Abstract
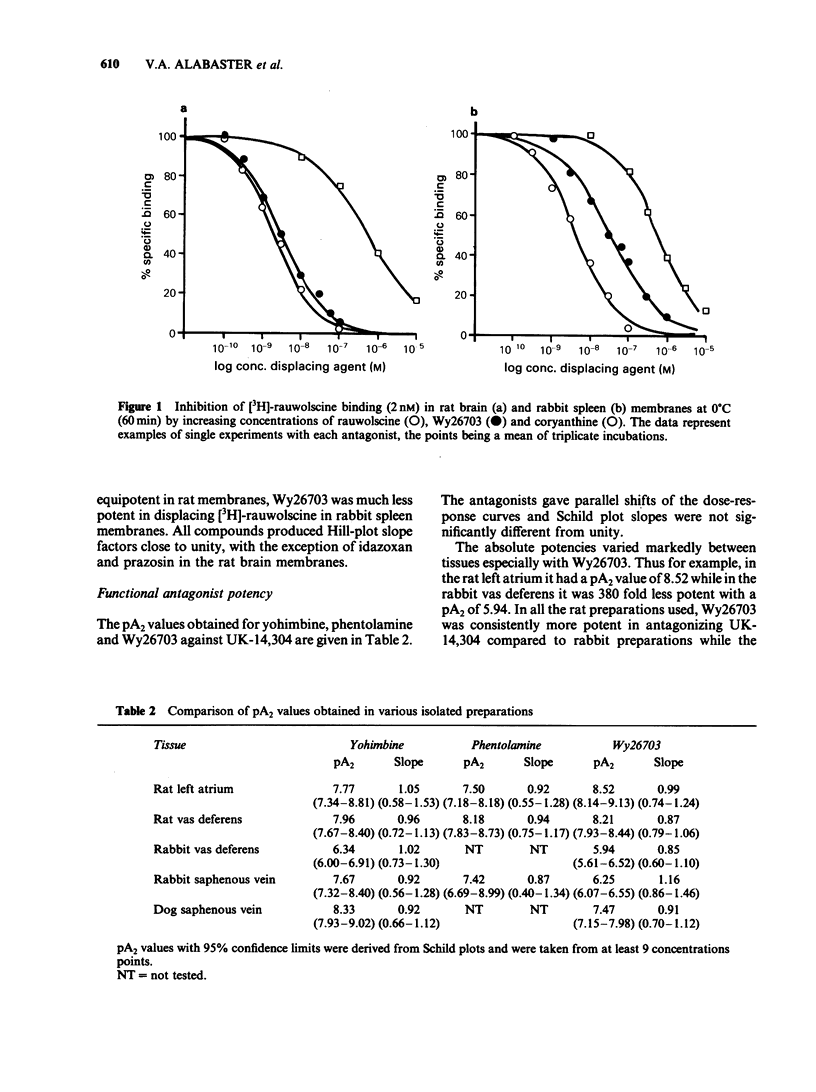
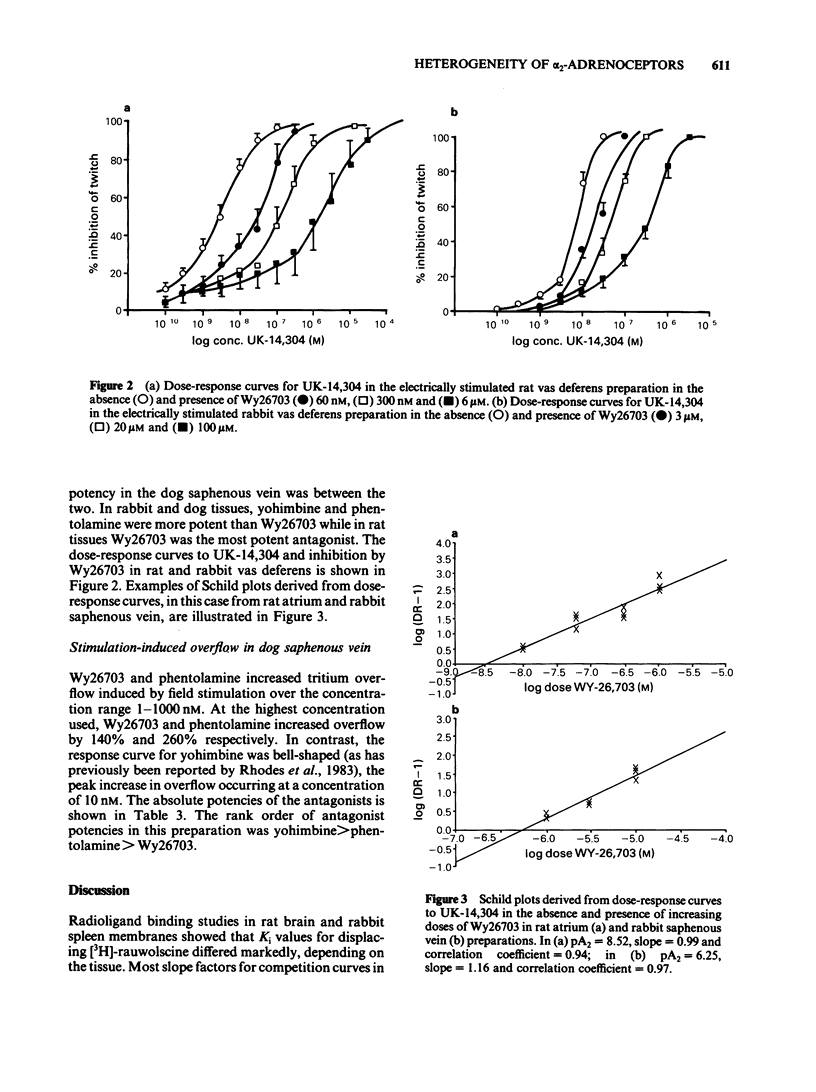
A comparison has been made of affinity of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists for alpha 2 binding sites in radioligand binding assays, and functional antagonist activity at pre- and postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in various in vitro preparations. The antagonists displaced [3H]-rauwolscine from rat brain and rabbit spleen membranes but there were substantial differences in rank order and absolute potency in the two tissues. pA2 values for yohimbine, phentolamine and Wy26703 against the selective alpha 2 agonist UK-14,304 were determined in the rat left atrium, rat and rabbit vas deferens and rabbit saphenous vein preparations. The pA2 values varied substantially between the tissues, differing by two orders of magnitude in the case of Wy26703. Yohimbine was more potent in rabbit preparations while Wy26703 was markedly more potent in all the rat preparations. Yohimbine and Wy26703 were compared in the dog saphenous vein preparation where pre- and postjunctional alpha 2 antagonist activity can be compared in the same tissue. As in the rabbit preparations, yohimbine was more potent than Wy26703 at both sites but the absolute potencies were different. It is concluded that alpha 2-adrenoceptors are a heterogeneous population, different subgroups being more apparent between species rather than between tissue types or location.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alabaster V. A., Keir R. F., Peters C. J. Comparison of activity of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists in dog and rabbit saphenous vein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;330(1):33–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00586706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alabaster V., Davey M. Precapillary vessels: effects of the sympathetic nervous system and of catecholamines. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 2):S365–S376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D. UK-14,304, a potent and selective alpha2-agonist for the characterisation of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. [3H]Rauwolscine and [3H]yohimbine binding to rat cerebral and human platelet membranes: possible heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge A., Santing P. N., Timmermans P. B., Van Zwieten P. A. A comparison of peripheral pre- and postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptors using meta-substituted imidazolidines. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;1(5):377–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara R. S., Bylund D. B. Solubilization and characterization of putative alpha-2 adrenergic isoceptors from the human platelet and the rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):603–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latifpour J., Jones S. B., Bylund D. B. Characterization of [3H]yohimbine binding to putative alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in neonatal rat lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Dec;223(3):606–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattimer N., Rhodes K. F. A difference in the affinity of some selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists when compared on isolated vasa deferentia of rat and rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 May;329(3):278–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00501880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Hoffman B. B., Lefkowitz R. J. Differential regulation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by Na+ and guanine nucleotides. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):709–711. doi: 10.1038/288709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Barnett D. B., Cheung Y. D. alpha-Adrenoceptor-effector coupling: affinity states or heterogeneity of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor? Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):39s–42s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. [3H]-rauwolscine binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the mammalian kidney: apparent receptor heterogeneity between species. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):349–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry B. D., U'Prichard D. C. [3H]rauwolscine (alpha-yohimbine): a specific antagonist radioligand for brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 17;76(4):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C., Bevan J. A. The release of H3-norepinephrine in arterial strips studied by the technique of superfusion and transmural stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Mar;172(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. T., Pierce D. L., Bylund D. B. Alpha-2 adrenergic regulation of norepinephrine release in the rat submandibular gland as measured by HPLC-EC. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 24;35(13):1385–1394. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90396-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Somogyi G. T., Hadházy P., Knoll J. Effect of duration and frequency of stimulation on the presynaptic inhibition by alpha-adrenoceptor stimulation of the adrenergic transmission. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;280(1):79–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00505357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfall J. F., Rhodes K. F., Lattimer N. Studies of alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist potency in vitro: comparisons in tissues from rats, rabbits, dogs and humans. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):21s–24s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


