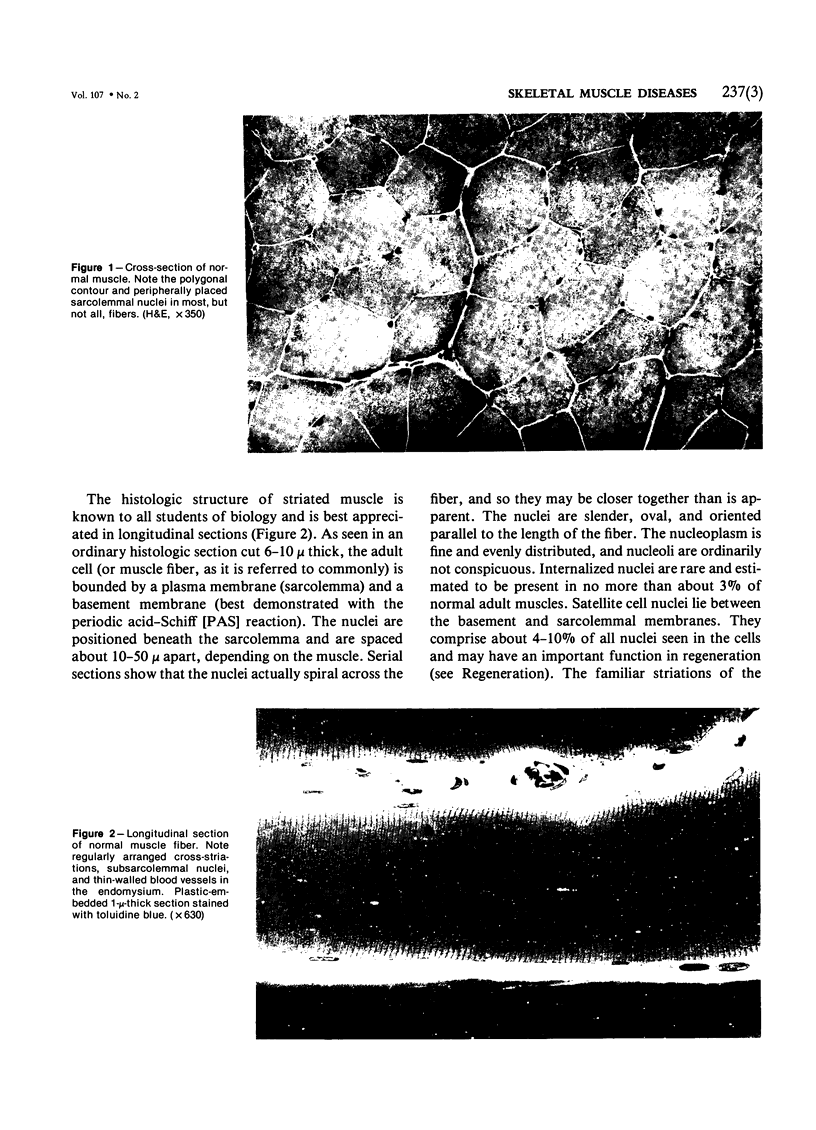
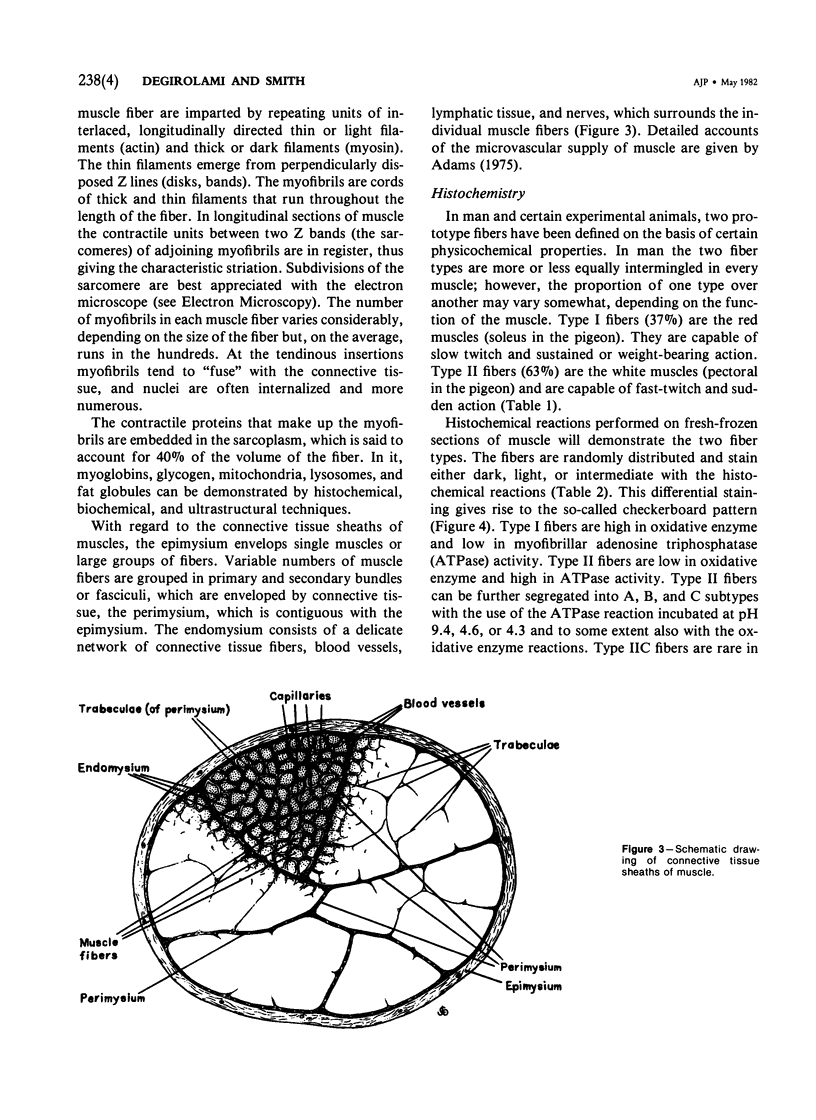
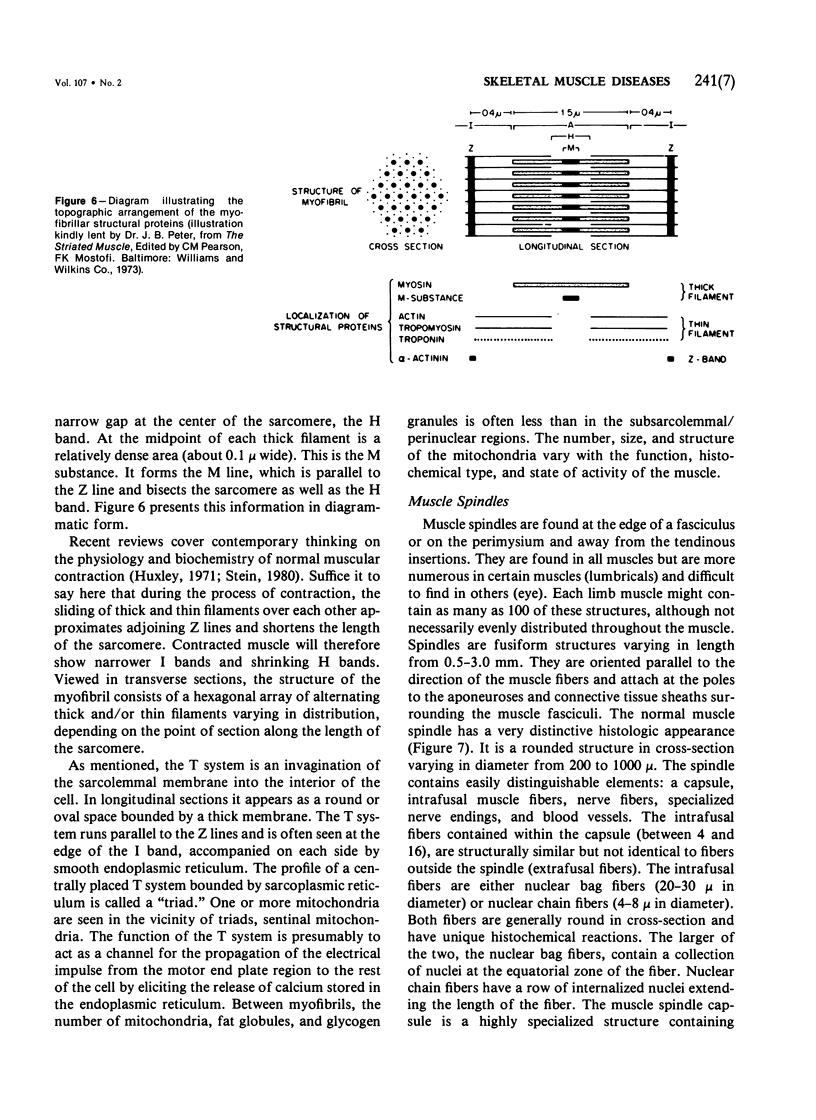
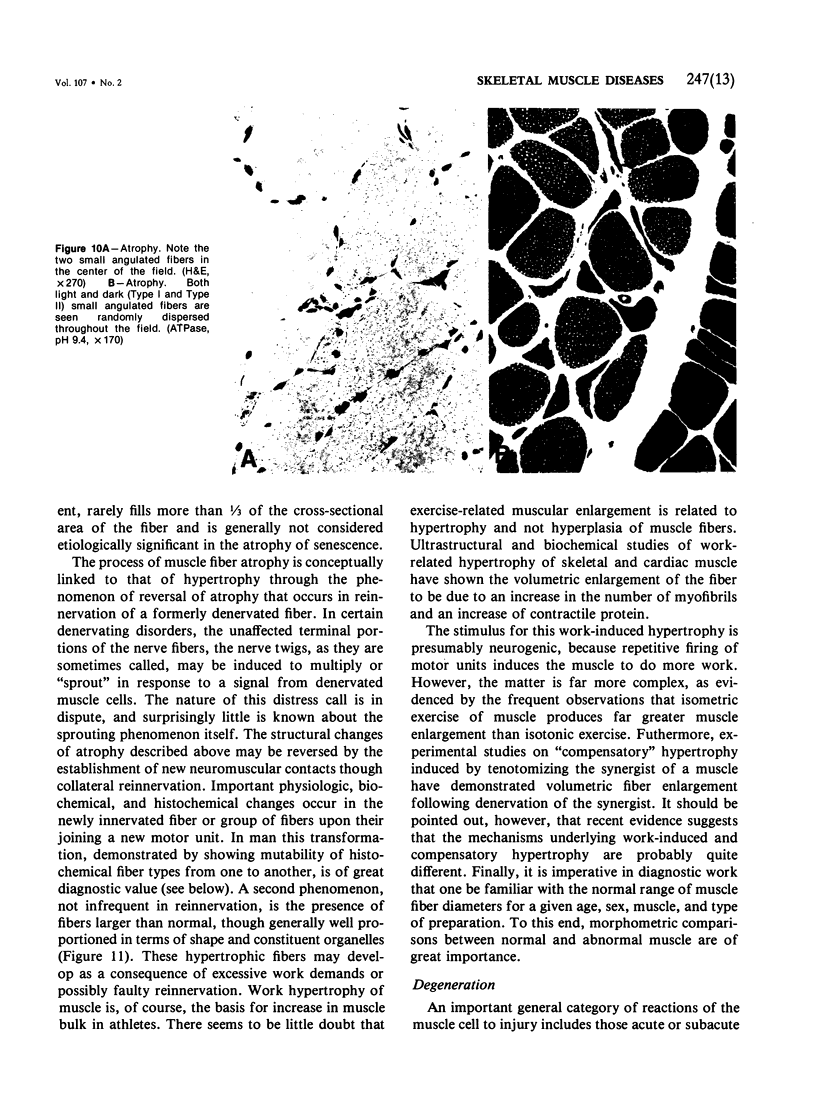
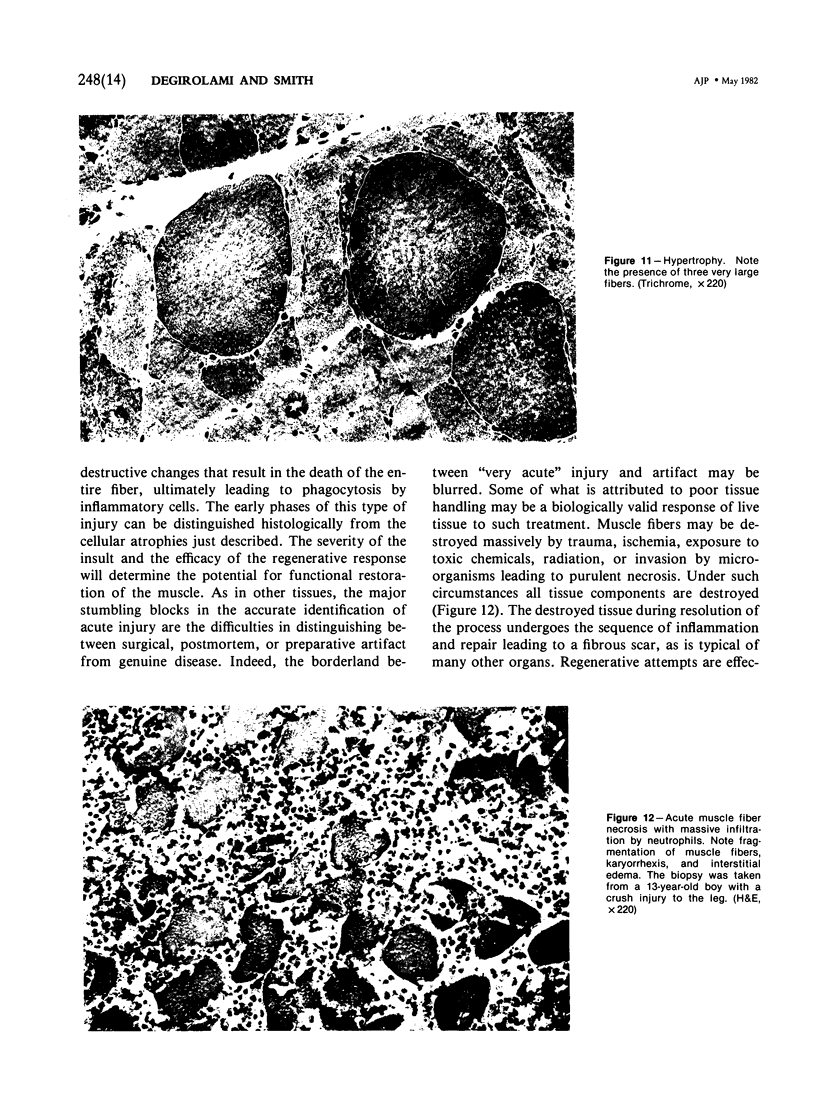
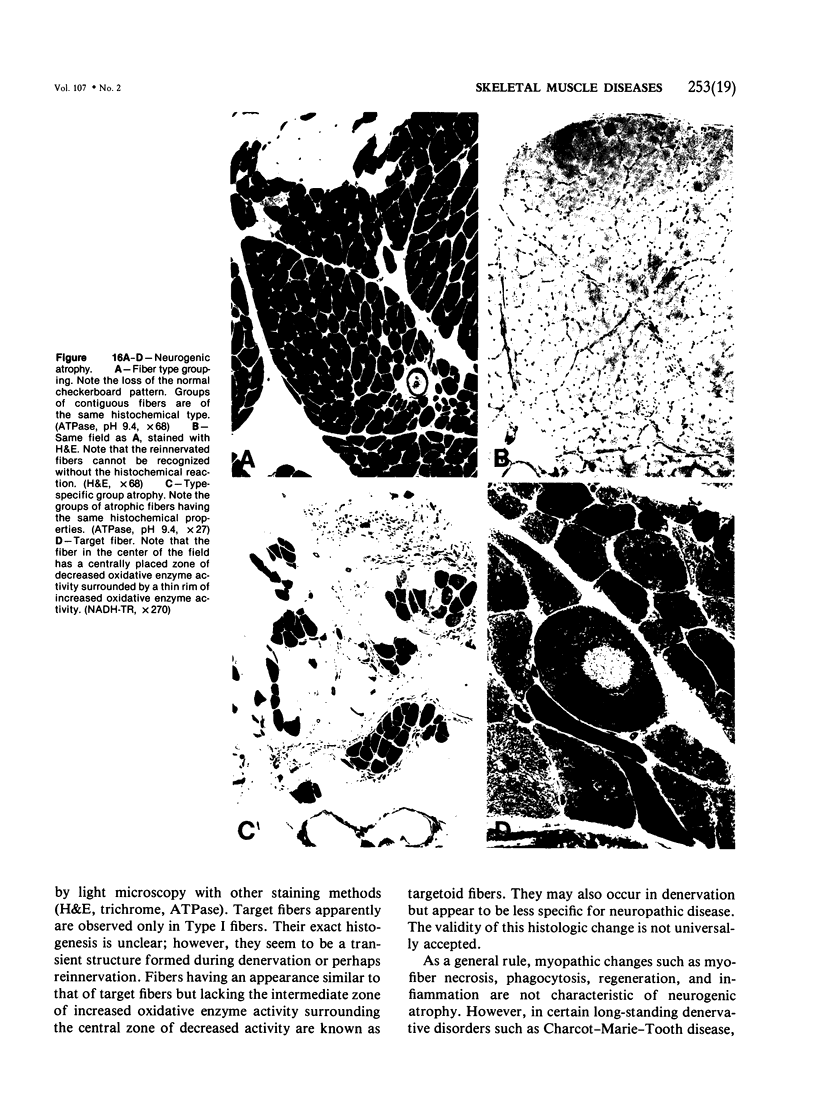
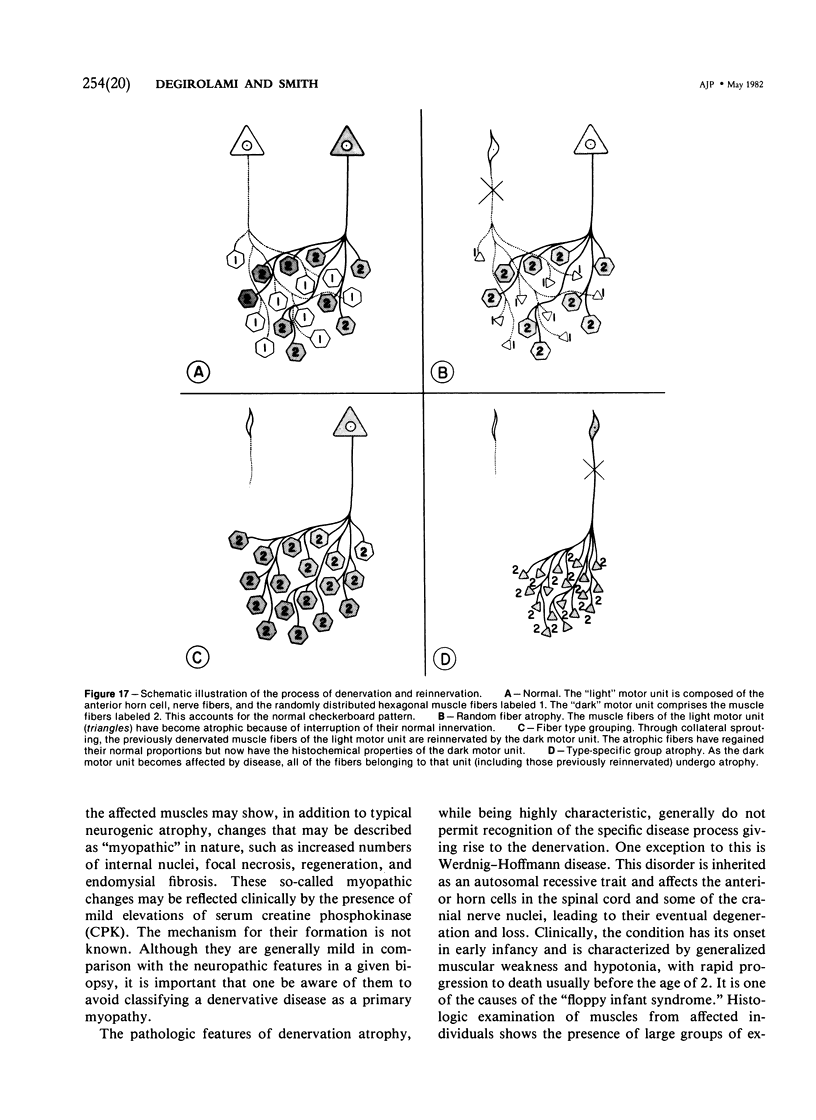
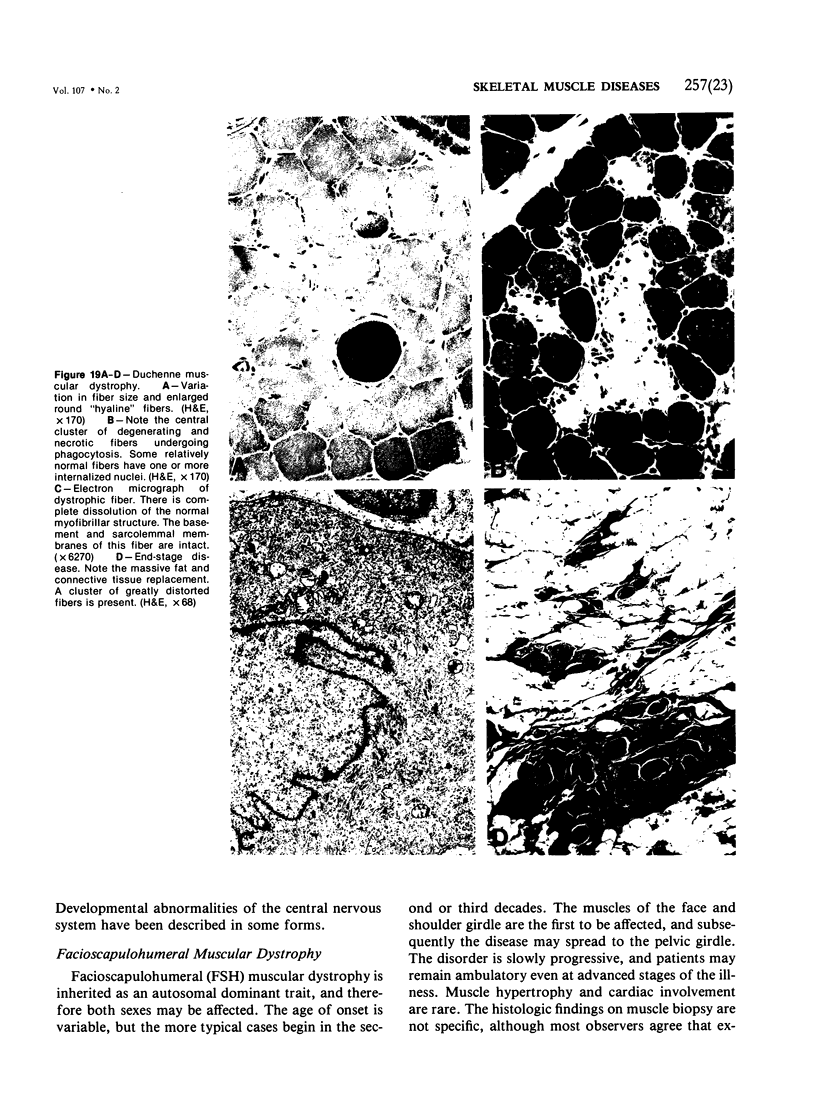
Full text
PDF




















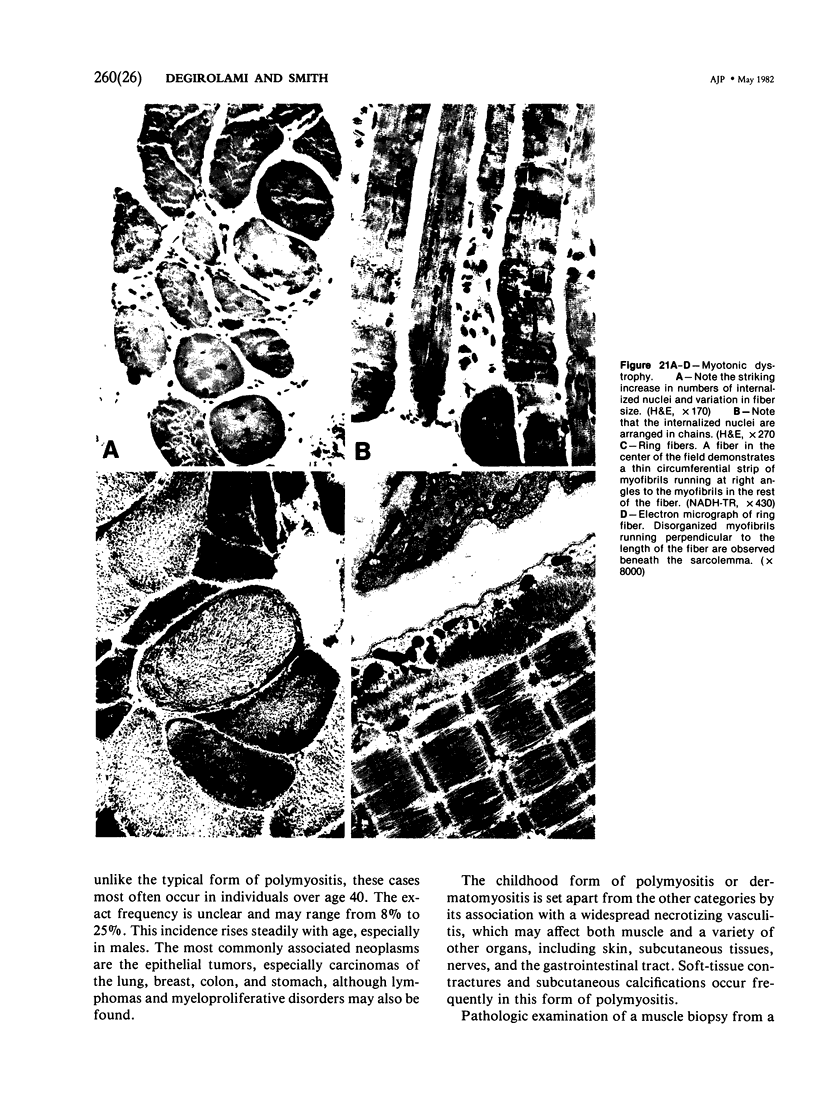

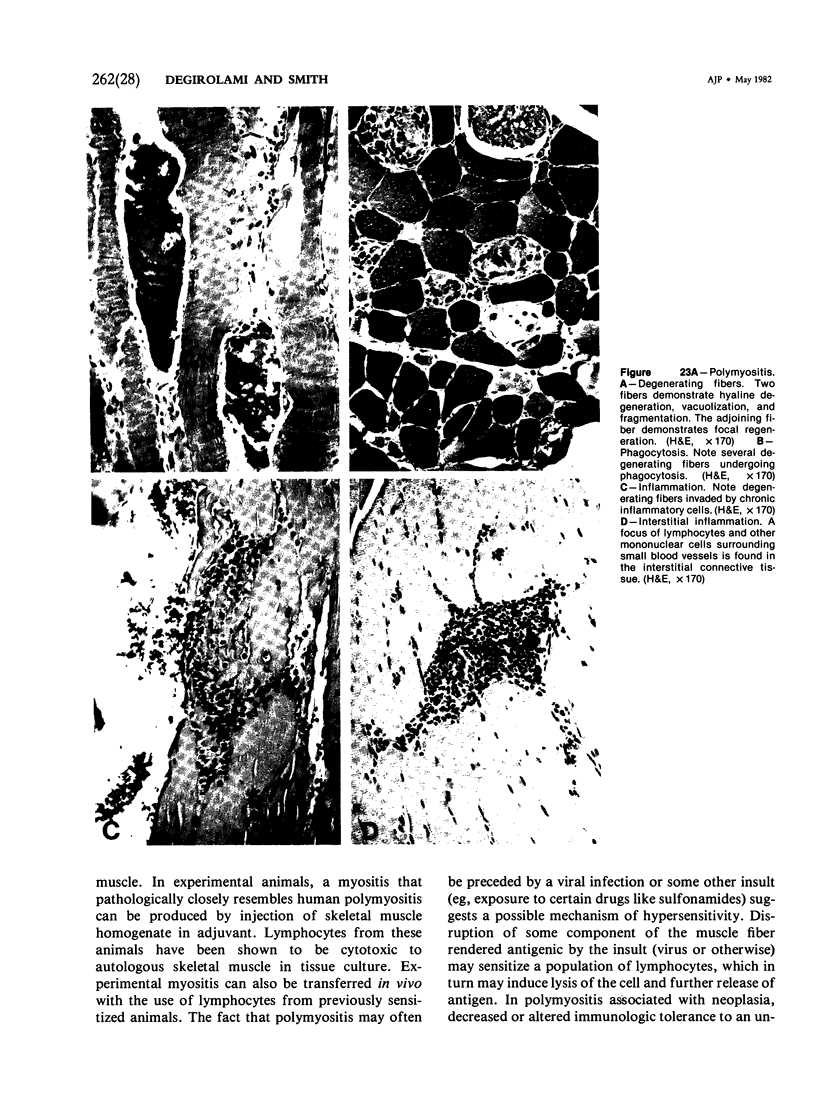






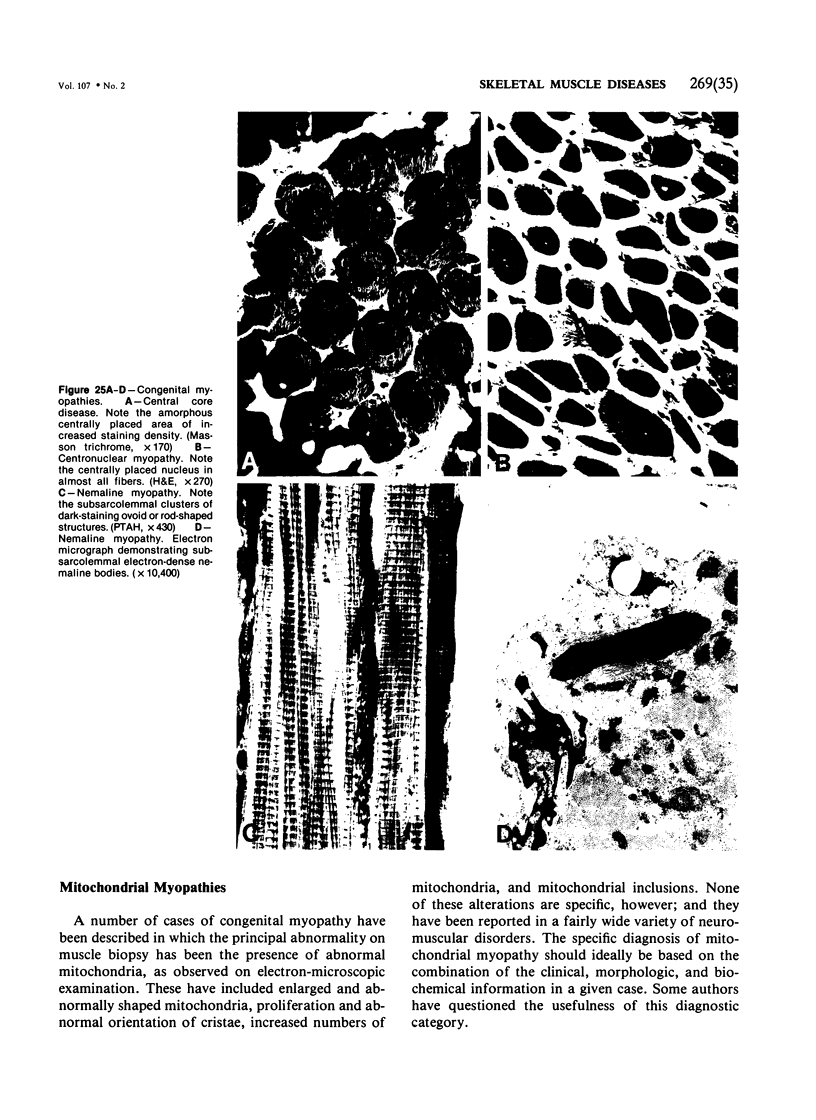







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTROM K. E., KUGELBERG E., MULLER R. Hypothyroid myopathy. Arch Neurol. 1961 Nov;5:472–482. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1961.00450170010002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afifi A. K., Aleu F. P., Goodgold J., MacKay B. Ultrastructure of atrophic muscle in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology. 1966 May;16(5):475–481. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.5.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afifi A., Zellweger H., McCormick W. F. Congenital muscular dystrophy: light and electron microscopic observations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Aug;32(4):273–280. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.4.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanas V., Engel W. K. Distinct subtypes of type I fibers of human skeletal muscle. Neurology. 1975 Sep;25(9):879–887. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.9.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Differentiation of fast and slow muscles in the cat hind limb. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:399–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS R. K., BANKER B. Q. Infantile muscular atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1961 Aug;5:140–164. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1961.00450140022003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baloh R., Cancilla P. A. An appraisal of histochemical fiber types in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology. 1972 Dec;22(12):1243–1252. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.12.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker B. Q., Girvin J. P. The ultrastructural features of the mammalian muscle spindle. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Apr;30(2):155–195. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197104000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker B. Q., Victor M. Dermatomyositis (systemic angiopathy) of childhood. Medicine (Baltimore) 1966 Jul;45(4):261–289. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196607000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Physical probes of biological membranes in studies of the muscular dystrophies. Muscle Nerve. 1980 Jan-Feb;3(1):82–97. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumli H. P., Mumenthaler M. The perifascicular atrophy factor. An aid in the histological diagnosis of polymyositis. J Neurol. 1977 Jan 13;214(2):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF02430350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenberg R. A., Pellock J. M., DiMauro S., Schotland D. L., Bonilla E., Eastwood A., Hays A., Vicale C. T., Behrens M., Chutorian A. Lumping or splitting? "Ophthalmoplegia-plus" or Kearns-Sayre syndrome? Ann Neurol. 1977 Jan;1(1):37–54. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlem J., van Gool J., Hülsmann W. C., Meijer A. E. Familial non-progressive myopathy with muscle cramps after exercise. A new disease associated with cores in the muscle fibres. Brain. 1966 Sep;89(3):569–588. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.3.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlem J., van Wijngaarden G. K., Meijer A. E., Hülsmann W. C. Neuromuscular disease with type I fiber atrophy, central nuclei, and myotube-like structures. Neurology. 1969 Jul;19(7):705–710. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.7.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 20;292(8):403–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G. Adynamia episodica hereditaria. Clinical, pathological and electrophysiological studies in an affected family. Brain. 1969;92(2):345–378. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G., Hudgson P., Gardner-Medwin D., Walton J. N. The syndrome of myosclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Aug;36(4):651–660. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.4.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G., Hudgson P., Larson P. F., Papapetropoulos T. A., Jenkison M. Structural changes in the early stages of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Aug;35(4):451–455. