Abstract
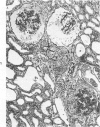
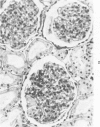
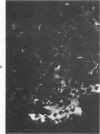
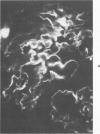
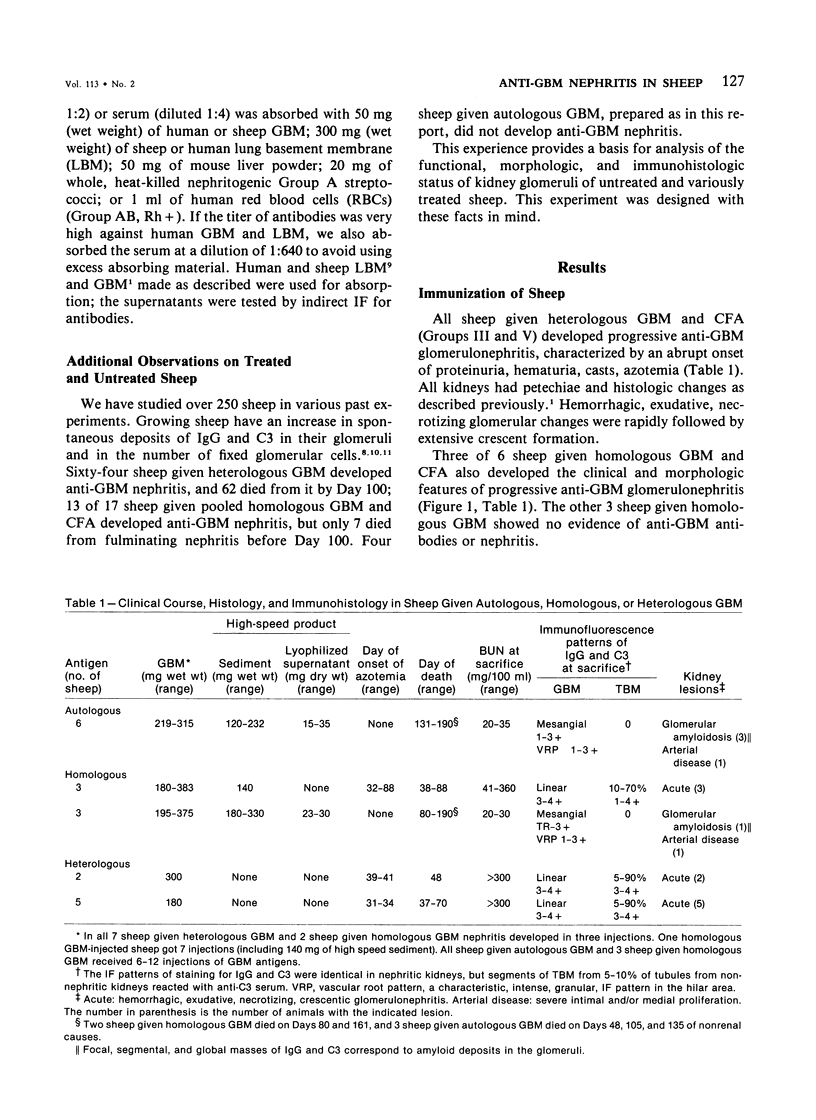
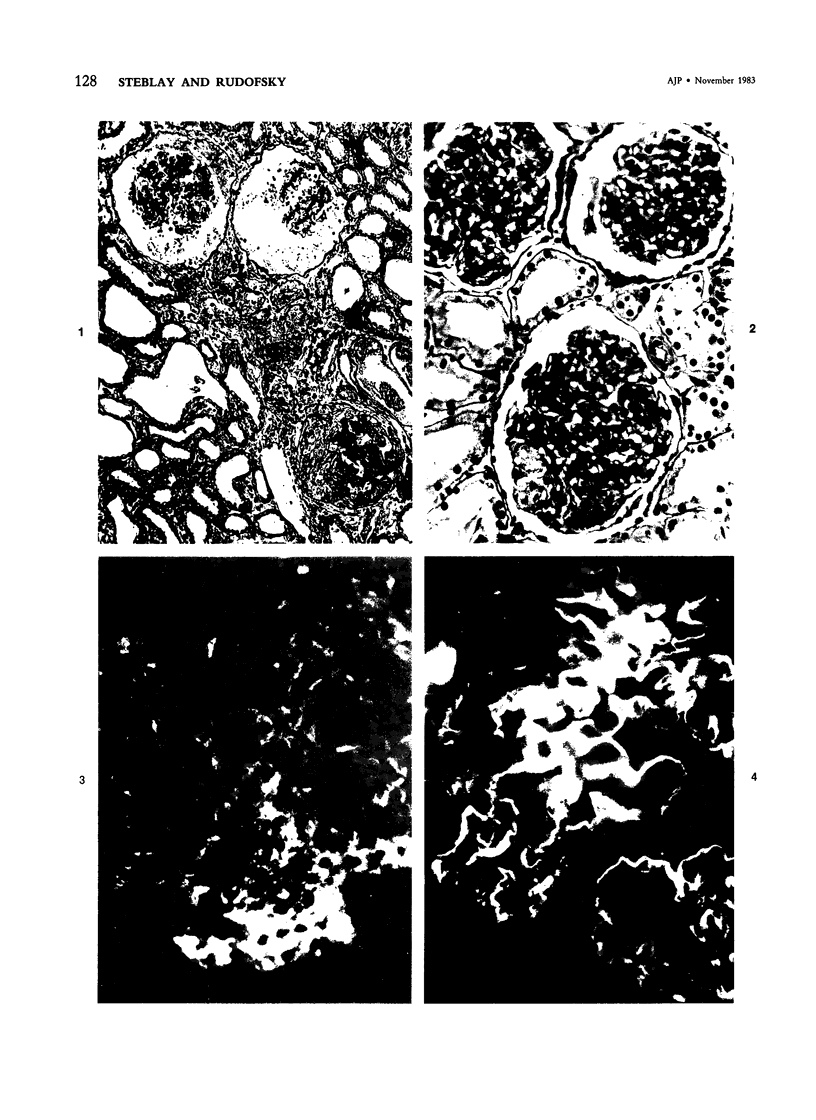
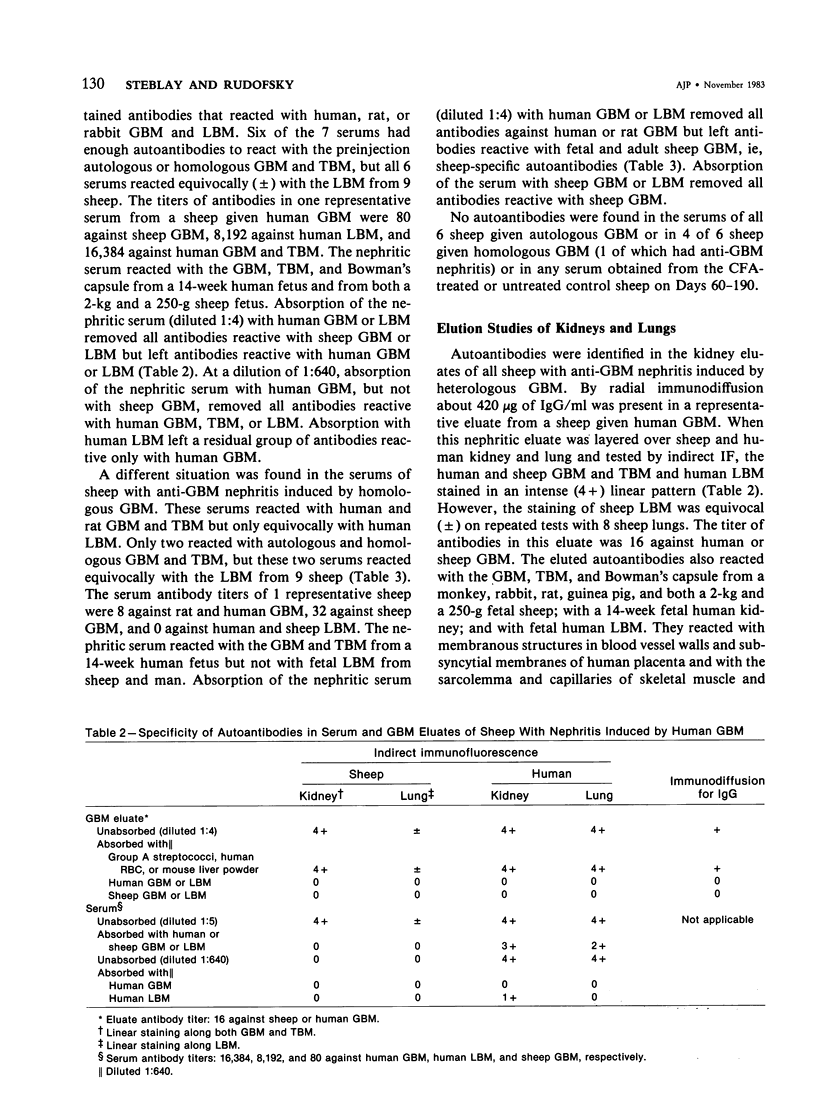
The effects of injecting human, rabbit, rat, or single-kidney homologous glomerular basement membrane (GBM) or autologous GBM, each in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), into 15- to 18-month-old sheep are compared. All sheep receiving heterologous GBM and 3 of 6 sheep receiving homologous GBM had anti-GBM nephritis, but such sheep did not bind autoantibodies or have Goodpasturelike lesions in their lungs. Sheep given injections of human GBM had autoantibodies to antigenic determinants shared by fetal or adult sheep and human GBM, by lung basement membranes, and by certain nonvascular basement membranes. Sheep given homologous GBM had two populations of autoantibodies: one was neither species- nor organ-specific; the other was sheep-specific. No sheep given autologous GBM had any evidence of anti-GBM autoantibodies or nephritis. Their kidneys were indistinguishable by histologic, immunohistologic, and functional studies from CFA-treated controls. Thus, sheep seem very tolerant to autologous GBM. These findings suggest that human anti-GBM nephritis may occur if the GBM is altered so that it becomes cross-reacting and induces autoantibodies, as does homologous GBM.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jennings L., Roholt O. A., Pressman D., Blau M., Andres G. A., Brentjens J. R. Experimental anti-alveolar basement membrane antibody-mediated pneumonitis. I. The role of increased permeability of the alveolar capillary wall induced by oxygen. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeraj K., Michael A. F., Fish A. J. Immunologic similarities between Goodpasture's and Steblay's antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. The chemistry and structure of basement membranes. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Aug;12(4):427–443. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous glomerulonephritis in sheep. Lab Invest. 1966 Jul;15(7):1279–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Dixon F. J. Transfer of ovine experimental allergic glomerulonephritis (EAG) with serum. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):431–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Characterization of human anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies eluted from glomerulonephritic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):308–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI106240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Immunoreactive basement membrane antigens in normal human urine and serum. J Exp Med. 1969 Dec 1;130(6):1395–1409. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W. Glomerulonephritis induced in sheep by injections of heterologous glomerular basement membrane and Freund's complete adjuvant. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:253–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W. Animal model of human disease: anti-glomerular-basement-membrane glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1979 Sep;96(3):875–878. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W., Rudofsky U. H. Experimental autoimmune antiglomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis. I. The effects of injecting sheep with human, homologous or autologous lung basement membranes and complete Freund's adjuvant. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W., Rudofsky U. An experimental model relevant to recurrent autoimmune glomerulonephritis in transplanted human kidneys. Transplant Proc. 1969 Mar;1(1):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W., Rudofsky U. Autoimmune glomerulonephritis induced in sheep by injections of human lung and Freund's adjuvant. Science. 1968 Apr 12;160(3824):204–206. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3824.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W., Rudofsky U. In vitro and in vivo properties of autoantibodies eluted from kidneys of sheep with autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Nature. 1968 Jun 29;218(5148):1269–1271. doi: 10.1038/2181269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J., Feldman J. D. Experimental allergic glomerulonephritis induced in the rabbit with homologous renal antigens. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):163–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Analysis of autoimmunity through experimental models of thyroiditis and allergic encephalomyelitis. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:159–273. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby W. F., Dixon F. J. Experimental hemorrhagic pneumonitis produced by heterologous anti-lung antibody. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):28–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1973 Feb;3(2):74–89. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]