Abstract
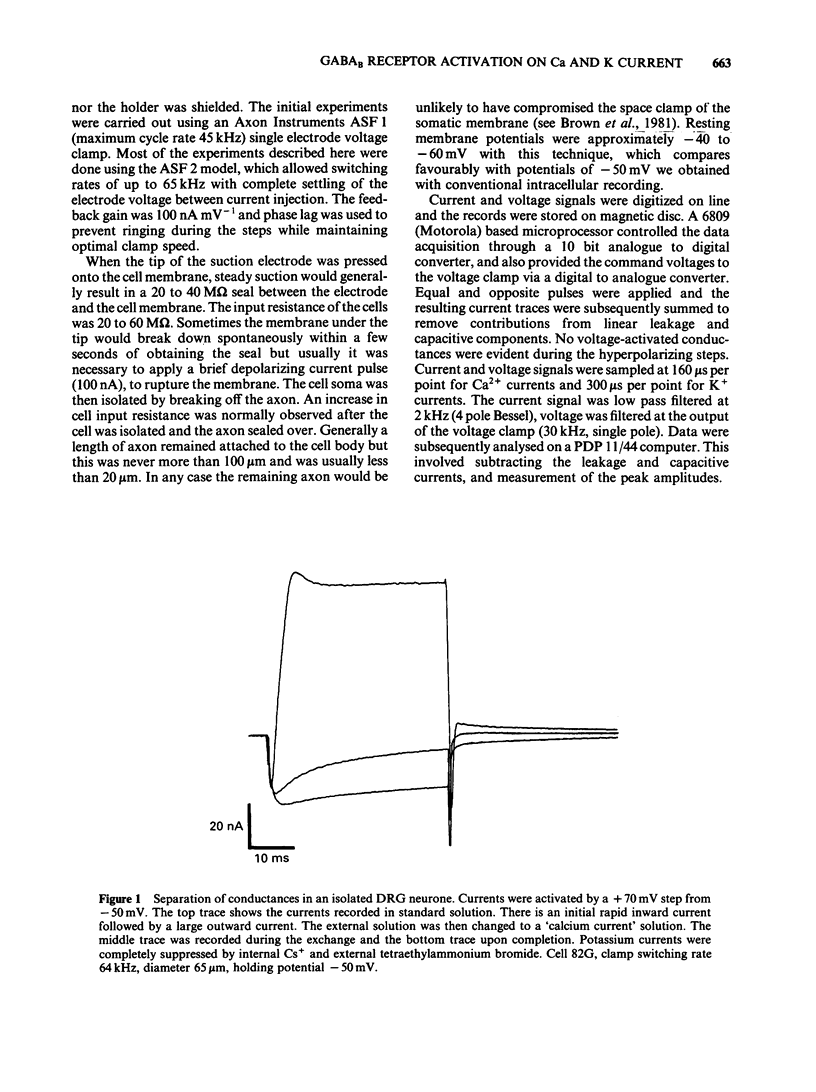
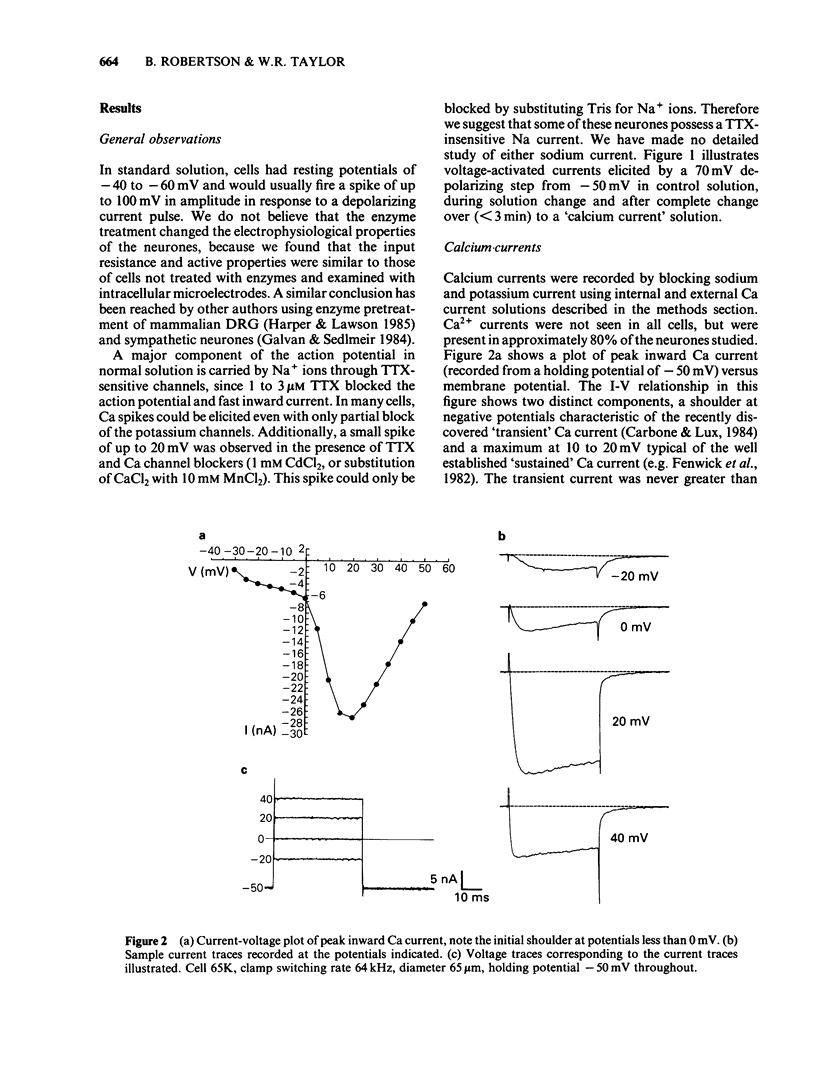
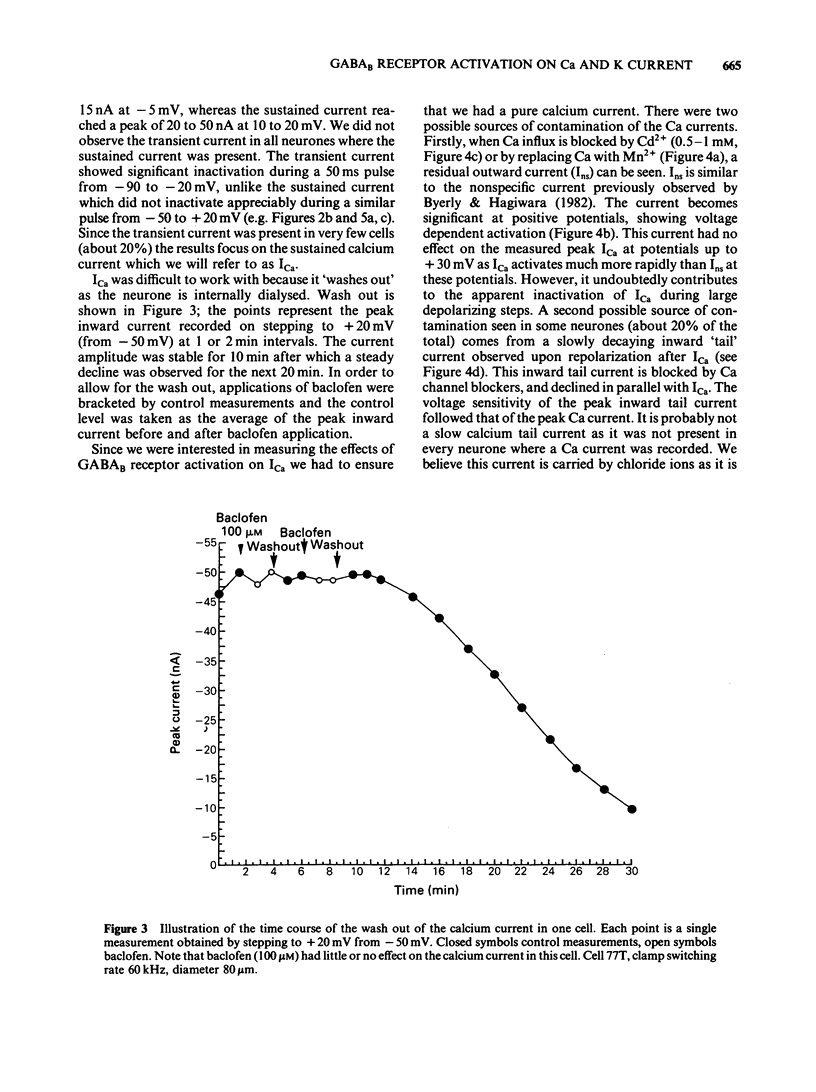
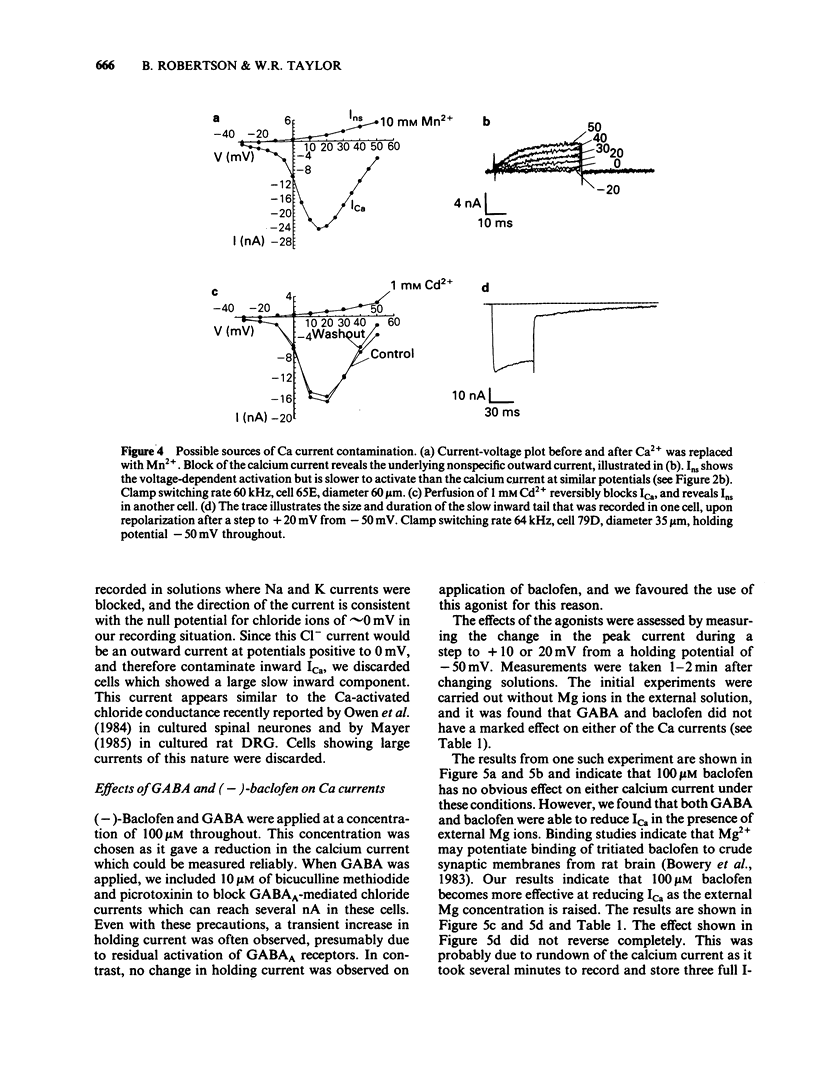
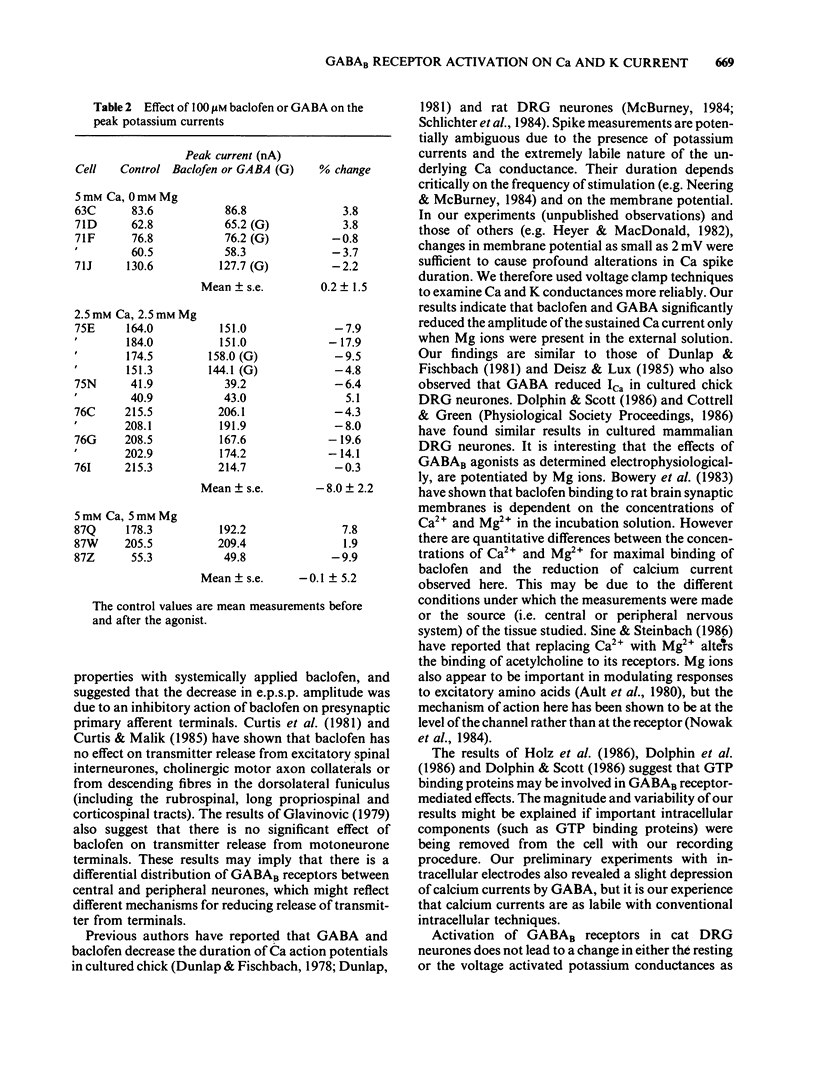
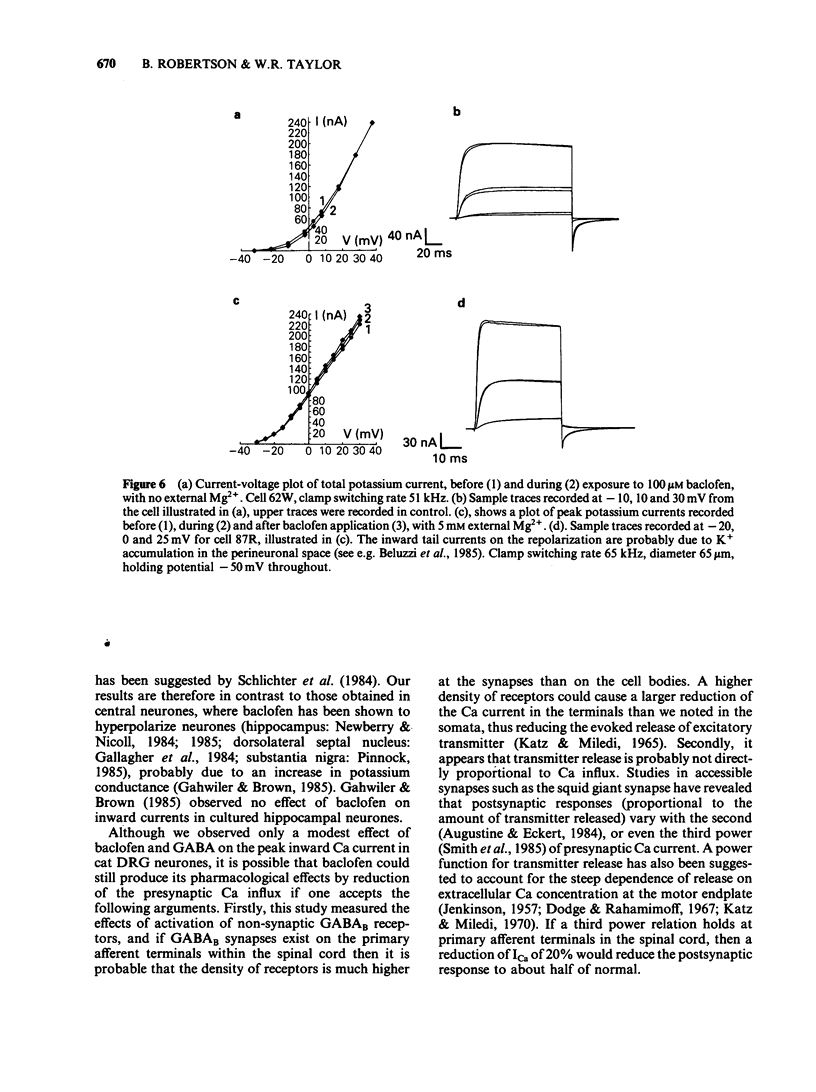
Calcium and potassium currents were examined in dialysed, isolated dorsal root ganglion neurones of the cat by use of a single electrode voltage clamp. Two calcium currents were identified, a low threshold inactivating (transient) current and a higher threshold slowly inactivating (sustained) current. Both currents were blocked by 1 mM cadmium and replacement of calcium with manganese, which revealed an underlying nonspecific outward current. The sustained current disappeared with internal dialysis over a period of 20 to 30 min. (-)-Baclofen (100 microM) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA, 100 microM) were found to reduce the peak amplitude of the sustained calcium current, an effect which became more pronounced with increasing concentrations of external magnesium (1-5 mM). In 5 mM external magnesium, 100 microM baclofen reduced the calcium current by 28%. The voltage-activated delayed rectifier appeared to be the most prominent potassium current in these cells. We were unable to find any evidence for a significant contribution from calcium-activated potassium conductance or a transient potassium conductance under our recording conditions. Baclofen and GABA at 100 microM had no consistent effect on the voltage-activated potassium current. Baclofen did not change the resting potassium conductance.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Matteson D. R. Two distinct populations of calcium channels in a clonal line of pituitary cells. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):65–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2578071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Eckert R. Divalent cations differentially support transmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:257–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:413–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H. The depressant action of baclofen on the isolated spinal cord of the neonatal rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 May 22;71(4):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Baclofen selectively inhibits transmission at synapses made by axons of CA3 pyramidal cells in the hippocampal slice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E. A transient calcium-dependent chloride current in the immature Xenopus oocyte. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:309–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O., Wanke E. A fast transient outward current in the rat sympathetic neurone studied under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:91–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Feltz A. Patch-clamp study of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current in group C sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Oct 12;51(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90558-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L. Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):191–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Perkel D. H., Norris J. C., Peacock J. H. Electrotonic structure and specific membrane properties of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):1–15. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated calcium conductance in embryonic chick sensory neurons. Biophys J. 1984 Sep;46(3):413–418. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84037-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Bornstein J. C., Peet M. J. Selective effects of (-)-baclofen on spinal synaptic transmission in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(2):158–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00236902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Malik R. The differential effects of baclofen on segmental and descending excitation of spinal interneurones in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1985;58(2):333–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00235314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Selective depression of synaptic excitation in cat spinal neurones by baclofen: an iontophoretic study. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):373–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisz R. A., Lux H. D. gamma-Aminobutyric acid-induced depression of calcium currents of chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 May 14;56(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Forda S. R., Scott R. H. Calcium-dependent currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones are inhibited by an adenosine analogue. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:47–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Scott R. H. Inhibition of calcium currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones by (-)-baclofen. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium conductance activated by depolarization of embryonic chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:519–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium ocmponent of sensory neurone action potentials. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):837–839. doi: 10.1038/276837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K. Two types of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor on embryonic sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Désarmenien M., Feltz P., Occhipinti G., Santangelo F., Schlichter R. Coexistence of GABAA and GABAB receptors on A delta and C primary afferents. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;81(2):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freschi J. E. Membrane currents of cultured rat sympathetic neurons under voltage clamp. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1460–1478. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego R. The ionic basis of action potentials in petrosal ganglion cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:591–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Sedlmeir C. Outward currents in voltage-clamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. GABAB-receptor-activated K+ current in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. A., Lawson S. N. Electrical properties of rat dorsal root ganglion neurones with different peripheral nerve conduction velocities. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:47–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer E. J., Macdonald R. L. Calcium- and sodium-dependent action potentials of mouse spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Apr;47(4):641–655. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Matsuo T., Ogata N. Characterization of pre- and postsynaptic actions of (-)-baclofen in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;84(4):843–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb17378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further study of the role of calcium in synaptic transmission. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):789–801. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Akaike N., Brown A. M. The suction pipette method for internal perfusion and voltage clamp of small excitable cells. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Feb;2(1):51–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L. A calcium-activated chloride current generates the after-depolarization of rat sensory neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:217–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neering I. R., McBurney R. N. Role for microsomal Ca storage in mammalian neurones? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):158–160. doi: 10.1038/309158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of the action of baclofen with gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Segal M., Barker J. L. A Ca-dependent Cl- conductance in cultured mouse spinal neurones. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):567–570. doi: 10.1038/311567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierau F. K., Zimmermann P. Action of a GABA-derivative on postsynaptic potentials and membrane properties of cats' spinal motoneurones. Brain Res. 1973 May 17;54:376–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnock R. D. Hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on neurons in the rat substantia nigra slice. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 26;322(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter R., Demeneix B. A., Desarmenien M., Desaulles E., Loeffler J. P., Feltz P. Properties of the GABA receptors located on spinal primary afferent neurones and hypophyseal neuroendocrine cells of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 29;47(3):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Acetylcholine receptor activation by a site-selective ligand: nature of brief open and closed states in BC3H-1 cells. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:357–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P. Transmission at voltage-clamped giant synapse of the squid: evidence for cooperativity of presynaptic calcium action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):622–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Matsuda Y., Samejima A. Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium and calcium components of action potentials in dorsal root ganglion cells of the adult mouse. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