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G., Jones M. Z., Mussini J. M., Fawcett P. R. Becker-type muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Mar-Apr;1(2):111–132. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G., Price D. L., Watanabe C. K. Familial centronuclear myopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;33(5):687–693. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Engel W. K. The histologic diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases: a review of 79 biopsies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1966 Mar;47(3):99–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Some comments on the histochemical characterization of muscle adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Jun;17(6):431–432. doi: 10.1177/17.6.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Three "myosin adenosine triphosphatase" systems: the nature of their pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Sep;18(9):670–672. doi: 10.1177/18.9.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaplan H. Muscle pathology in rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, and polymyositis: a histochemical study. Arch Pathol. 1972 Aug;94(2):101–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Neville H. E. Reducing body myopathy. Neurology. 1972 Aug;22(8):829–840. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.8.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell B., Hughes J. T. Degeneration of muscle in association with carcinoma of the bronchus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Apr;38(4):363–370. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.4.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell B., Hughes J. T., Goldby F. S., Woods H. F. McArdle's myopathy. A report of a case with observations on the muscle ultrastructure. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Nov-Dec;9(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. J., Rebeiz J. J., Walton J. N. Myotubular, centronuclear or Peri-Centronuclear myopathy? J Neurol Sci. 1969 May-Jun;8(3):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cape C. A., Johnson W. W., Pitner S. E. Nemaline structures in polymyositis. A nonspecific pathological reaction of skeletal muscles. Neurology. 1970 May;20(5):494–502. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.5.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Karpati G. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: plasma membrane loss initiates muscle cell necrosis unless it is repaired. Brain. 1979 Mar;102(1):147–161. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Karpati G., Rothman S., Watters G. The childhood type of dermatomyositis. Neurology. 1976 Oct;26(10):952–962. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.10.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzato G., Walton J. N. The pathology of the muscle spindle. A study of biopsy material in various muscular and neuromuscular diseases. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Jul-Aug;7(1):15–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. M., Fakadej A. V. Ultrastructure of chromatolytic motoneurons and anterior spinal roots in a case of Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jul;30(3):368–379. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197107000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. M. Myxovirus-like structures in a case of human chronic polymyositis. Science. 1967 Dec 15;158(3807):1453–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3807.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. M., Nonaka I. Satellite cells and muscle regeneration in diseased human skeletal muscles. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Oct;34(1):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Climie A. R. Muscle biopsy: technic and interpretation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Dec;60(6):753–770. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coërs C., Telerman-Toppet N. Differential diagnosis of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1979 Jul;29(7):957–972. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.7.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews J., Kaiser K. K., Brooke M. H. Muscle pathology of myotonia congenita. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Aug;28(4):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. J., Fulthorpe J. J. Stages in fibre breakdown in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. An electron-microscopic study. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Feb;24(2):179–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. M., Spong F. L., Harrington J. F. McArdle's disease: lack of muscle phosphorylase. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Aug;69(2):229–235. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVere R., Bradley W. G. Polymyositis: its presentation, morbidity and mortality. Brain. 1975 Dec;98(4):637–666. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Hartwig G. B., Hays A., Eastwood A. B., Franco R., Olarte M., Chang M., Roses A. D., Fetell M., Schoenfeldt R. S. Debrancher deficiency: neuromuscular disorder in 5 adults. Ann Neurol. 1979 May;5(5):422–436. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Schotland D. L., Bonilla E., Lee C. P., Gambetti P., Rowland L. P. Progressive ophthalmoplegia, glycogen storage, and abnormal mitochondria. Arch Neurol. 1973 Sep;29(3):170–179. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490270052008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. A., Tuncbay T. O. The remote myopathy of trichinosis. Neurology. 1965 Dec;15(12):1127–1135. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.12.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Fambrough D. M. Are muscle fibers denervated in myotonic dystrophy? Arch Neurol. 1976 Jul;33(7):485–488. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500070027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Murphy S. R., Nigam M. P., Hills J. R. "Myopathic" changes in chronically denervated muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jan;16(1):14–24. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470190018002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B. Myasthenia gravis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 19;298(3):136–142. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801192980305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V., Roy S. Central core disease of muscle: clinical, histochemical and electron microscopic studies of an affected mother and child. Brain. 1970;93(1):133–146. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKBOM K., HED R., KIRSTEIN L., ASTROM K. E. MUSCULAR AFFECTIONS IN CHRONIC ALCOHOLISM. Arch Neurol. 1964 May;10:449–458. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460170019003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL W. K., CUNNINGHAM G. G. RAPID EXAMINATION OF MUSCLE TISSUE. AN IMPROVED TRICHROME METHOD FOR FRESH-FROZEN BIOPSY SECTIONS. Neurology. 1963 Nov;13:919–923. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.11.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL W. K. Muscle target fibres, a newly recognized sign of denervation. Nature. 1961 Jul 22;191:389–390. doi: 10.1038/191389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R., Young A., Wiles M. Needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in the diagnosis of myopathy and the clinical study of muscle function and repair. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 31;302(5):261–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001313020504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Angelini C., Gomez M. R. Fingerprint body myopathy, a newly recognized congenital muscle disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Jun;47(6):377–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Banker B. Q., Eiben R. M. Carnitine deficiency: clinical, morphological, and biochemical observations in a fatal case. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Apr;40(4):313–322. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Evolution and content of vacuoles in primary hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;45(11):774–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Gomez M. R., Groover R. V. Multicore disease. A recently recognized congenital myopathy associated with multifocal degeneration of muscle fibers. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Oct;46(10):666–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Gomez M. R., Seybold M. E., Lambert E. H. The spectrum and diagnosis of acid maltase deficiency. Neurology. 1973 Jan;23(1):95–106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K. Fiber-type nomenclature of human skeletal muscle for histochemical purposes. Neurology. 1974 Apr;24(4):344–348. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.4.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K. Selective and nonselective susceptibility of muscle fiber types. A new approach to human neuromuscular diseases. Arch Neurol. 1970 Feb;22(2):97–117. