Abstract
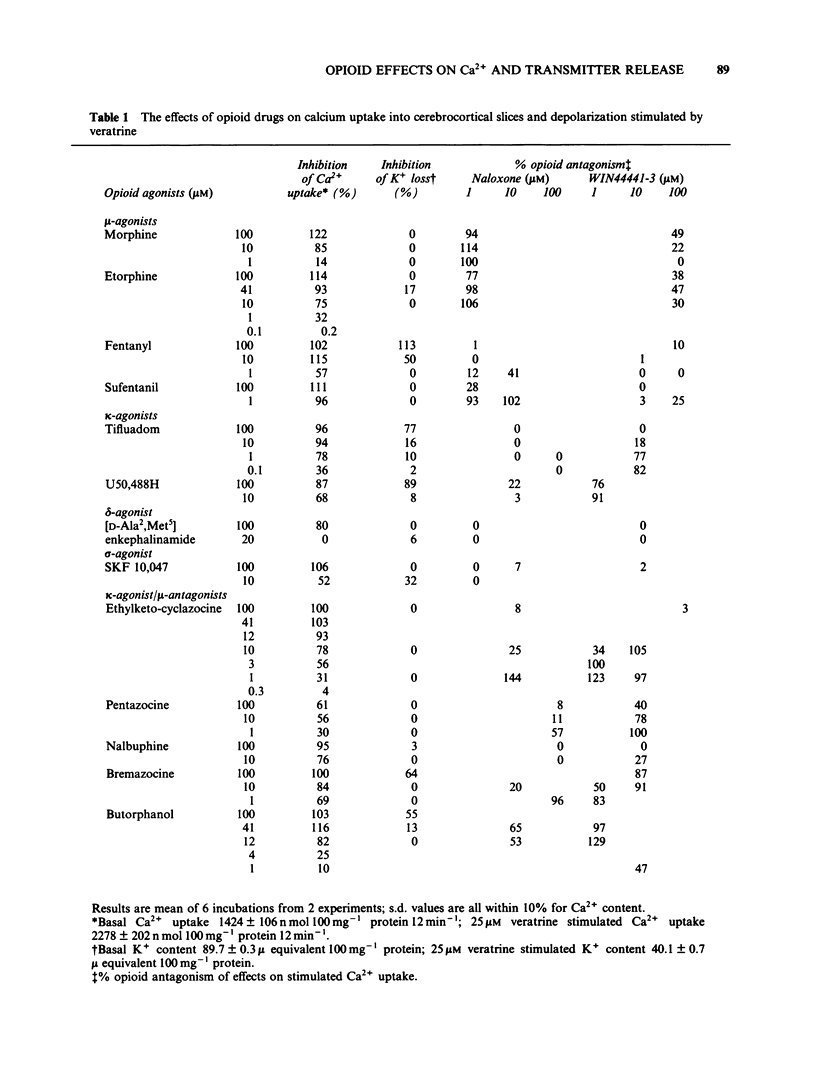
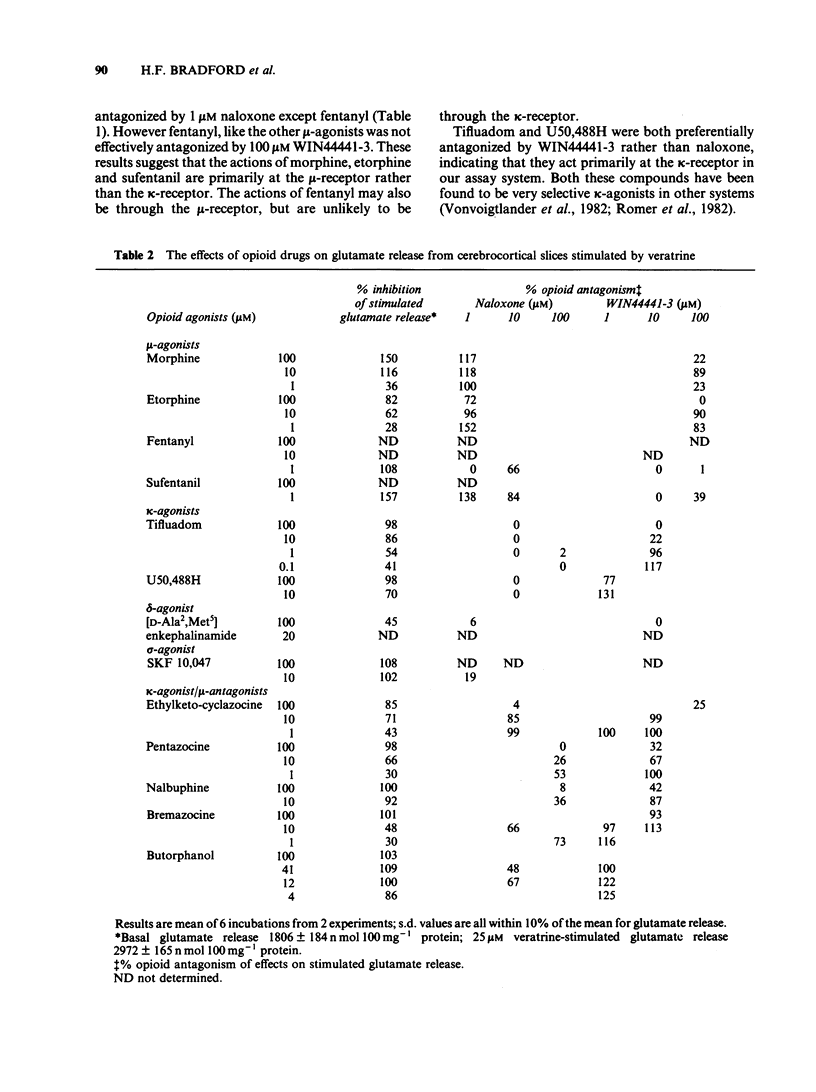
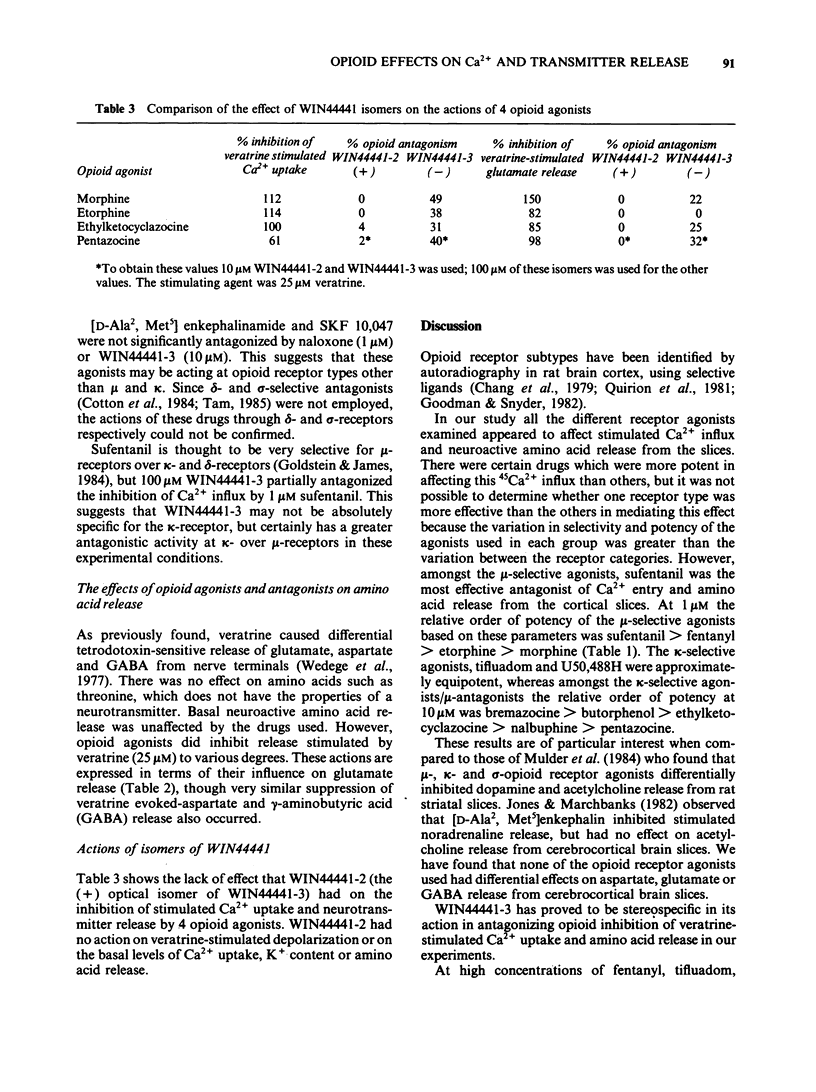
The effects of opioid agonists on veratrine-stimulated Ca2+ influx and amino acid neurotransmitter release in rat cerebrocortical brain slices were studied. Inhibitory effects were seen on both of these parameters with all of the opioid agonists used. None of the drugs used affected basal 45Ca2+ uptake, basal K+ content or basal amino acid release from the slices. At high concentrations (100 microM) fentanyl, tifluadom, U50,488H, butorphanol and bremazocine greatly inhibited the depolarization of the slices by veratrine as determined by the reduced release of K+. The opioid receptor subtypes at which the drugs were acting were characterized by the antagonistic effects of naloxone and WIN44441-3. The opioid-induced inhibition of stimulated Ca2+ uptake and amino acid release were not antagonized by WIN44441-2, the inactive enantiomer of WIN44441-3. It is concluded that opioid agonists acting through mu- and kappa-receptors and probably through delta- and sigma-receptors, have an inhibitory effect on Ca2+ uptake into cerebrocortical brain slices and the subsequent release of aspartate, glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang K. J., Cooper B. R., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors: different regional distribution in the brain and differential binding of opiates and opioid peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):91–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R., Giles M. G., Miller L., Shaw J. S., Timms D. ICI 174864: a highly selective antagonist for the opioid delta-receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal D., Bradford H. F. Inhibition of depolarization-coupled calcium fluxes and transmitter release in vitro by morphine. