Abstract
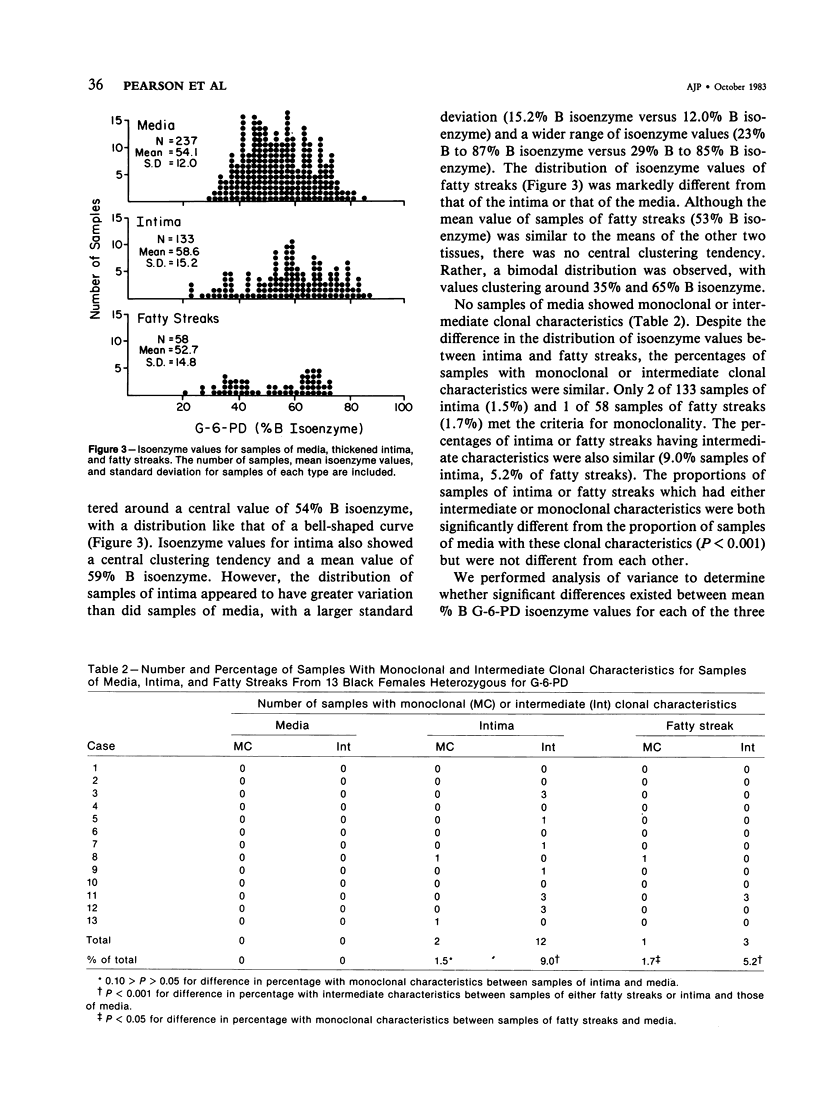
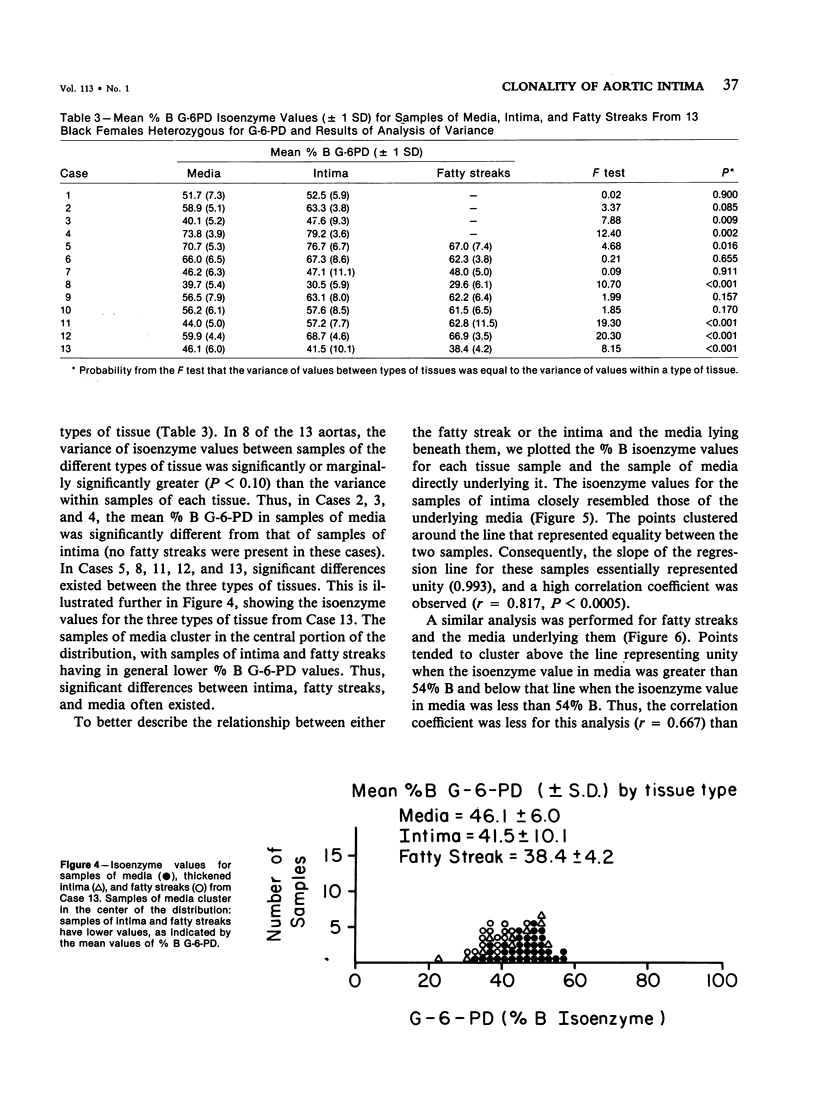
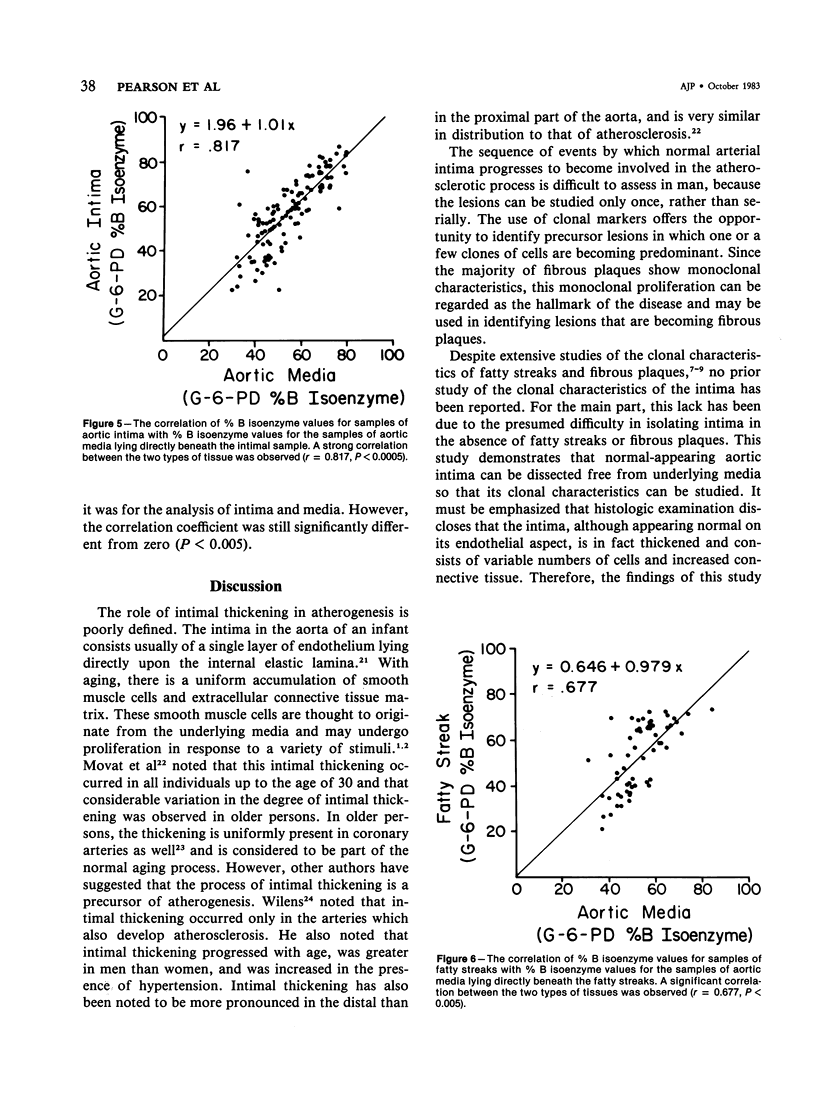
The clonal characteristics of normal-appearing but thickened aortic intima were studied by the use of the isoenzymes of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) as cellular markers in females heterozygous for this X-linked enzyme. Isoenzyme patterns of 133 samples of intima were compared with those of 237 samples of underlying media and with those of 58 fatty streaks dissected from the same aortas. The proportion of samples of intima and fatty streaks with monoclonal or intermediate characteristics was the same, but both had more monoclonal or intermediate samples than underlying media (P less than 0.05). However, samples of intima showed a central clustering tendency of isoenzyme values similar to that of underlying media, while values from fatty streaks showed a bimodal distribution suggesting the presence of cell populations in the process of becoming monoclonal. The data suggest that clonal proliferation may begin in normal-appearing intima but that it progresses through a fatty streak stage before proceeding to the monoclonal fibrous plaque.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benditt E. P., Benditt J. M. Evidence for a monoclonal origin of human atherosclerotic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1753–1756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P. Implications of the monoclonal character of human atherosclerotic plaques. Beitr Pathol. 1976 Sep;158(4):405–416. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(76)80137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. The origin and development of human tumors studied with cell markers. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 4;291(1):26–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407042910109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEER J. C., McGILL H. C., Jr, STRONG J. P. The fine structure of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1961 Mar;38:263–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geer J. C., McGill H. C., Jr, Robertson W. B., Strong J. P. Histologic characteristics of coronary artery fatty streaks. Lab Invest. 