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480200003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K., Vick N. A., Glueck C. J., Levy R. I. A skeletal-muscle disorder associated with intermittent symptoms and a possible defect of lipid metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 26;282(13):697–704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003262821301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fardeau M., Harpey J. P., Caille B. Disproportion congénitale des différents types de fibre musculaire, avec petitesse relative des fibres de type I. Documents morphologiques concernant les biopsies musculaires prélevées chez trois membres d'une même famille. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1975 Nov;131(11):745–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel K. A., Rosser R. J. The pathology of the heart in progressive muscular dystrophy: epimyocardial fibrosis. Hum Pathol. 1976 Jul;7(4):375–386. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa K. Some observations on the skeletal musculature of aged rats. I. Histological aspects. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Jul;22(3):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa K. Some observations on the skeletal musculature of aged rats. Part 2. Fine morphology of diseased muscle fibres. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Apr;24(4):447–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GONATAS N. K., PEREZ M. C., SHY G. M., EVANGELISTA I. CENTRAL "CORE" DISEASE OF SKELETAL MUSCLE. ULTRASTRUCTURAL AND CYTOCHEMICAL OBSERVATIONS IN TWO CASES. Am J Pathol. 1965 Sep;47:503–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENFIELD J. G., CORNMAN T., SHY G. M. The prognostic value of the muscle biopsy in the floppy infant. Brain. 1958 Dec;81(4):461–484. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Thorpe C. Muscle weakness due to sarcoid myopathy. Six case reports and an evalation of steroid therapy. Neurology. 1972 Sep;22(9):917–928. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.9.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Dunn R. A. Ultrastructural and cytochemical features of mammalian skeletal muscle fibres following denervation. J Cell Sci. 1973 Mar;12(2):525–547. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.2.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldspink D. F. The effects of denervation on protein turnover of rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):71–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1560071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Shy G. M., Godfrey E. H. Nemaline myopathy. The origin of nemaline structures. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 10;274(10):535–539. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603102741002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E. Neurotrophic relations. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:177–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller R. G., Drachman D. B. Alcoholic rhabdomyolysis: an experimental model in the rat. Science. 1980 Apr 25;208(4442):412–415. doi: 10.1126/science.7189294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway P. W., Engel W. K., Zellweger H. Experimental myopathy after microarterial embolization; comparison with childhood x-linked pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy. Arch Neurol. 1970 Apr;22(4):365–378. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480220079011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. D. Skeletal-muscle regeneration. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 6;284(18):1033–1034. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105062841812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazama R., Tsujihata M., Mori M., Mori K. Muscular dystrophy in six young girls. Neurology. 1979 Nov;29(11):1486–1491. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.11.1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffner R. R., Jr, Armbrustmacher V. W., Earle K. M. Focal myositis. Cancer. 1977 Jul;40(1):301–306. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197707)40:1<301::aid-cncr2820400142>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffner R. R., Jr Electron microscopy of disorders of skeletal muscle. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;5(5):338–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffner R. R., Jr Myopathy of embolic origin in patients with carcinoma. Neurology. 1971 Aug;21(8):840–846. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett R. H., Brownell B. Granulomatous myopathy: its relationship to sarcoidosis and polymyositis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Nov;38(11):1090–1099. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.11.