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80575-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium ocmponent of sensory neurone action potentials. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):837–839. doi: 10.1038/276837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H. Kappa opiate receptors localized by autoradiography to deep layers of cerebral cortex: relation to sedative effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Goldstein A. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. A., Marchbanks R. M. Effects of (D-alanine2, methionine5) enkephalinamide on the release of acetylcholine and noradrenaline from brain slices and isolated nerve terminals. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 1;31(3):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H. Techniques in tissue metabolism. 5. Chopping and slicing tissue samples. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:213–218. doi: 10.1042/bj0780213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Classification of opioid receptors. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Hammer R. P., Jr, Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Phencyclidine (angel dust)/sigma "opiate" receptor: visualization by tritium-sensitive film. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5881–5885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. S., Holford N. H., Richards M. L., Aman R. A., Sadée W. Discrimination of three types of opioid binding sites in rat brain in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):242–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer D., Büscher H. H., Hill R. C., Maurer R., Petcher T. J., Zeugner H., Benson W., Finner E., Milkowski W., Thies P. W. An opioid benzodiazepine. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):759–760. doi: 10.1038/298759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer D., Büscher H., Hill R. C., Maurer R., Petcher T. J., Welle H. B., Bakel H. C., Akkerman A. M. Bremazocine: a potent, long-acting opiate kappa-agonist. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 15;27(11):971–978. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Portoghese P. S. Comparative antagonism by naltrexone and naloxone of mu, kappa, and delta agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 3;104(1-2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90374-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W. (+)-[3H]SKF 10,047, (+)-[3H]ethylketocyclazocine, mu, kappa, delta and phencyclidine binding sites in guinea pig brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 12;109(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90536-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Pierson A. K., Michne W. F. Multiple opioid receptor profile in vitro and activity in vivo of the potent opioid antagonist Win 44,441-3. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90503-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedege E., Luqmani Y., Bradford H. F. Stimulated incorporation of amino acids into proteins of synaptosomal fractions induced by depolarizing treatments. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):527–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Harris R. A., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Effects of acute and chronic morphine treatments on calcium localization and binding in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 May;205(2):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


