Abstract
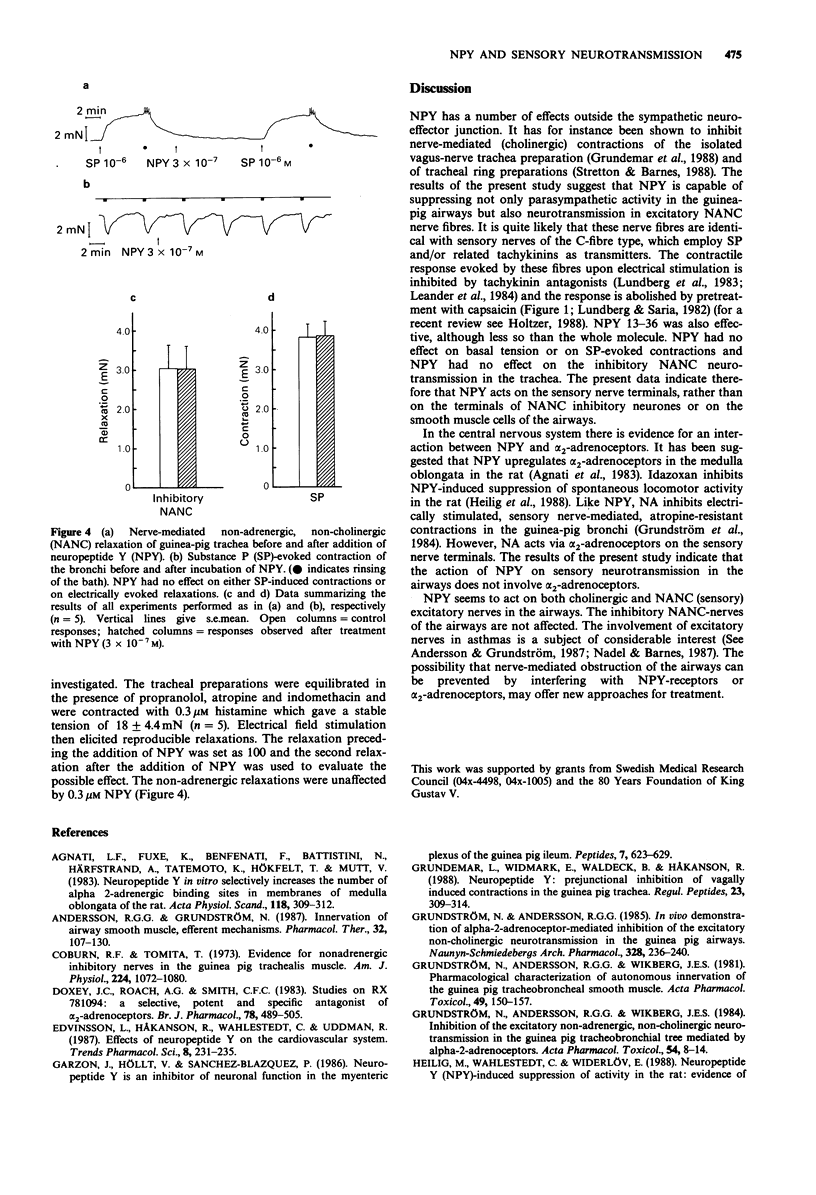
1. In the present study we have examined whether neuropeptide Y (NPY) interferes with non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve-mediated contractions and relaxations in the guinea-pig airways. In these experiments we have used ring preparations of bronchi and trachea, incubated in the presence of atropine, propranolol and indomethacin (each 1 microM). 2. The contractile response to electrical stimulation of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve fibres was suppressed by NPY and NPY 13-36 in a concentration-dependent manner, these agents having similar inhibitory potencies. NPY caused a more complete inhibition than the C terminal fragment. 3. NPY affected neither the basal tension nor the substance P-evoked contraction in the bronchi and trachea and did not interfere with nerve-mediated, non-adrenergic relaxation in the trachea. 4. On the basis of these results, it is suggested that NPY may act on the terminals of sensory neurones in the airways to prevent antidromic, excitatory neurotransmission by inhibiting transmitter release.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson R. G., Grundström N. Innervation of airway smooth muscle. Efferent mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;32(2):107–130. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn R. F., Tomita T. Evidence for nonadrenergic inhibitory nerves in the guinea pig trachealis muscle. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1072–1080. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbro D., Fändriks L., Rosell S., Folkers K. Inhibition of antidromically induced stimulation of gastric motility by substance P receptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Aug;118(4):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzón J., Höllt V., Sánchez-Blázquez P. Neuropeptide Y is an inhibitor of neural function in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Peptides. 1986 Jul-Aug;7(4):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundemar L., Widmark E., Waldeck B., Håkanson R. Neuropeptide Y: prejunctional inhibition of vagally induced contractions in the guinea pig trachea. Regul Pept. 1988 Dec;23(3):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(88)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G. In vivo demonstration of alpha-2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of the excitatory non-cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig airways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;328(3):236–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00515547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Inhibition of the excitatory non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neurotransmission in the guinea pig tracheo-bronchial tree mediated by alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1984 Jan;54(1):8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1984.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological characterization of the autonomous innervation of the guinea pig tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1981 Aug;49(2):150–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1981.tb00884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):739–768. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander S., Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Håkanson R. Neuronally mediated non-cholinergic contraction of guinea-pig bronchial smooth muscle is inhibited by a substance P antagonist. Agents Actions. 1984 Apr;14(3-4):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01973819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Brodin E., Rosell S., Folkers K. A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Bronchial smooth muscle contraction induced by stimulation of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):473–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. K. Prolonged non-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac vagal action following sympathetic stimulation: neuromodulation by neuropeptide Y? Neurosci Lett. 1985 Mar 15;54(2-3):117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernquist M., Emson P., Owman C., Sjöberg N. O., Sundler F., Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y in the female reproductive tract of the rat. Distribution of nerve fibres and motor effects. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Sep 9;39(3):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton C. D., Barnes P. J. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig trachea by neuropeptide Y. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):672–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szolcsányi J., Barthó L. Capsaicin-sensitive non-cholinergic excitatory innervation of the guinea-pig tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Dec 31;34(3):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Sundler F., Emson P. Occurrence and distribution of neuropeptide-Y-immunoreactive nerves in the respiratory tract and middle ear. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(2):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00217151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


