Abstract
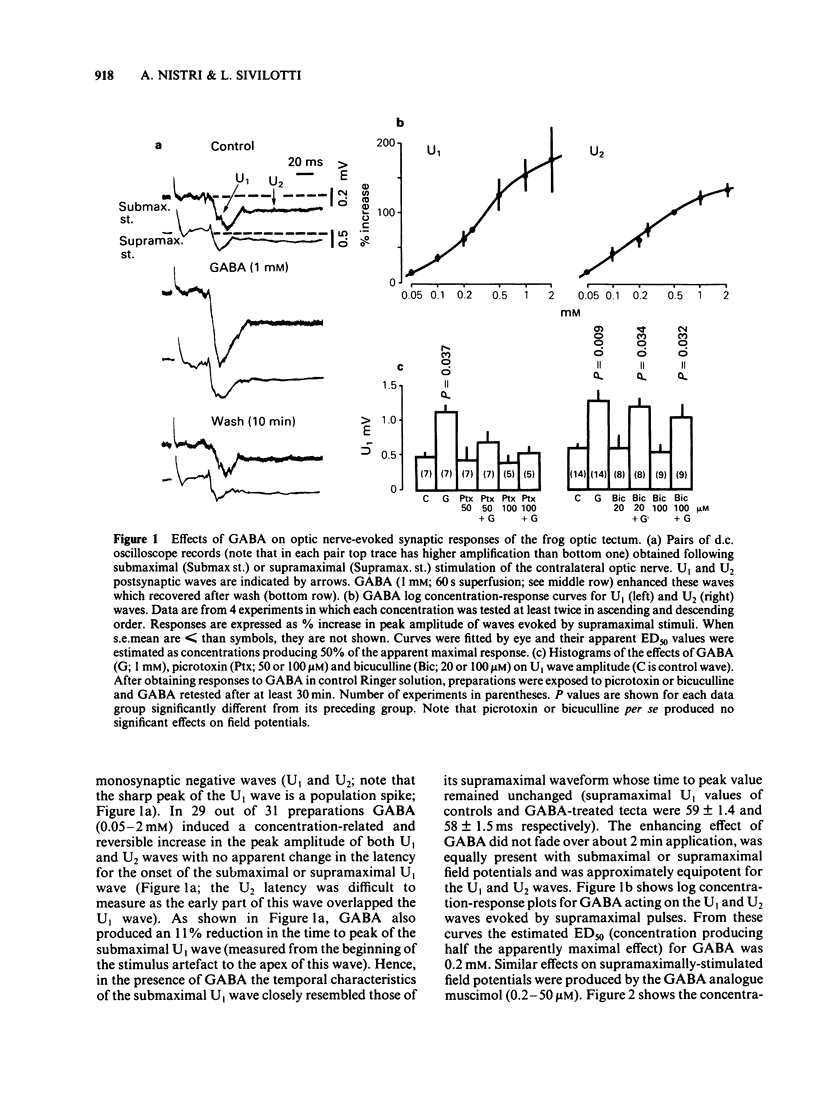
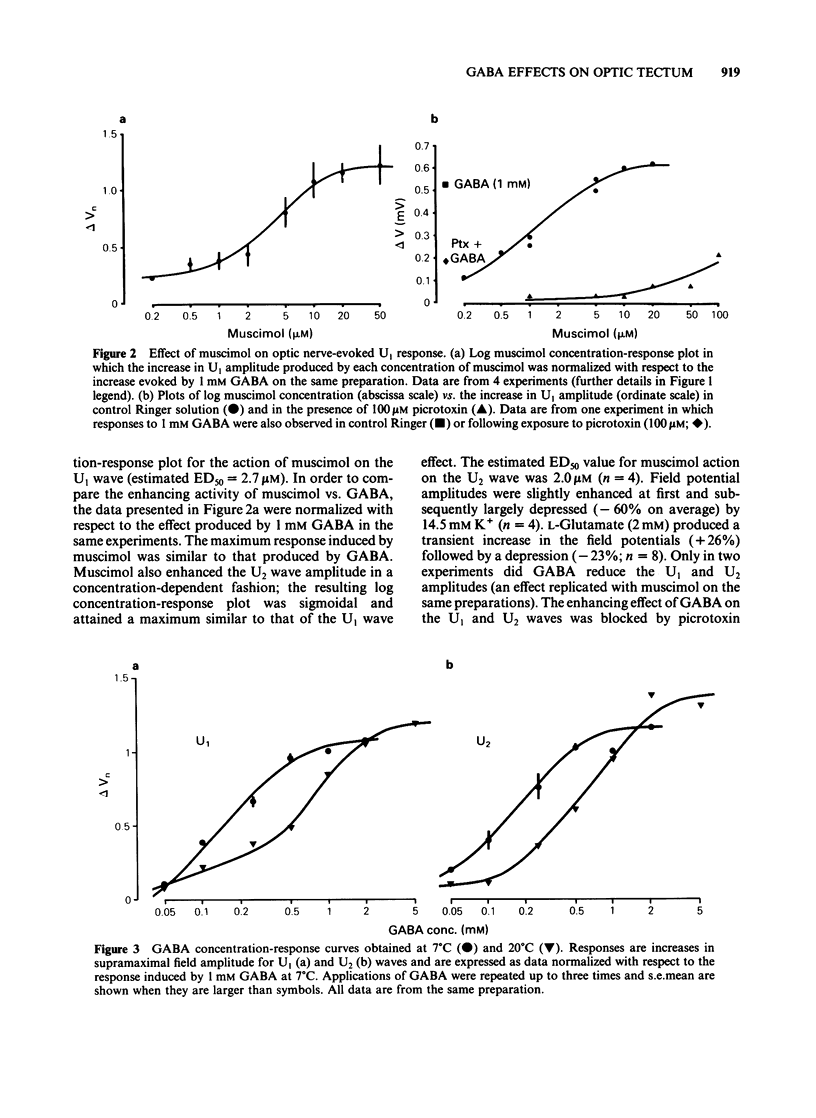
Bath-applied gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) enhanced, in a dose-dependent fashion, the amplitude of optic nerve-evoked monosynaptic excitatory responses of the frog optic tectum superfused in vitro at 7 degrees C. Muscimol was more potent than GABA in eliciting similar effects. GABA-induced responses were antagonized by picrotoxin and were insensitive to bicuculline or strychnine. Raising the bath temperature to 20 degrees C reduced the potency of GABA on these preparations. No significant effect of GABA on the compound action potential of the whole optic nerve was found. These data indicate that GABA can amplify visual inputs to the tectum through bicuculline-insensitive mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Dingledine R., Gjerstad L., Langmoen I. A., Laursen A. M. Two different responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to application of gamma-amino butyric acid. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:279–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L. Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):191–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. H., Bliss T. V., Keating M. J. The synaptic organization of optic afferents in the amphibian tectum. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Nov 19;187(1089):421–447. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Adair R. High affinity amino acid transport by frog spinal cord slices. J Neurochem. 1975 Mar;24(3):545–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. The Ferrier Lecture, 1983. Amino acids and peptides: fast and slow chemical signals in the nervous system? Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):245–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATURANA H. R., LETTVIN J. Y., MCCULLOCH W. S., PITTS W. H. Anatomy and physiology of vision in the frog (Rana pipiens). J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jul;43(6):129–175. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.6.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


