Abstract
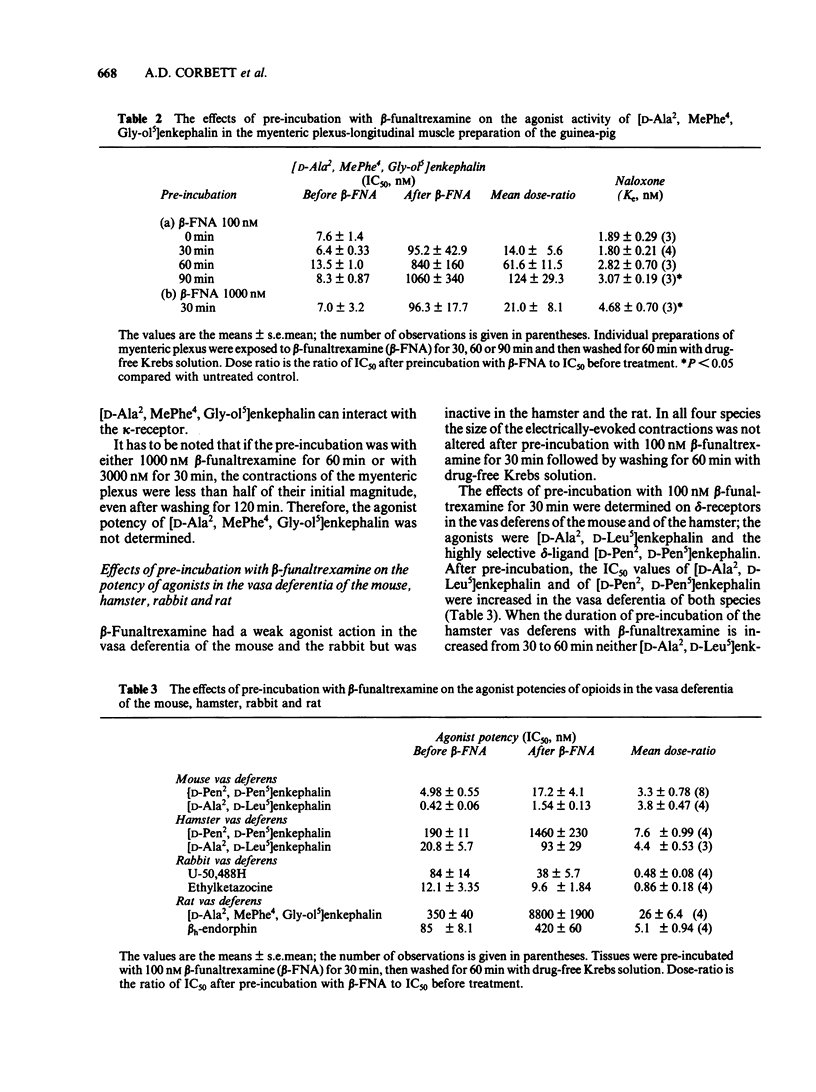
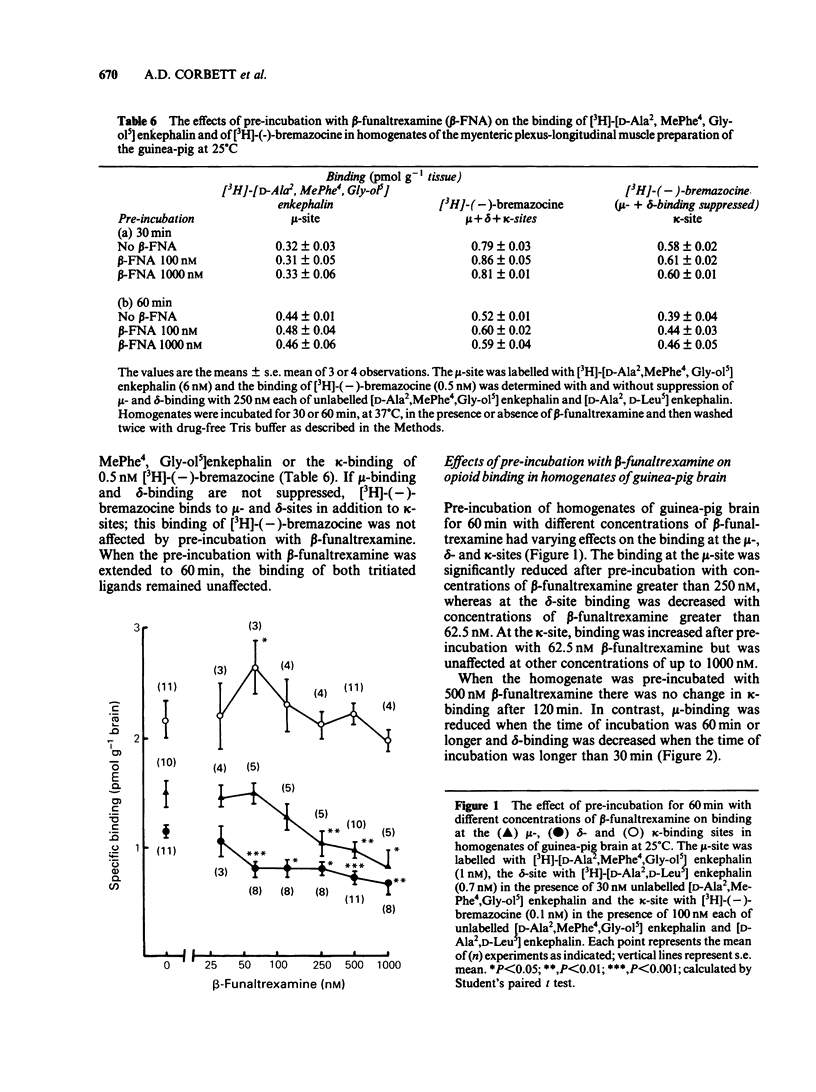
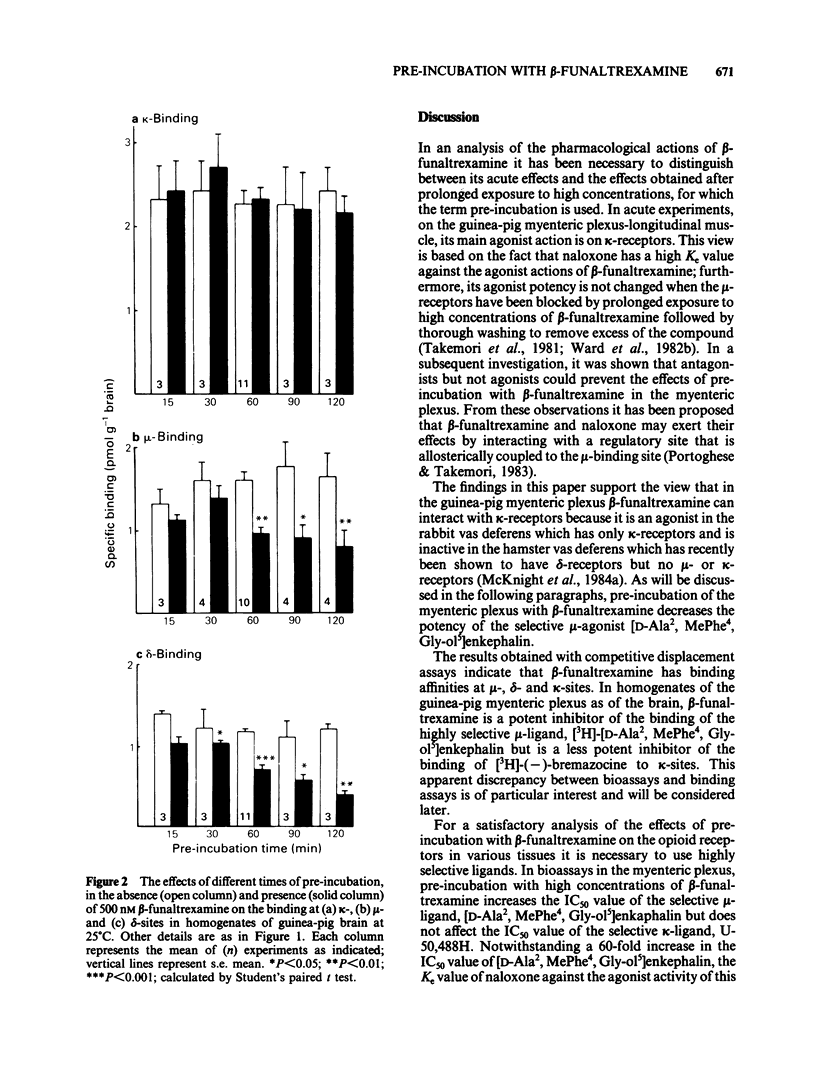
The acute effects of beta-funaltrexamine and the effects of pre-incubation with this compound were examined in five in vitro assay tissues and in selective binding assays in homogenates of guinea-pig brain and myenteric plexus. In competitive displacement assays with selective ligands, beta-funaltrexamine had highest affinity for the mu-binding site in the myenteric plexus and brain of guinea-pig. Its affinity for the kappa-site was about 15% of that for the mu-site. Pre-incubation of the assay tissues with beta-funaltrexamine caused an increase in the IC50 values of mu- and delta-receptor agonists but not of kappa-agonists. Although in bioassays on the myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle preparation of the guinea-pig, the IC50 value of the mu-receptor ligand [D-Ala2, MePhe4, Gly-ol5] enkephalin was increased up to 124 fold, its binding at the mu-site in homogenates of the preparation was not affected by this treatment. These findings indicate that the effects of pre-incubation with beta-funaltrexamine on agonist potency of the mu-receptor ligand are due to an interference with the coupling mechanism between the mu-binding site and the effector system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., Goldstein A. Specific receptor for the opioid peptide dynorphin: structure--activity relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6543–6547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., McKnight A. T., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Selectivities of opioid peptide analogues as agonists and antagonists at the delta-receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):271–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., Magnan J. Unexpected antagonism in the rat vas deferens by benzomorphans which are agonists in other pharmacological tests. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;72(1):13–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro-Toro J. P., Yoshimura K., Way E. L. Application of an irreversible opiate antagonist (beta-FNA, beta-funal-trexamine) to demonstrate dynorphin selectivity for K-opioid sites. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 29;31(22):2409–2416. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90744-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M., Waterfield A. A. Assessment in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens of benzomorphans which have strong antinociceptive activity but do not substitute for morphine in the dependent monkey. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;55(4):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Kinetic parameters of narcotic agonists and antagonists, with particular reference to N-allylnoroxymorphone (naloxone). Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):266–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie F. M., Kosterlitz H. W. Comparison of binding of [3H]-methionine-enkephalin, [3H]-naltrexone and [3H]-dihydromorphine in the mouse vas deferens and the myenteric plexus and brain of the ginea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 1;56(4):379–383. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Kosterlitz H. W. Increase in potencies of opioid peptides after peptidase inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Marcoli M., Kosterlitz H. W. Hamster vas deferens contains delta-opioid receptors. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Paterson S. J., Corbett A. D., Kosterlitz H. W. Acute and persistent effects of beta-funaltrexamine on the binding and agonist potencies of opioids in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoghese P. S., Larson D. L., Sayre L. M., Fries D. S., Takemori A. E. A novel opioid receptor site directed alkylating agent with irreversible narcotic antagonistic and reversible agonistic activities. J Med Chem. 1980 Mar;23(3):233–234. doi: 10.1021/jm00177a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Different receptor sites mediate opioid agonism and antagonism. J Med Chem. 1983 Oct;26(10):1341–1343. doi: 10.1021/jm00364a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Bowen W. D., Schumacher U. K., Pert C. B. Effect of beta-FNA on opiate receptor binding: preliminary evidence for two types of mu receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov 11;95(1-2):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Larson D. L., Portoghese P. S. The irreversible narcotic antagonistic and reversible agonistic properties of the fumaramate methyl ester derivative of naltrexone. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90355-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Improved assays for the assessment of kappa- and delta-properties of opioid ligands. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov 19;85(2):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Pharmacological profiles of beta-funaltrexamine (beta-FNA) and beta-chlornaltrexamine (beta-CNA) on the mouse vas deferens preparation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 4;80(4):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüster M., Schulz R., Herz A. Specificity of opioids towards the mu-, delta- and epsilon-opiate receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Dec;15(2-3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


