Abstract
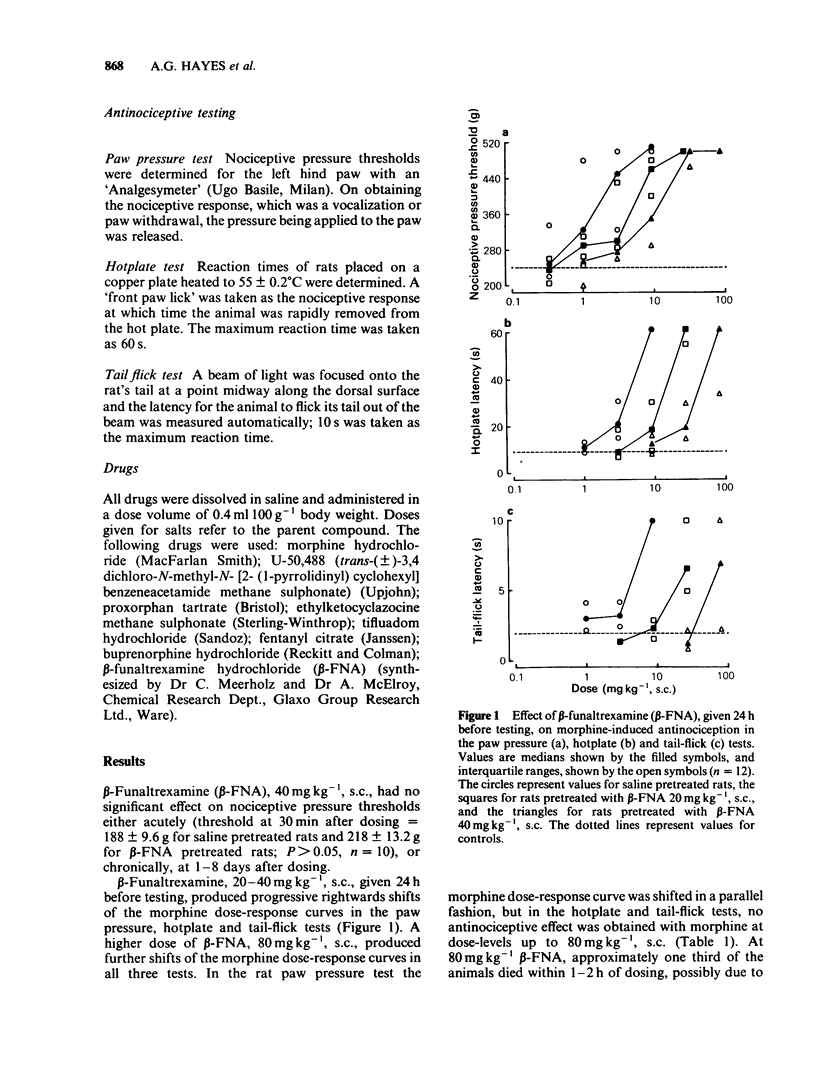
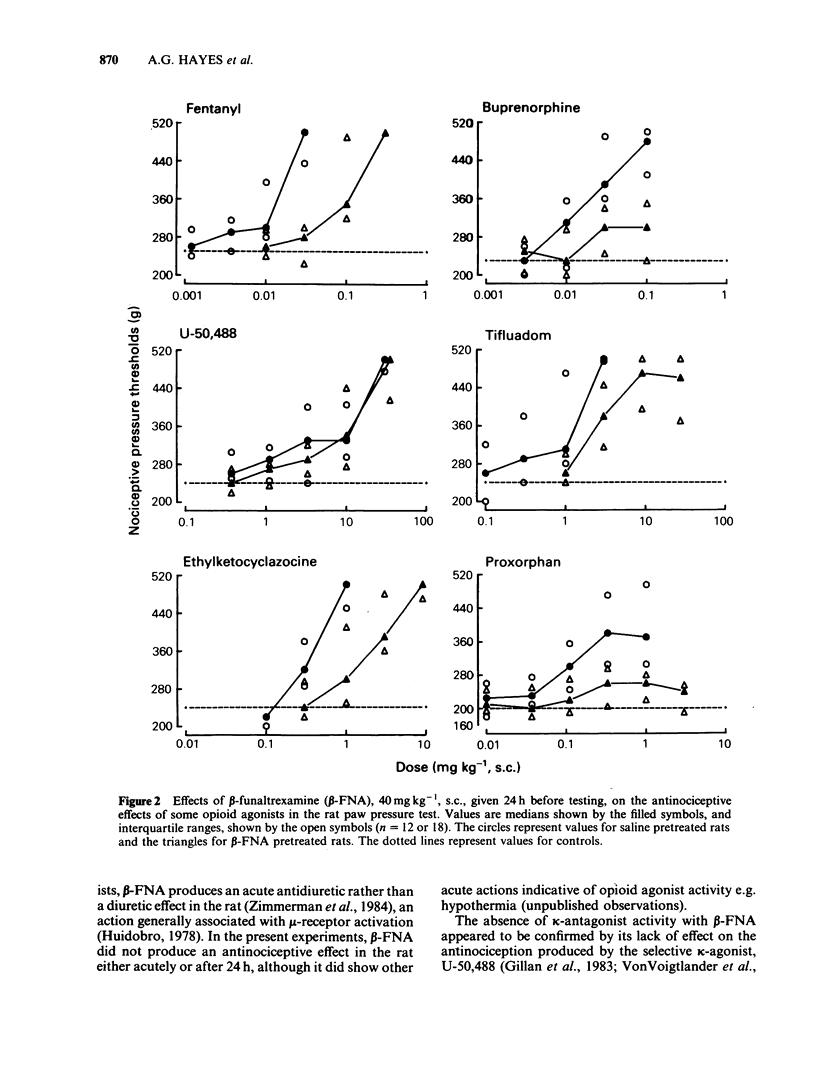
The effect of the irreversible opioid receptor antagonist, beta-funaltrexamine (beta-FNA), on antinociception produced by mu- and kappa-receptor agonists was studied in the rat. beta-FNA, 20 to 80 mg kg-1, s.c., given 24 h before testing, produced a dose-related antagonism of the effects of morphine in the paw pressure, hotplate and tail-flick tests. Following the 80 mg kg-1 dose, the degree of antagonism of morphine was stable for up to 48 h after dosing, but was reduced by 5 days and had disappeared by 8 days. In the paw pressure test, beta-FNA, 40 mg kg-1, s.c., antagonized the effects of fentanyl, buprenorphine, tifluadom, ethylketocyclazocine and proxorphan; it was without effect against the highly selective kappa-agonist, U-50,488. In light of these results, the possible opioid receptor selectivities of both the agonists and beta-FNA are reassessed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll J. A., Miller L., Shaw J. S., Downes C. P. Mu-receptor binding in physiological media: comparison with isolated tissue data. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet P., Coulaud A., Zajac J. M., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Costentin J., Roques B. P. The mu rather than the delta subtype of opioid receptors appears to be involved in enkephalin-induced analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 18;101(1-2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Kostelitz H. W., McKnight A. T., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Pre-incubation of guinea-pig myenteric plexus with beta-funaltrexamine: discrepancy between binding assays and bioassays. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;85(3):665–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb10562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan A., Doxey J. C., Harry E. J. The animal pharmacology of buprenorphine, an oripavine analgesic agent. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):547–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligan J. J., Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Burks T. F. Cerebral delta opioid receptors mediate analgesia but not the intestinal motility effects of intracerebroventricularly administered opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jun;229(3):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzón J., Sánchez-Blázquez P., Lee N. M. [3H]Ethylketocyclazocine binding to mouse brain membranes: evidence for a kappa opioid receptor type. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Oct;231(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W. Spectrum of the mu, delta- and kappa-binding sites in homogenates of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;77(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., James I. F. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. II. Pharmacological selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Sheehan M. J., Tyers M. B. Determination of the receptor selectivity of opioid agonists in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens by use of beta-funaltrexamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;86(4):899–904. