Abstract
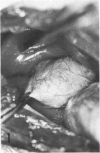
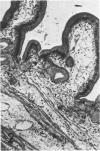
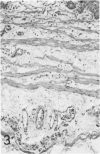
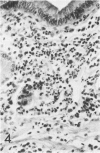
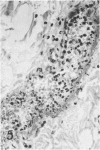
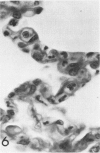
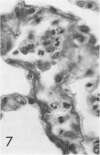
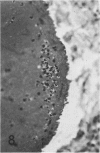
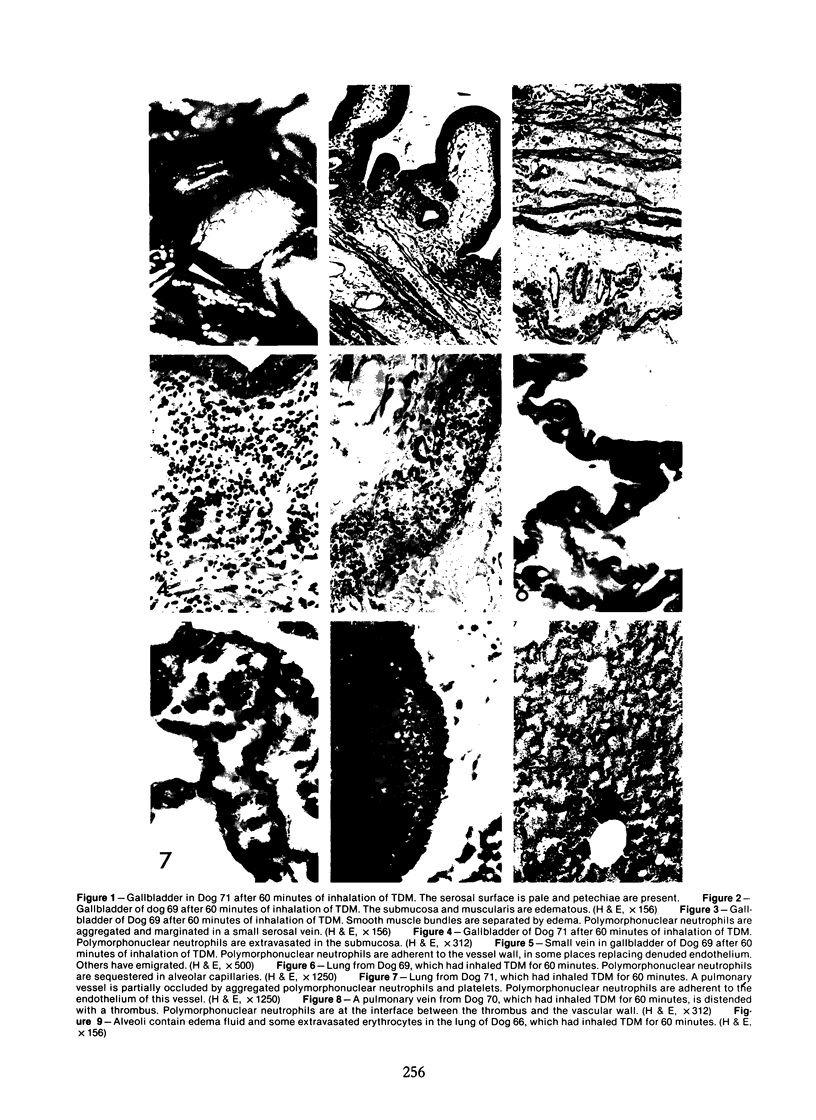
In previous studies in this laboratory it was demonstrated that 1) constituents of the water-soluble phase of cigarette smoke condensate can activate Hageman-factor-dependent pathways of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation; and 2) that in vivo activation of Hageman-factor-dependent pathways by intravenous injection of plant polyphenols in dogs and AFrican Green monkeys can induce acute acalculous cholecystitis and alveolitis. The purpose of this communication is to report that inhalation of the water-soluble, nondialyzable constituents of cigarette smoke condensate, or "tar," can activate Hageman-factor-dependent pathways in the dog and induce acute acalculous cholecystitis, pneumonitis, and the formation of thrombi in branches of pulmonary vessels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker C. G., Dubin T. Activation of factor XII by tobacco glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):457–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Dubin T., Glenn F. Induction of acute cholecystitis by activation of factor XII. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):81–90. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Van Hamont N., Wagner M. Tobacco, cocoa, coffee, and ragweed: cross-reacting allergens that activate factor-XII-dependent pathways. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):861–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Activation of the classical pathway of complement by Hageman factor fragment. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):665–676. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn F., Becker C. G. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. An increasing entity. Ann Surg. 1982 Feb;195(2):131–136. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198202000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Majno G. Endothelial changes induced by arterial spasm. Am J Pathol. 1981 Mar;102(3):346–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVALCIK V. THE RESPONSE OF THE ISOLATED DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS TO OXYGEN AND ANOXIA. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:185–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., CRUM J. D. ACTIVATION OF HAGEMAN FACTOR BY SOLUTIONS OF ELLAGIC ACID. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Mar;63:359–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Despland E., Scott C. F., Boxer L. A., Colman R. W. Purified human plasma kallikrein aggregates human blood neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1199–1202. doi: 10.1172/JCI110557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Giclas P. C., Henson P. M. Chemotactic activity generated from the fifth component of complement by plasma kallikrein of the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]