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W. Mechanisms of muscular hypertrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Mar;45(2-3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins I. J., Lindsey J. R., Ford F. R. Nemaline myopathy. A long-term clinicopathologic study of affected mother and daughter. Brain. 1966 Jun;89(2):299–310. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Jr, Price H. M., Blumberg J. M., Pearson C. M. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Electromicroscopic changes in the sarcoplasm. Neurology. 1966 Mar;16(3):242–256. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.3.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgson P., Fulthorpe J. J. The pathology of type II skeletal muscle glycogenosis. A light and electron-microscopic study. J Pathol. 1975 Jul;116(3):139–147. doi: 10.1002/path.1711160303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. T., Brownell B. Ultrastructure of muscle in Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Mar-Apr;8(2):361–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. T., Esiri M. M. Ultrastructural studies in human polymyositis. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Jul;25(3):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huijing F. Glycogen metabolism and glycogen-storage diseases. Physiol Rev. 1975 Oct;55(4):609–658. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1975.55.4.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs H., Heffron J. J., Badenhorst M. Central core disease. A correlated genetic, histochemical, ultramicroscopic, and biochemical study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Dec;38(12):1177–1186. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.12.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerusalem F., Engel A. G., Gomez M. R. Sarcotubular myopathy. A newly recognized, benign, congenital, familial muscle disease. Neurology. 1973 Sep;23(9):897–906. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.9.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerusalem F., Engel A. G., Peterson H. A. Human muscle fiber fine structure: morphometric data on controls. Neurology. 1975 Feb;25(2):127–134. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEARNS T. P., SAYRE G. P. Retinitis pigmentosa, external ophthalmophegia, and complete heart block: unusual syndrome with histologic study in one of two cases. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Aug;60(2):280–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILOH L. G., NEVIN S. Progressive dystrophy of the external ocular muscles (ocular myopathy). Brain. 1951;74(2):115–143. doi: 10.1093/brain/74.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Carpenter S., Engel A. G., Watters G., Allen J., Rothman S., Klassen G., Mamer O. A. The syndrome of systemic carnitine deficiency. Clinical, morphologic, biochemical, and pathophysiologic features. Neurology. 1975 Jan;25(1):16–24. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Carpenter S., Nelson R. F. Type I muscle fibre atrophy and central nuclei. A rare familial neuromuscular disease. J Neurol Sci. 1970 May;10(5):489–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korényi-Both A., Smith B. H., Baruah J. K. McArdle's syndrome. Fine structural changes in muscle. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Sep 26;40(1):11–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00688569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovarsky J., Schochet S. S., Jr, McCormick W. F. The significance of target fibers: a clinicopathologic review of 100 patients with neurogenic atrophy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jun;59(6):790–797. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.6.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E., Fiehn W., Seiler D., Schröder J. M. The autosomal recessive (Becker) form of myotonia congenita. Muscle Nerve. 1979 Mar-Apr;2(2):109–117. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzer R. B., Rowland L. P., Ranney H. M. Muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency. Arch Neurol. 1967 Nov;17(5):512–523. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470290066009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzer R. B., Shearn M. A., Satya-Murti S. Eosinophilic polymyositis. Ann Neurol. 1977 Jan;1(1):65–71. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legato M. J. Sarcomerogenesis in human myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1970 Dec;1(4):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(70)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manz H. J. Pathology of skeletal muscle: principles of reaction patterns and histochemistry and experience with 195 biopsies. