Abstract
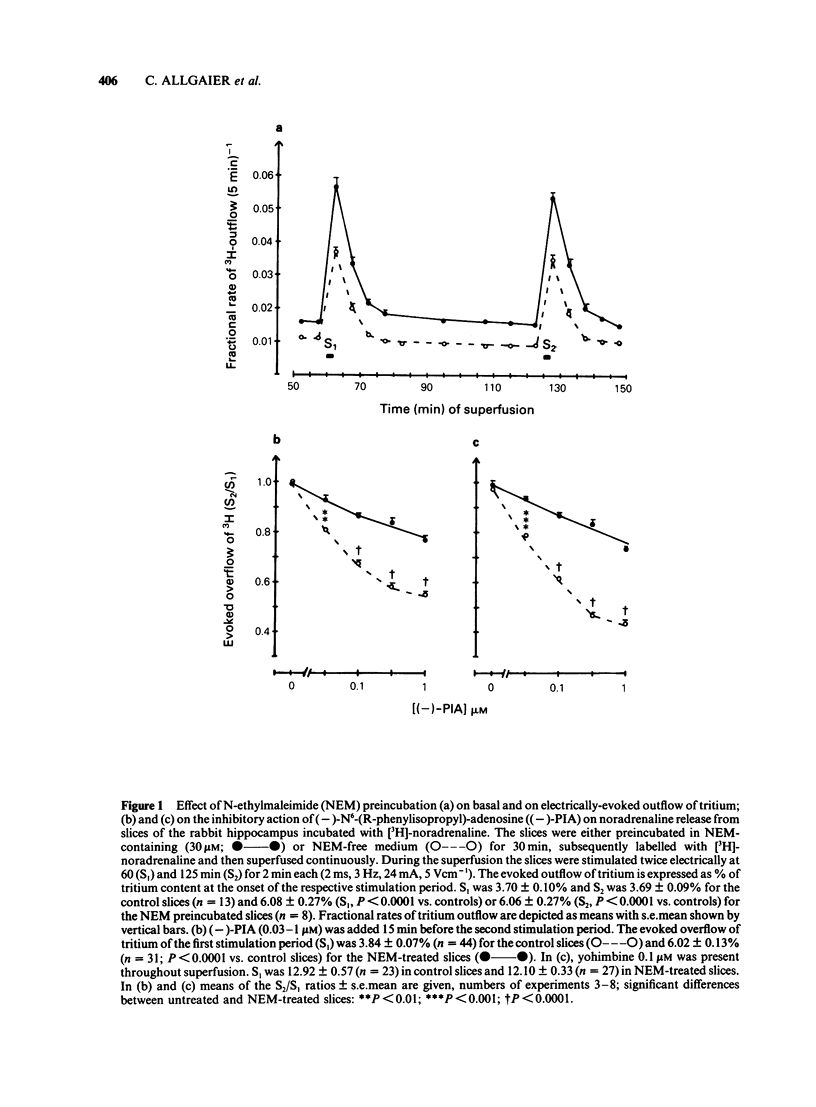
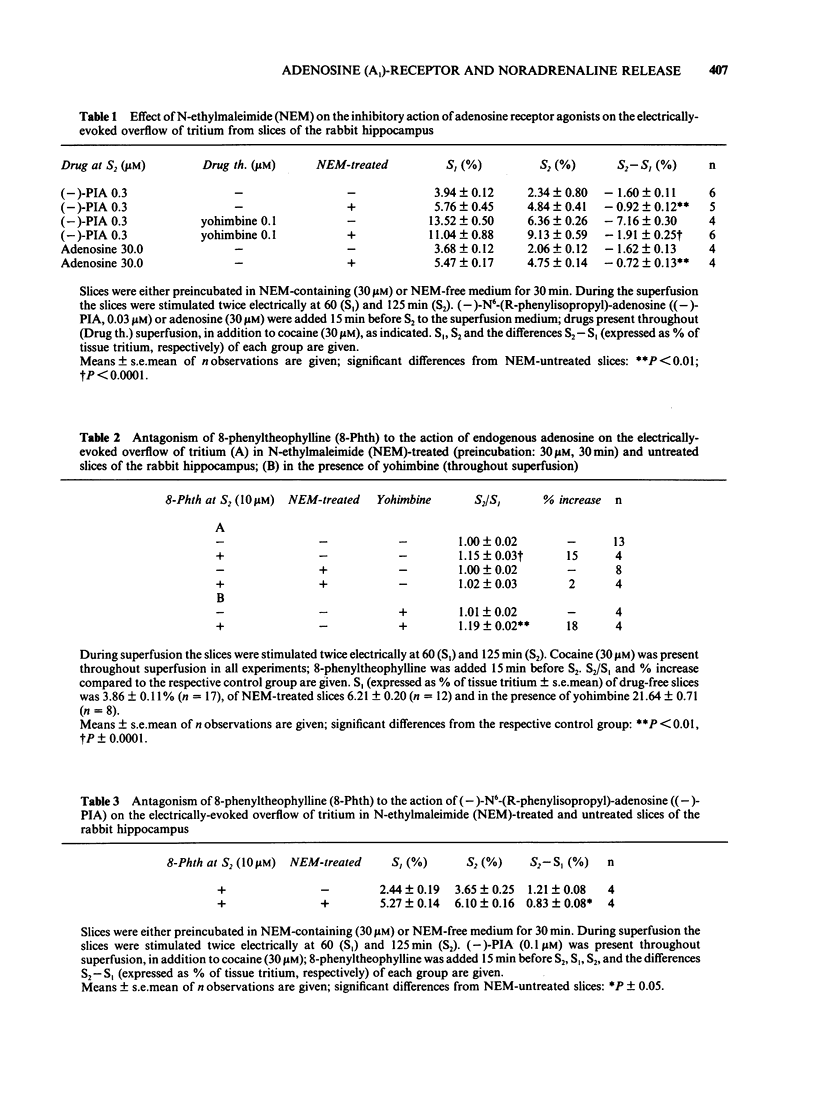
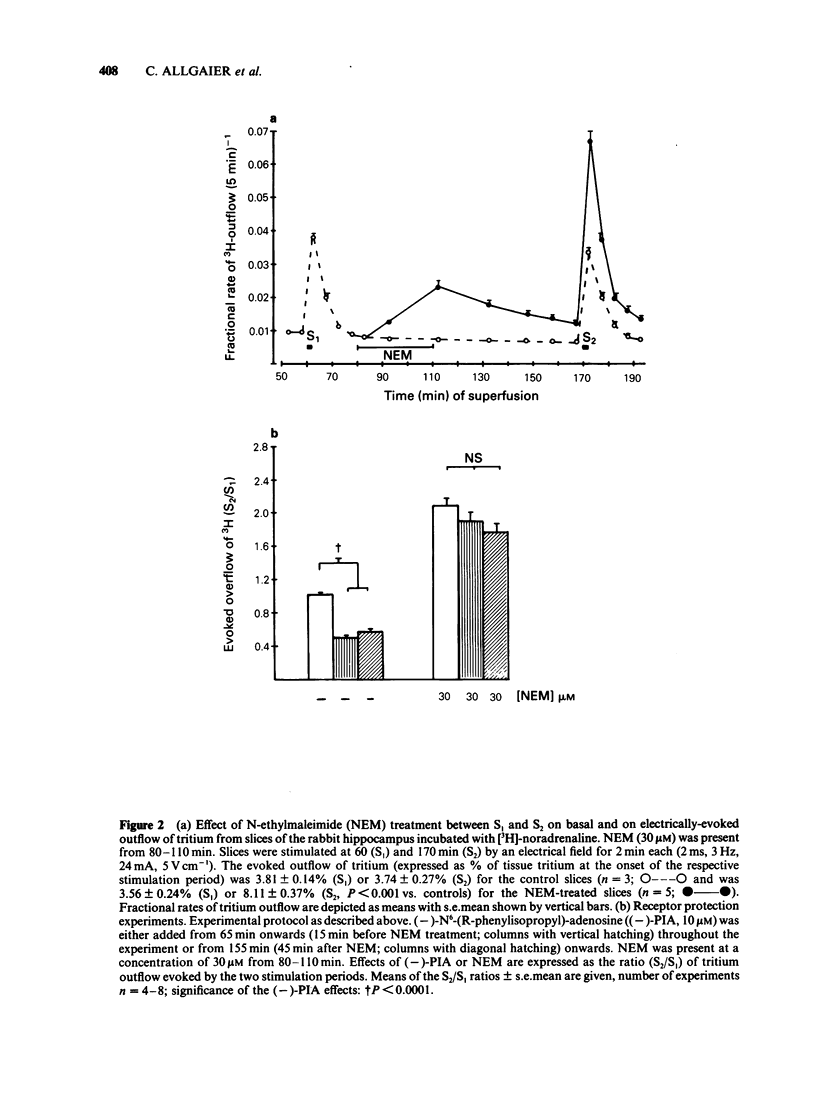
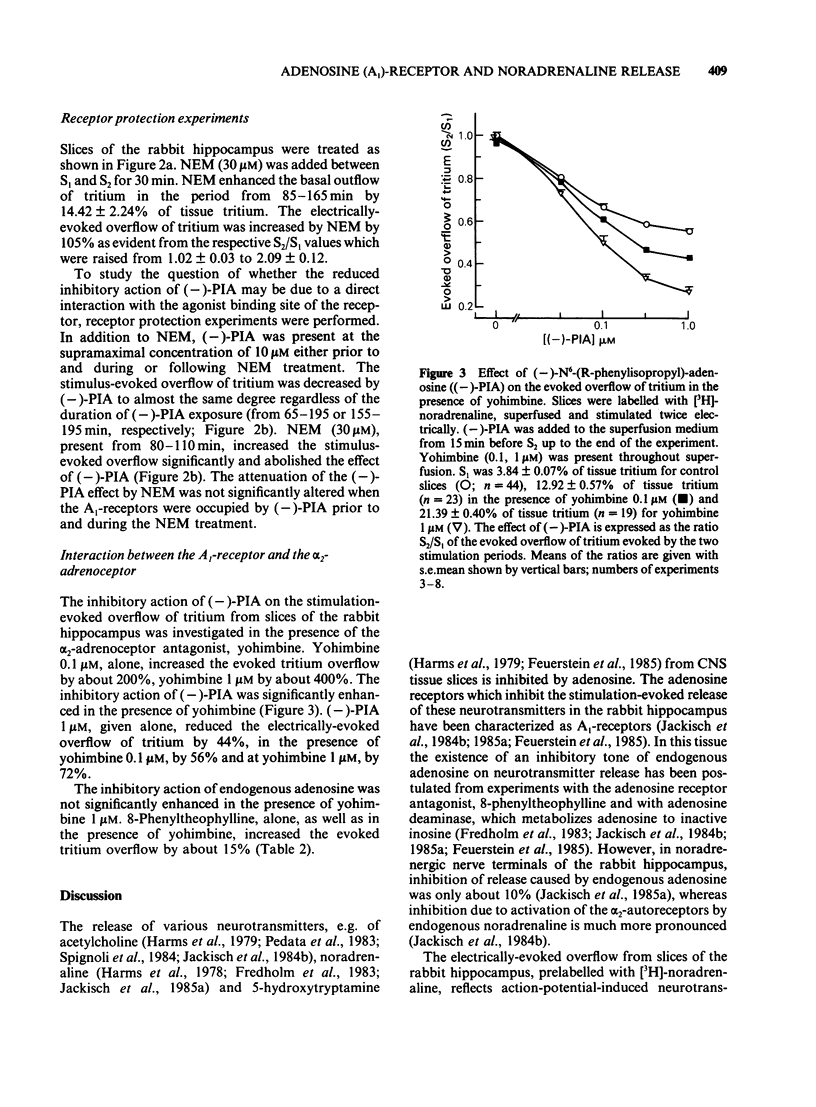
The stimulation-evoked overflow of [3H]-noradrenaline from slices of the rabbit hippocampus is inhibited by alpha 2-autoreceptors as well as by adenosine (A1)-receptors. Slices of rabbit hippocampus were labelled with [3H]-noradrenaline, superfused continuously and stimulated twice electrically (rectangular pulses; 2 ms, 3 Hz, 24 mA, 5 V cm-1). Treatment of hippocampal slices with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM, 30 microM; 30 min), which functionally disturbs certain N-proteins, decreased the inhibitory action of adenosine receptor agonists like (-)-N6-(R-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine ((-)-PIA) and adenosine on noradrenaline release. Release inhibition caused by (-)-PIA (0.03-1 microM) was antagonized by NEM in a non-competitive manner in the absence and in the presence of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine. The adenosine receptor antagonist 8-phenyltheophylline significantly increased the evoked noradrenaline release by about 15% in control slices by diminishing the inhibitory action of endogenous adenosine. In NEM-treated slices this effect of 8-phenyltheophylline was not seen. In the presence of (-)-PIA (0.1 microM), i.e. under conditions of an increased inhibitory tone, release facilitation by 8-phenyltheophylline was decreased by NEM compared to that in the respective controls. Occupation of the A1-receptor with (-)-PIA prior to and during the NEM treatment did not protect the A1-receptor-coupled signal transduction system from being affected by NEM. In the presence of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine, the inhibitory action of (-)-PIA was strongly increased. The above results suggest the involvement of a regulatory N-protein in the A1-receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release and an interaction between the alpha 2-autoreceptor and the A1-receptor-coupled signal transduction system, possibly at the level of a N-protein.