Abstract
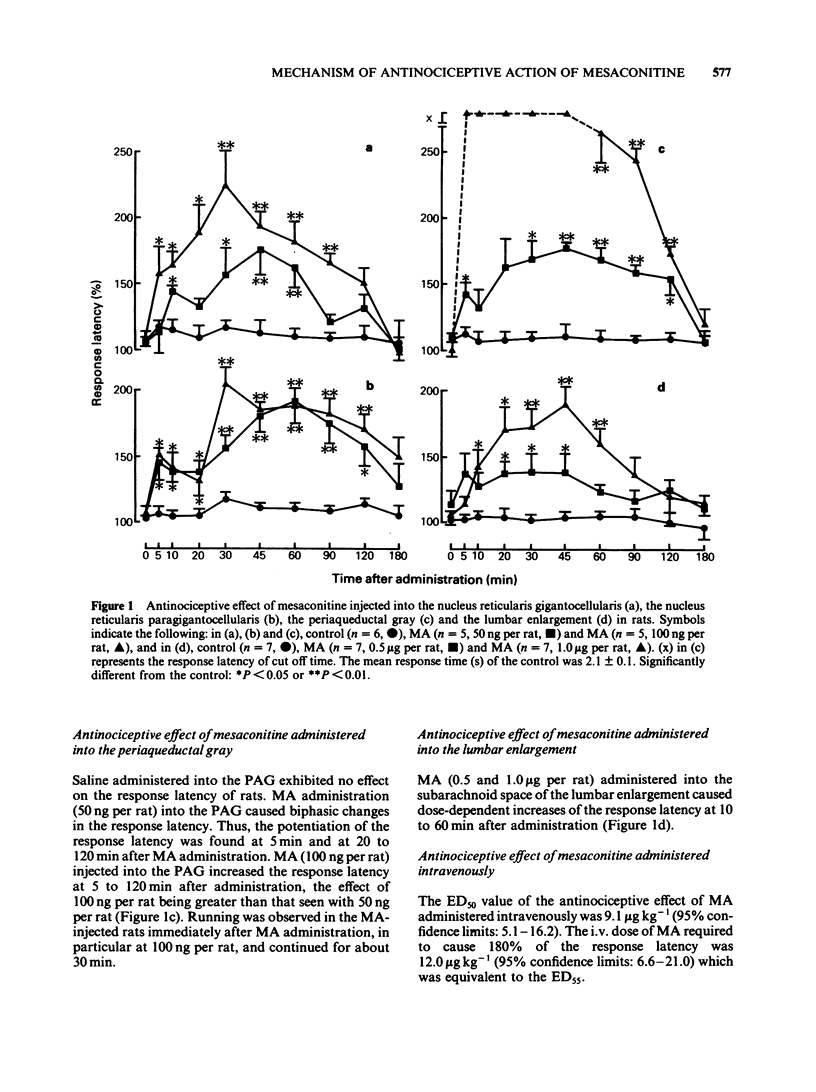
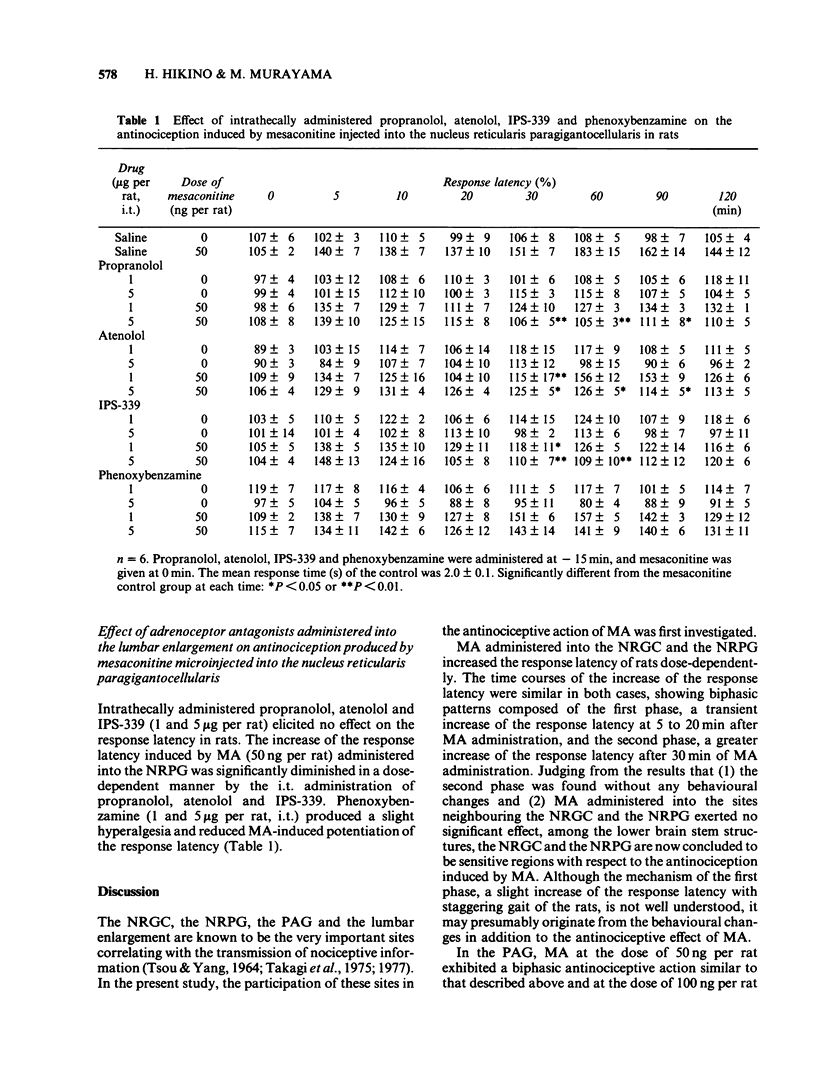
The antinociceptive action of mesaconitine (MA) microinjected into the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis (NRGC), the nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis (NRPG), the periaqueductal gray (PAG) or the lumbar enlargement was investigated in rats by use of the tail immersion test. In addition, the effects of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists and an alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist administered intrathecally (i.t.) on the antinociceptive action of MA given into the NRPG were also examined by the tail immersion test. MA (50, 100 ng per rat) microinjected into the NRGC, the NRPG, and PAG and the lumbar enlargement increased the response latency in rats in a dose-dependent fashion. MA (50 ng per rat) microinjected into neighbouring sites, the nucleus reticularis parvocellularis, the nucleus originis nervi abducentis and the fasciculus longitudinalis medialis, elicited no significant effect. Intrathecally administered propranolol (1 and 5 micrograms per rat), atenolol (1 and 5 micrograms per rat) and IPS-339 (1 and 5 micrograms per rat) remarkably inhibited the increase of the response latency induced by MA (50 ng per rat) given into the NRPG. Intrathecally administered phenoxybenzamine (1 and 5 micrograms per rat) inhibited the increase of the response latency induced by MA (50 ng per rat) injected into the NRPG but to a lesser extent than the beta-adrenoceptor antagonists. It is concluded that the NRGC, the NRPG, the PAG and the lumbar enlargement are involved in the sites of the antinociceptive action of MA and that the antinociceptive effect of MA administered into NRPG is elicited by activation of the inhibitory noradrenergic neurones from the NRPG in particularly via beta-receptor-mediated effects of noradrenaline.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN-BASSAT J., PERETZ E., SULMAN F. G. Analgesimetry and ranking of analgesic drugs by the receptacle method. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Nov 1;122:434–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvillo O., Henry J. L., Neuman R. S. Action of narcotic analgesics and antagonists on spinal units responding to natural stimulation in the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;57(6):652–663. doi: 10.1139/y79-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstens E., Yokota T., Zimmermann M. Inhibition of spinal neuronal responses to noxious skin heating by stimulation of mesencephalic periaqueductal gray in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):558–568. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Suppression of transmission of nociceptive impulses by morphine: selective effects of morphine administered in the region of the substantia gelatinosa. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):65–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama M., Hikino H. Effect of cyclic AMP on mesaconitine-induced analgesia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 15;108(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama M., Ito T., Konno C., Hikino H. Mechanism of analgesic action of mesaconitine. I. Relationship between analgesic effect and central monoamines or opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 18;101(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. V. Surgery in the rat during electrical analgesia induced by focal brain stimulation. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):444–445. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Yamada C., Konno C., Ohizumi Y., Endo K., Hikino H. Pharmacological actions of aconitine alkaloids. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1979 Jun;128(2):175–187. doi: 10.1620/tjem.128.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSOU K., JANG C. S. STUDIES ON THE SITE OF ANALGESIC ACTION OF MORPHINE BY INTRACEREBRAL MICRO-INJECTION. Sci Sin. 1964 Jul;13:1099–1109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Doi T., Kawasaki K. Effects of morphine, L-DOPA and tetrabenazine on the lamina V cells of spinal dorsal horn. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Satoh M., Akaike A., Shibata T., Kuraishi Y. The nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis of the medulla oblongata is a highly sensitive site in the production of morphine analgesia in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep 1;45(1):91–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976 Dec;17(6):1031–1036. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(76)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