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1980;386(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00432641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markesbery W. R. Pathology of muscular dystrophy and related disorders. Adv Neurol. 1977;17:175–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A. J., McNeer K. W., Hay S. H., Watson A. Extraocular muscles: morphogenetic study in humans. Light microscopy and ultrastructural features. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 May 16;38(2):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00688553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L., Walton J. N. Coxsackie virus-like particles in skeletal muscle from a case of polymyositis. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Dec;11(6):593–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara S., Mair W. G. Ultrastructural changes in polymyositis. Brain. 1979 Dec;102(4):701–725. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mc Comas A. J., Sica R. E., Currie S. Muscular dystrophy: evidence for a neural factor. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1263–1264. doi: 10.1038/2261263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. Y., Kuncl R. W., Yang V. Incidence of Z band streaming and myofibrillar disruptions in skeletal muscle from healthy young people. Neurology. 1976 Sep;26(9):853–857. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.9.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell J. R., Engel W. K. The fine structure of type II muscle fiber atrophy. Neurology. 1971 Apr;21(4):358–365. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.4.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel D., Tommasi M., Rousset H., Bady B., Schott B. Myosite granulomateuse au cours d'une collagénose (une observation) et d'un dysgerminome suprasellaire (une observation). Rev Neurol (Paris) 1979 Jan;135(1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikol F., Stagel M., Mikol J. Etude de cinq cas de myopathie oculaire. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1976 May;132(5):325–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokri B., Engel A. G. Duchenne dystrophy: electron microscopic findings pointing to a basic or early abnormality in the plasma membrane of the muscle fiber. Neurology. 1975 Dec;25(12):1111–1120. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.12.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Piper D., Cancilla P., Mednick J. Inflammatory myopathy with facioscapulohumeral distribution. Neurology. 1972 Apr;22(4):335–347. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.4.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Thompson L. R., Coleman R. F. Centronuclear ("myotubular") myopathy. Arch Neurol. 1969 Feb;20(2):120–131. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480080020002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Woods R., Fowler W., Pearson C. M. Neurogenic muscular atrophy of infancy with prolonged survival. The variable course of Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease. Brain. 1969 Mar;92(1):9–24. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard D. B., Haddad H., Blain J. G., Beaudry R., Devroede G., Massé S. Granulomatous myositis and myopathy associated with crohn's colitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 7;295(15):818–819. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610072951506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Brunner N. G., Grob D. Idiopathic giant cell polymyositis. Report of a case and review of the syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1974 Jul;31(1):27–30. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490370053007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris F. H., Jr, Panner B. J. Hypothyroid myopathy. Clinical, electromyographical, and ultrastructural observations. Arch Neurol. 1966 Jun;14(6):574–589. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470120006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. Factors affecting the activity of adenosine triphosphatase and other phosphatases as measured by histochemical techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):161–169. doi: 10.1177/3.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):170–195. doi: 10.1177/3.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Histopathological features of muscle in the preclinical stages of muscular dystrophy. Brain. 1962 Mar;85:109–120. doi: 10.1093/brain/85.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson V. H., Hill T. R., Fletcher P. J., Heron J. R. Central core disease: clinical and pathological evidence of progression within a family. Brain. 