1968 May;18(5):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geer J. C., Webster W. S. Morphology of mesenchymal elements of normal artery, fatty streaks, and plaques. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;43(0):9–33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3243-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haust M. D. The morphogenesis and fate of potential and early atherosclerotic lesions in man. Hum Pathol. 1971 Mar;2(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(71)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder D., Gartler S. M. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mosaicism: utilization as a cell marker in the study of leiomyomas. Science. 1965 Oct 1;150(3692):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3692.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., MORE R. H., HAUST M. D. The diffuse intimal thickening of the human aorta with aging. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1023–1031. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill H. C., Jr Fatty streaks in the coronary arteries and aorta. Lab Invest. 1968 May;18(5):560–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro M. R., Eggen D. A. Topography of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries. Lab Invest. 1968 May;18(5):586–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIOR J. T., JONES D. B. Structural alterations within the aortic intima in infancy and childhood. Am J Pathol. 1952 Sep-Oct;28(5):937–951. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. A., Dillman J. M., Solex K., Heptinstall R. H. Clonal markers in the study of the origin and growth of human atherosclerotic lesions. Circ Res. 1978 Jul;43(1):10–18. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. A., Dillman J. M., Solez K., Heptinstall R. H. Clonal characteristics of cutaneous scars and implications for atherogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jan;102(1):49–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. A., Dillman J. M., Solez K., Heptinstall R. H. Evidence for two populations of fatty streaks with different roles in the atherogenic process. Lancet. 1980 Sep 6;2(8193):496–498. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91831-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. A., Wang B. A., Solez K., Heptinstall R. H. Clonal characteristics of fibrous plaques and fatty streaks from human aortas. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):379–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. Atherosclerosis and the arterial smooth muscle cell: Proliferation of smooth muscle is a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1332–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):420–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ C. J., MITCHELL J. R. Observations on localization of arterial plaques. Circ Res. 1962 Jul;11:63–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRONG J. P., McGILL H. C., Jr The natural history of coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1962 Jan;40:37–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B. Molecular interactions in human atherosclerotic plaques. Am J Pathol. 1977 Mar;86(3):665–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stary H. C. Proliferation of arterial cells in atherosclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;43(0):59–81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3243-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. A., Reiner J. M., Janakidevi K., Florentin R. A., Lee K. T. Population dynamics of arterial cells during atherogenesis. X. Study of monotypism in atherosclerotic lesions of black women heterozygous for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD). Exp Mol Pathol. 1979 Dec;31(3):367–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(79)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILENS S. L. The nature of diffuse intimal thickening of arteries. Am J Pathol. 1951 Sep-Oct;27(5):825–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]