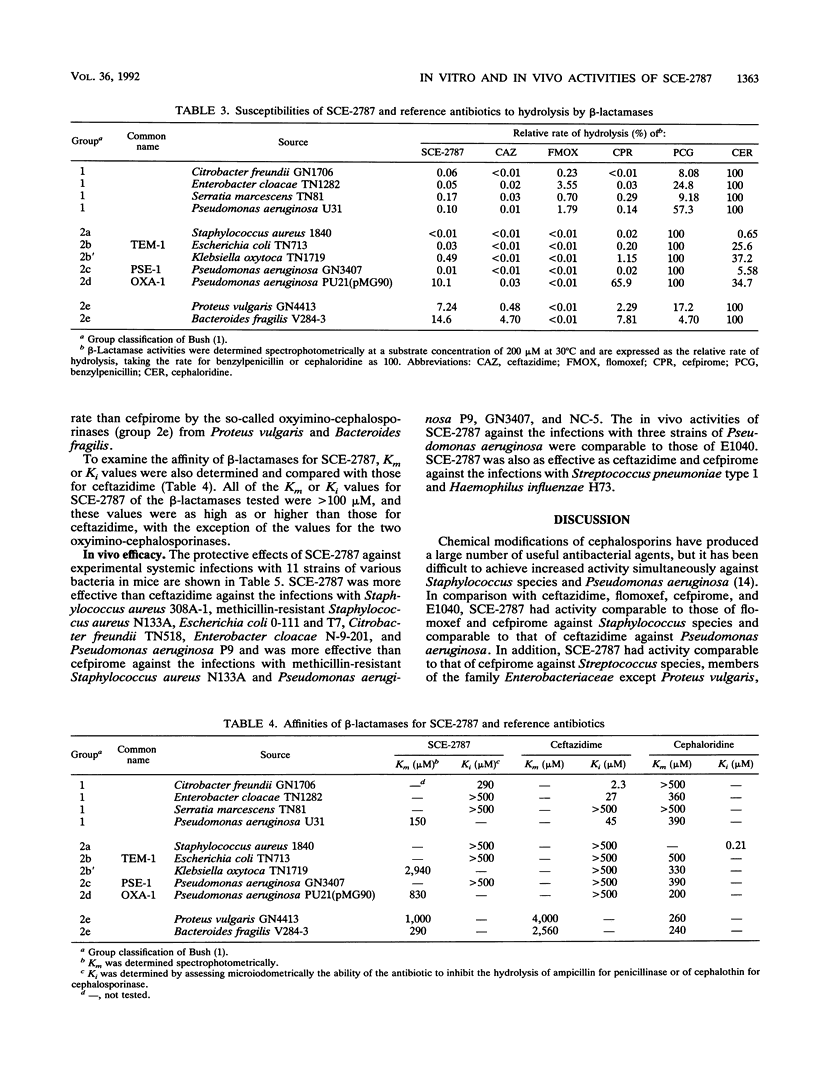
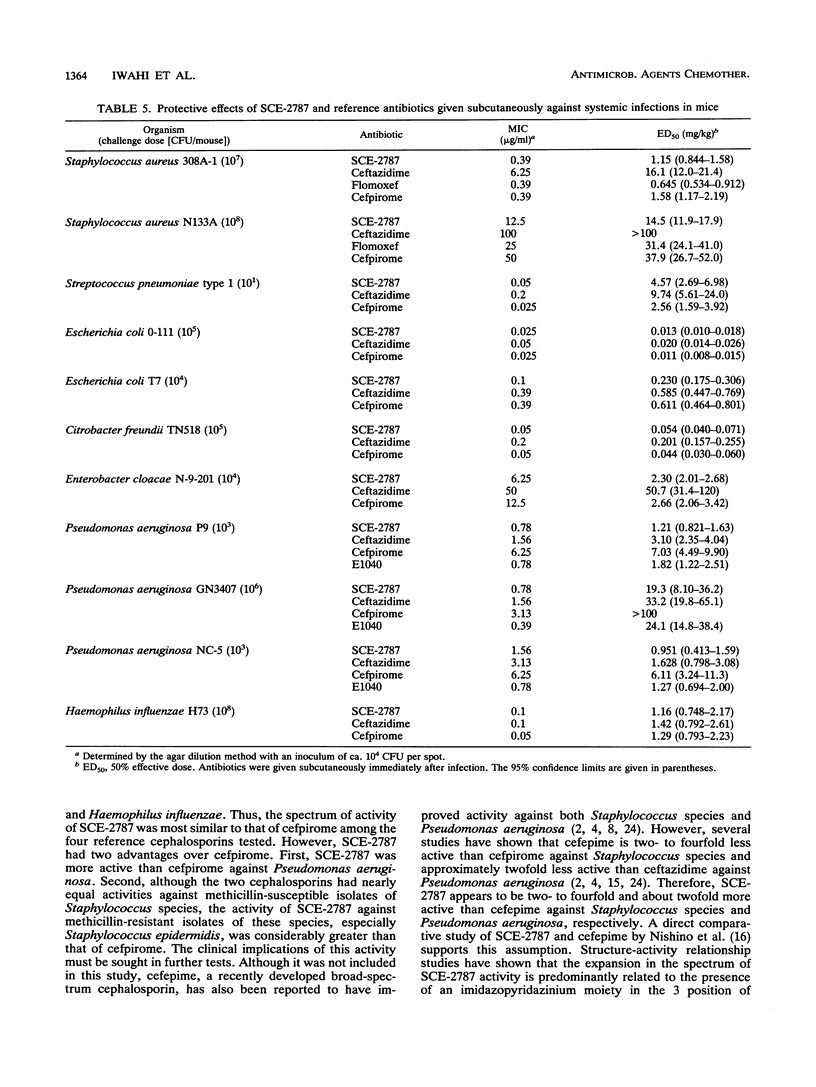
SCE-2787, a new cephalosporin having a condensed azolium moiety in the 3 position and an aminothiadiazolyl group in the 7 beta side chain, was evaluated for its in vitro and in vivo activities in comparison with those of ceftazidime, flomoxef, cefpirome, and E1040. Against methicillin-susceptible strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, SCE-2787 was more active than ceftazidime and E1040 and was as active as flomoxef and cefpirome, with MICs for 90% of strains tested (MIC90s) being 1.56 micrograms/ml or less. SCE-2787 was also active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, for which the MIC90 was 6.25 micrograms/ml, which was lower than that of cefpirome and comparable to that of ceftazidime. SCE-2787 was marginally active against methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococci and Enterococcus faecalis, although its MIC90s were the lowest among those of the antibiotics tested. The activities of SCE-2787 against Streptococcus species, most members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, and Haemophilus influenzae exceeded those of ceftazidime and flomoxef and were comparable to those of cefpirome. Furthermore, MIC90s of SCE-2787 were significantly lower than those of ceftazidime for ceftazidime-resistant isolates of Citrobacter freundii and Enterobacter cloacae. SCE-2787 was resistant to hydrolysis by various types of beta-lactamases, including the Bush group 1 beta-lactamases, and had low affinities for these enzymes, with Km or Ki values of greater than 100 microM. The in vitro activity of SCE-2787 was reflected in its efficacy in mouse protection tests. Thus, SCE-2787 appears to be a promising cephalosporin that should be further evaluated in clinical trials.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bush K. Characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):259–263. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. M., Zemcov S. J., Wright J. M. HR 810 and BMY-28142, two new cephalosporins with broad-spectrum activity: an in-vitro comparison with other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Mar;15(3):305–310. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. C., Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C. Evaluation of the in vitro activity of BMY-28142, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):679–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: genetics and mechanisms of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):991–994. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada A., Kondo M., Okonogi K., Yukishige K., Kuno M. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of carumonam (AMA-1080), a new N-sulfonated monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):821–827. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Bies M., Buck R. E., Chisholm D. R., Pursiano T. A., Tsai Y. H., Misiek M., Price K. E., Leitner F. Comparison of a new cephalosporin, BMY 28142, with other broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Arai S., Hayashi S., Fujimoto K. Beta-lactamase stability of cefpirome (HR 810), a new cephalosporin with a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):713–718. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M. Clinical significance of beta-lactamase induction and stable derepression in gram-negative rods. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF02013107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Novelli A. In vitro activity of E-1040, a novel cephalosporin with potent activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1666–1675. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. beta-Lactam antibiotics: structural relationships affecting in vitro activity and pharmacologic properties. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 3):S237–S259. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Acred P., Harper P. B., Ryan D. M., Kirby S. M., Harding S. M. GR 20263, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin with anti-pseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):876–883. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okonogi K., Kuno M., Kida M., Mitsuhashi S. Beta-lactamase stability and antibacterial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):171–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. J., Carlton D. D., Farrell C. A., Kessler R. E. Affinity of cephalosporins for beta-lactamases as a factor in antibacterial efficacy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):845–848. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Chromosomal cephalosporinases responsible for multiple resistance to newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:573–593. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Microbial resistance to newer generation beta-lactam antibiotics: clinical and laboratory implications. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):399–406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert G., Klesel N., Limbert M., Schrinner E., Seeger K., Winkler I., Lattrell R., Blumbach J., Dürckheimer W., Fleischmann K. HR 810, a new parenteral cephalosporin with a broad antibacterial spectrum. Arzneimittelforschung. 1983;33(8):1084–1086. doi: 10.1002/chin.198350201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Maniatis A., Bertram M. A., Young L. S. In vitro activity of BMY-28142 in comparison with those of other beta-lactam antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):515–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji T., Satoh H., Narisada M., Hamashima Y., Yoshida T. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 6315-S, a new member of the oxacephem antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Apr;38(4):466–476. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Katsu K., Moriyama M., Kitoh K. In vitro evaluation of E1040, a new cephalosporin with potent antipseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):693–701. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