1979 Sep;102(3):581–594. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. H., Carter C. O., Wilson J. The genetic identity of acute infantile spinal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1973 Sep;96(3):463–470. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.3.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. M., Bohan A. The spectrum of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Med Clin North Am. 1977 Mar;61(2):439–457. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. M. Polymyositis. Annu Rev Med. 1966;17:63–82. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.17.020166.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino C., Franzini-Armstrong C. Recent contributions of electron microscopy to the study of normal and pathological muscle. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1969;7:139–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett J. B., Layzer R. B., Levin S. R., Scheider V., Campbell M. J., Sumner A. J. Neuromuscular complications of acromegaly. Neurology. 1975 Jul;25(7):638–645. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.7.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett J. B. Nerve terminals are as metabolically different as the muscle fibers they innervate. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):927–928. doi: 10.1126/science.7434009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plishker G. A., Gitelman H. J., Appel S. H. Myotonic muscular dystrophy: altered calcium transport in erythrocytes. Science. 1978 Apr 21;200(4339):323–325. doi: 10.1126/science.635589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porro R. S., Webster H. F., Tobin W. Needle biopsy of skeletal muscle: a phase and electron microscopic evaluation of its usefulness in the study of muscle dsease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1969 Apr;28(2):229–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price H. M., Gordon G. R., Munsat T. L., Pearson C. M. Myopathy with atypical mitochondria in type I skeletal muscle fibers. A histochemical and ultrastructural study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jul;26(3):475–497. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196707000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosman N. P., Kakulas B. A. Mental deficiency associated with muscular dystrophy. A neuropathological study. Brain. 1966 Dec;89(4):769–788. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.4.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosman N. P., Rebeiz J. J. The cerebral defect and myopathy in myotonic dystrophy. A comparative clinicopathological study. Neurology. 1967 Nov;17(11):1106–1112. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.11.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. P. Biochemistry of muscle membranes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1980 Jan-Feb;3(1):3–20. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. P. Pathogenesis of muscular dystrophies. Arch Neurol. 1976 May;33(5):315–321. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500050001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. Alcoholic myopathy in heart and skeletal muscle. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):28–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCARPELLI D. G., HESS R., PEARSE A. G. The cytochemical localization of oxidative enzymes. I. Diphosphopyridine nucleotide diaphorase and triphosphopyridine nucleotide diaphorase. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):747–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R., HAMMAKER L. Hereditary absence of muscle phosphorylase (McArdle's syndrome). N Engl J Med. 1961 Feb 2;264:223–225. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196102022640504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHY G. M., ENGEL W. K., SOMERS J. E., WANKO T. NEMALINE MYOPATHY. A NEW CONGENITAL MYOPATHY. Brain. 1963 Dec;86:793–810. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.4.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHY G. M., GONATAS N. K. HUMAN MYOPATHY WITH GIANT ABNORMAL MITOCHONDRIA. Science. 1964 Jul 31;145(3631):493–496. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3631.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltis L. M., Mendell J. R. The fine structural differences in human muscle fiber types based on peroxidatic activity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Oct;33(5):632–640. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197410000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Hanzlíková V. On the mechanism of compensatory hypertrophy in skeletal muscles. Experientia. 