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb11112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A., Kelly A. Profile of activity of kappa receptor agonists in the rabbit vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 16;110(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90558-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro F. Antidiuretic effect of morphine in the rat: tolerance and physical dependence. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;64(2):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Goldstein A. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Characterization of the kappa-subtype of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):939–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. A kappa opioid effect: increased urination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. Further study of kappa opioids on increased urination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance M. J. Animal and molecular pharmacology of mixed agonist-antagonist analgesic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979;7 (Suppl 3):281S–286S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rónai A. Z., Berzétei I. P., Székely J. I., Miglécz E., Kurgyis J., Bajusz S. Enkephalin-like character and analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 29;69(3):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90472-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Pinsky C., LaBella F. S. On the specificity of naloxone as an opiate antagonist. Life Sci. 1979 Nov 5;25(19):1621–1632. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skingle M., Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Effects of opiates on urine output in the water-loaded rat and reversal by beta-funaltrexamine. Neuropeptides. 1985 Feb;5(4-6):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M. B. A classification of opiate receptors that mediate antinociception in animals. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M. B. Studies on the antinociceptive activities of mixtures of mu- and kappa-opiate receptor agonists and antagonists. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1233–1236. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton N., Sewell R. D., Spencer P. S. Analgesic actions of mu- and kappa-opiate agonists in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Apr;262(2):199–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiger J. W. Binding of buprenorphine to opiate receptors. Regulation by guanyl nucleotides and metal ions. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Mar;23(3):373–375. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Pharmacological characterization in vivo of the novel opiate, beta-funaltrexamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Mar;220(3):494–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Pharmacological profiles of beta-funaltrexamine (beta-FNA) and beta-chlornaltrexamine (beta-CNA) on the mouse vas deferens preparation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 4;80(4):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Takemori A. E. Relative involvement of mu, kappa and delta receptor mechanisms in opiate-mediated antinociception in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Mar;224(3):525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


