Abstract
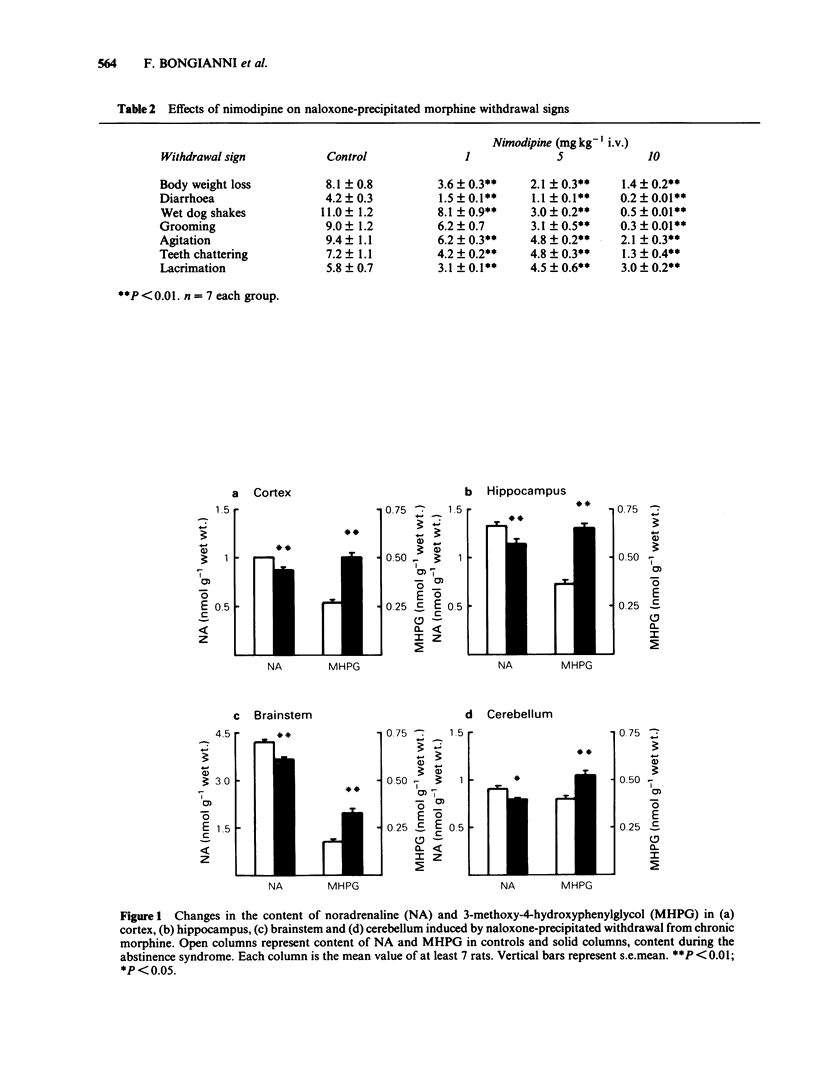
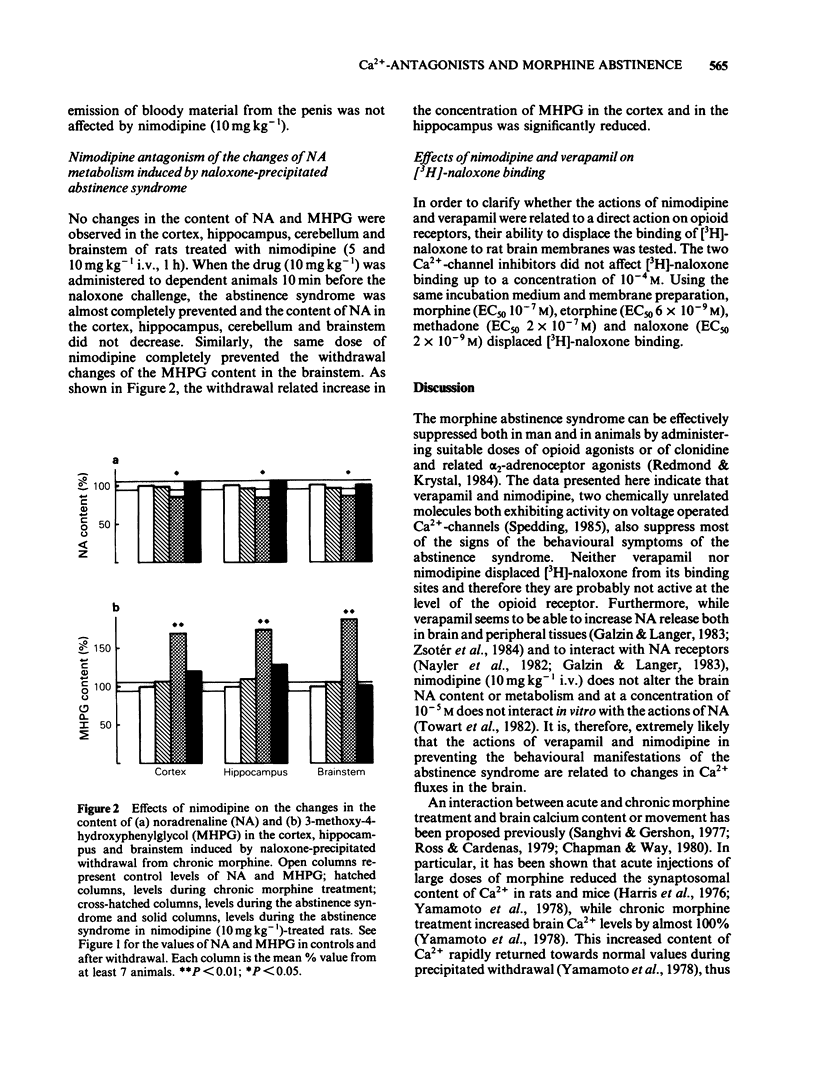
The effects of the Ca2+-channel blockers verapamil and nimodipine, on the behavioural signs of naloxone (1 mg kg-1)-induced abstinence syndrome in morphine-dependent rats, were evaluated. The content of noradrenaline (NA) and of its metabolite 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG) was measured, using high performance liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection or gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, in various brain regions of these animals. Possible interactions of nimodipine and verapamil with opioid receptors were evaluated by examining their ability to displace [3H]-naloxone binding to brain membranes. Verapamil (5, 10 and 50 mg kg-1) and nimodipine (1, 5 and 10 mg kg-1) dose-dependently reduced most of the signs of morphine abstinence. Naloxone-precipitated abstinence decreased the NA content in the cortex, hippocampus, brainstem and cerebellum. In the same brain regions the content of MHPG increased, suggesting an increased release of the amine during morphine abstinence. Nimodipine (10 mg kg-1 i.v.) did not change the content of NA or MHPG in the cortex, hippocampus and brainstem. However, nimodipine pre-treatment markedly reduced the changes in NA and MHPG content induced by the abstinence syndrome. Neither verapamil nor nimodipine displaced [3H]-naloxone from its binding sites. These results suggest that Ca2+-channel blockers suppress the behavioural and neurochemical expressions of morphine abstinence by a mechanism that differs from those of opioids or alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellemann P., Schade A., Towart R. Dihydropyridine receptor in rat brain labeled with [3H]nimodipine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2356–2360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sreti M. M., Gonzalez J. P., Sewell R. D. Effects of elevated calcium and calcium antagonists on 6,7-benzomorphan-induced analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 17;90(4):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90560-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava H. N. The effects of divalent ions on morphine analgesia and abstinence syndrome in morphine-tolerant and -dependent mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Apr 28;57(2):223–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00426892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. B., Way E. L. Metal ion interactions with opiates. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:553–579. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. B., Way E. L. Modification of endorphin/enkephalin analgesia and stress-induced analgesia by divalent cations, a cation chelator and an ionophore. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;75(2):389–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés R., Supavilai P., Karobath M., Palacios J. M. Calcium antagonist binding sites in the rat brain: quantitative autoradiographic mapping using the 1,4-dihydropyridines [3H]PN 200-110 and [3H]PY 108-068. J Neural Transm. 1984;60(3-4):169–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01249092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Laverty R., Roth R. H. Clonidine reversal of increased norepinephrine metabolite levels during morphine withdrawal. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug 1;57(2-3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90372-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell L. C., Barr E. M., Leslie S. W. 45Ca2+ uptake into rat whole brain synaptosomes unaltered by dihydropyridine calcium antagonists. J Neurochem. 1983 Nov;41(5):1455–1459. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzin A. M., Langer S. Z. Presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonism by verapamil but not by diltiazem in rabbit hypothalamic slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):571–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. D., Tingstad J. E. Formulation of a morphine implantation pellet suitable for tolerance-physical dependence studies in mice. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Mar;59(3):426–427. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H. Tissue heterogeneity of calcium channel antagonist binding sites labeled by [3H]nitrendipine. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunne L. M., Jonsson J., Fuxe K. Effects of morphine intoxication on brain catecholamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;5(4):338–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Antinociceptive effects of lanthanum and cerium in nontolerant and morphine tolerant-dependent animals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Feb;196(2):288–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Effects of divalent cations, cation chelators and an ionophore on morphine analgesia and tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Dec;195(3):488–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Spedding M. A functional correlate for the dihydropyridine binding site in rat brain. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):94–96. doi: 10.1038/314094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroni F., Peralta E., Cheney D. L., Costa E. On the regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid neurons in caudatus, pallidus and nigra: effects of opioids and dopamine agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Feb;208(2):190–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler W. G., Thompson J. E., Jarrott B. The interaction of calcium antagonists (slow channel blockers) with myocardial alpha adrenoceptors. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1982 Mar;14(3):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(82)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., El-Fakahany E. E. Increase in [3H]nitrendipine binding sites in the brain in morphine-tolerant mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 13;102(2):371–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90272-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond D. E., Jr, Krystal J. H. Multiple mechanisms of withdrawal from opioid drugs. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross D. H., Cardenas H. L. Nerve cell calcium as a messenger for opiate and endorphin actions. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1979;20:301–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghvi I. S., Gershon S. Commentary: Brain calcium and morphine action. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jul 1;26(13):1183–1185. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Späth L., Wichmann T. Effects of verapamil, diltiazem and ryosidine on the release of dopamine and acetylcholine in rabbit caudate nucleus slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;325(2):124–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00506191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towart R., Wehinger E., Meyer H., Kazda S. The effects of nimodipine, its optical isomers and metabolites on isolated vascular smooth muscle. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(4):338–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium channels in rat brain synaptosomes: identification and pharmacological characterization. High affinity blockade by organic Ca2+ channel blockers. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):841–849. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00841.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Valkenburg C., Tjaden U., Van der Krogt J., Van der Leden B. Determination of dopamine and its acidic metabolites in brain tissue by HPLC with electrochemical detection in a single run after minimal sample pretreatment. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):990–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Etienne P., Lal S., Gauthier S., Cajal S., Nair N. P. Reduced lumbar CSF somatostatin levels in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 8;31(19):2073–2079. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Harris R. A., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Effects of acute and chronic morphine treatments on calcium localization and binding in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 May;205(2):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsotér T. T., Wolchinsky C., Endrenyi L. Effects of verapamil on [3H]norepinephrine release. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984 Nov-Dec;6(6):1060–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