1970;26(2):152–153. doi: 10.1007/BF01895548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochet S. S., Jr, McCormick W. F., Zellweger H. Type IV glycogenosis (amylopectinosis). Light and electron microscopic observations. Arch Pathol. 1970 Oct;90(4):354–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochet S. S., Jr, Zellweger H., Ionasescu V., McCormick W. F. Centronuclear myopathy: disease entity or a syndrome? Light- and electron-microscopic study of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Jun;16(2):215–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq S. A., Gorycki M. A., Asiedu S. A., Milhorat A. T. Tenotomy. Effect on the fine structure of the soleus of the rat. Arch Neurol. 1969 Jun;20(6):625–633. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480120071006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq S. A., Milhorat A. T., Gorycki M. A. Fine structure of human muscle in neurogenic atrophy. Neurology. 1967 Oct;17(10):934–948. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.10.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shy G. M., Gonatas N. K., Perez M. Two childhood myopathies with abnormal mitochondria. I. Megaconial myopathy. II. Pleoconial myopathy. Brain. 1966 Mar;89(1):133–158. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. Z., Gruener R., Anderson R. M. External intercostal muscle biopsy. Arch Neurol. 1975 Nov;32(11):779–780. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490530101013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. Z., Payne C. M., Hannapel L. K. Acromegaly: histochemical and electron microscopic changes in deltoid and intercostal muscle. Neurology. 1974 Jun;24(6):589–593. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.6.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stonnington H. H., Engel A. G. Normal and denervated muscle. A morphometric study of fine structure. Neurology. 1973 Jul;23(7):714–724. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.7.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swash M., Fox K. P. The pathology of the muscle spindle in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Sep;29(1):17–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swash M., Schwartz M. S., Sargeant M. K. Pathogenesis of longitudinal splitting of muscle fibres in neurogenic disorders and in polymyositis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Mar-Apr;4(2):99–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb00551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennyson V. M., Kremzner L. T., Brzin M. Electron microscopic-cytochemical and biochemical studies of acetylcholinesterase activity in denervated muscle of rabbits. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Mar-Apr;36(2):245–275. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197703000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urich H., Wilkinson M. Necrosis of muscle with carcinoma: myositis or myopathy? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Jun;33(3):398–407. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VICTOR M., HAYES R., ADAMS R. D. Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. A familial disease of late life characterized by dysphagia and progressive ptosis of the evelids. N Engl J Med. 1962 Dec 20;267:1267–1272. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196212202672501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. N., Irving D., Tomlinson B. E. Spinal cord limb motor neurons in dystrophia myotonica. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Nov;34(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Engel W. K. Vascular deposits of immunoglobulin and complement in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 17;286(7):333–338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202172860701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikman-Coffelt J., Parmley W. W., Mason D. T. The cardiac hypertrophy process. Analyses of factors determining pathological vs. physiological development. Circ Res. 1979 Dec;45(6):697–707. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.6.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., Afifi A., McCormick W. F., Mergner W. Severe congenital muscular dystrophy. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Dec;114(6):591–602. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090270047003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijngaarden G. K., Bethlem J. Benign infantile spinal muscular atrophy. A prospective study. Brain. 1973;96(1):163–170. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]