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allgaier C., Feuerstein T. J., Hertting G. N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) diminishes alpha 2-adrenoceptor mediated effects on noradrenaline release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;333(2):104–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00506511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allgaier C., Feuerstein T. J., Jackisch R., Hertting G. Islet-activating protein (pertussis toxin) diminishes alpha 2-adrenoceptor mediated effects on noradrenaline release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;331(2-3):235–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00634243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Uncoupling of gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors from GTP-binding proteins by N-ethylmaleimide: effect of N-ethylmaleimide on purified GTP-binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;29(3):244–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., García A., Posadas C., García-Sáinz J. A. Differential effect of pertussis toxin on the affinity state for agonists of renal alpha 1- and alpha 2- adrenoceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8076–8079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Daly J. W., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptor binding: structure-activity analysis generates extremely potent xanthine antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2077–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M. Bimodal regulation of adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote T. E., Frey E. A., Sekura R. D. Altered activity of the inhibitory guanyl nucleotide-binding component (Ni) induced by pertussis toxin. Uncoupling of Ni from receptor with continued coupling of Ni to the catalytic unit. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8693–8698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Prestwich S. A. Pertussis toxin reverses adenosine inhibition of neuronal glutamate release. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):148–150. doi: 10.1038/316148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein T. J., Hertting G., Jackisch R. Modulation of hippocampal serotonin (5-HT) release by endogenous adenosine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 2;107(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Jonzon B., Lindström K. Adenosine receptor mediated increases and decreases in cyclic AMP in hippocampal slices treated with forskolin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Mar;117(3):461–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Lindgren E., Lindström K. Treatment with N-ethylmaleimide selectively reduces adenosine receptor-mediated decreases in cyclic AMP accumulation in rat hippocampal slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):509–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Lindgren E. Possible involvement of the Ni-protein in the prejunctional inhibitory effect of a stable adenosine analogue (R-PIA) on noradrenaline release in the rat hippocampus. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):307–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Scheer A. G., Smith M. M. Differential modification of the interaction of cardiac muscarinic cholinergic and beta-adrenergic receptors with a guanine nucleotide binding component(s). Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):570–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Wardeh G., Mulder A. H. Adenosine modulates depolarization-induced release of 3H-noradrenaline from slices of rat brain neocortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jun 1;49(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Wardeh G., Mulder A. H. Effect of adenosine on depolarization-induced release of various radiolabelled neurotransmitters from slices of rat corpus striatum. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Jul;18(7):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Sekura R. D., Codina J., Iyengar R., Manclark C. R., Birnbaumer L. Stimulation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclases mediated by distinct regulatory proteins. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):706–709. doi: 10.1038/302706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch R., Fehr R., Hertting G. Adenosine: an endogenous modulator of hippocampal noradrenaline release. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Jun;24(6):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch R., Geppert M., Illes P. Characterization of opioid receptors modulating noradrenaline release in the hippocampus of the rabbit. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1802–1810. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch R., Moll S., Feuerstein T. J., Hertting G. Dopaminergic modulation of hippocampal noradrenaline release. Evidence for alpha 2-antagonistic effects of some dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;330(2):105–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00499902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch R., Strittmatter H., Kasakov L., Hertting G. Endogenous adenosine as a modulator of hippocampal acetylcholine release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;327(4):319–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00506243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch R., Werle E., Hertting G. Identification of mechanisms involved in the modulation of release of noradrenaline in the hippocampus of the rabbit in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12A):1363–1371. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Lasch P., Minuth M., Aktories K., Schultz G. Uncoupling of alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of human platelet adenylate cyclase by N-ethylmaleimide. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2829–2833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Ui M. Functional uncoupling of muscarinic receptors from adenylate cyclase in rat cardiac membranes by the active component of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(4-5):305–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markstein R., Digges K., Marshall N. R., Starke K. Forskolin and the release of noradrenaline in cerebrocortical slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;325(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00507049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Loss of the inhibitory function of the guanine nucleotide regulatory component of adenylate cyclase due to its ADP ribosylation by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in adipocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3319–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura Y., Kitamura Y., Segawa T. Decrease of clonidine binding affinity to alpha 2-adrenoceptor by ADP-ribosylation of 41,000-dalton proteins in rat cerebral cortical membranes by islet-activating protein. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):364–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedata F., Antonelli T., Lambertini L., Beani L., Pepeu G. Effect of adenosine, adenosine triphosphate, adenosine deaminase, dipyridamole and aminophylline on acetylcholine release from electrically-stimulated brain slices. Neuropharmacology. 1983 May;22(5):609–614. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quennedey M. C., Bockaert J., Rouot B. Direct and indirect effects of sulfhydryl blocking agents on agonist and antagonist binding to central alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 15;33(24):3923–3928. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spignoli G., Pedata F., Pepeu G. A1 and A2 adenosine receptors modulate acetylcholine release from brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):341–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena D., Poeschla E., Hüttemann E., Schwabe U. Effects of N-ethylmaleimide on adenosine receptors of rat fat cells and human platelets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;327(3):247–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00502457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemer J., Schoffelmeer A. N., Mulder A. H. Effects of cyclic AMP analogues and phosphodiesterase inhibitors on K+-induced [3H]noradrenaline release from rat brain slices and on its presynaptic alpha-adrenergic modulation. J Neurochem. 1982 Aug;39(2):349–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb03954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung S. M., Green R. D. Agonist and antagonist affinities for inhibitory adenosine receptors are reciprocally affected by 5'-guanylylimidodiphosphate or N-ethylmaleimide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2334–2339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


