Abstract
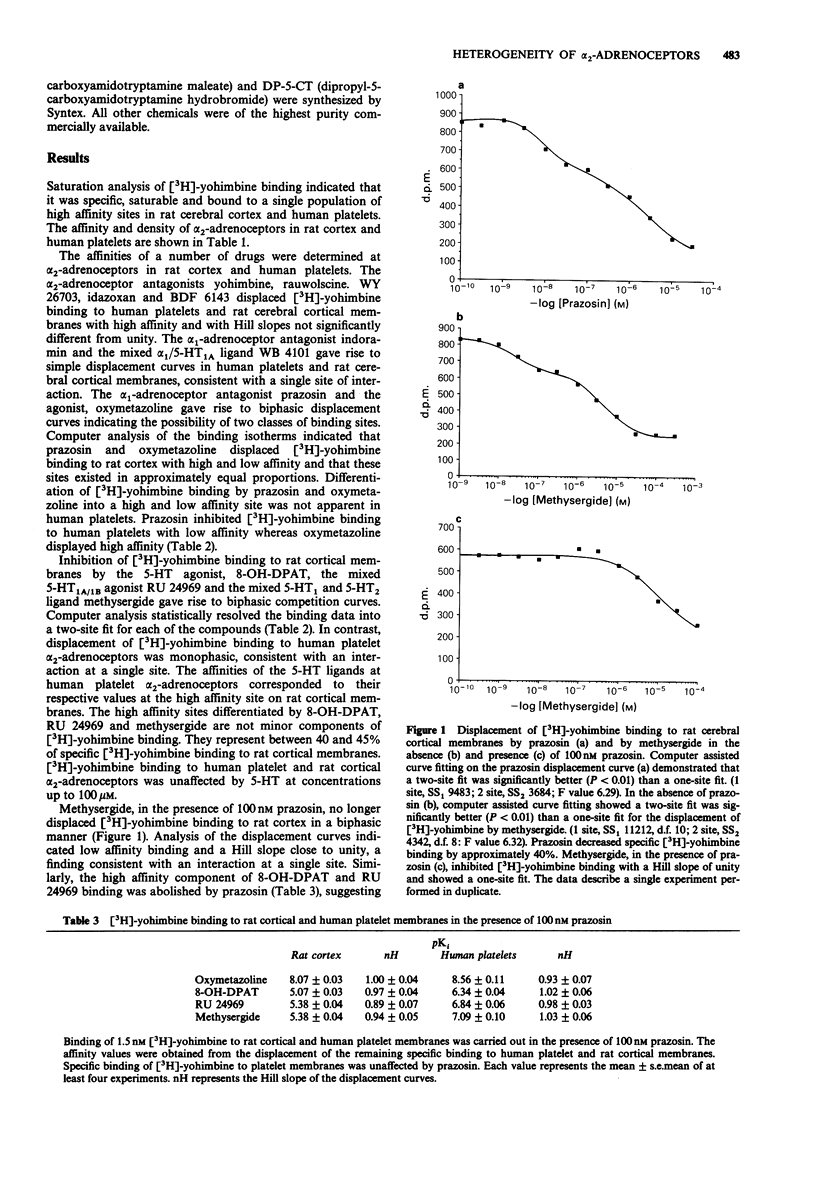
1. Saturation experiments indicated that [3H]-yohimbine binding was specific, saturable and labelled a single population of sites in rat cerebral cortex (Kd 5.3 +/- 0.9 nM, Bmax 121 +/- 10 fmol mg-1 protein) and human platelets (Kd 0.7 +/- 0.1 nM, Bmax 152 +/- 10 fmol mg-1 protein). 2. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists, yohimbine, rauwolscine, WY 26703, idazoxan and BDF 6143 displaced [3H]-yohimbine binding to each tissue in a simple manner, with high affinity and Hill slopes close to unity. 3. The alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonist, oxymetazoline and the antagonist prazosin inhibited the binding of [3H]-yohimbine to rat in a complex manner consistent with an interaction at more than one site. However, indoramin and WB 4101 only appeared to interact with one site. In contrast, in human platelets, all antagonists gave rise to monophasic displacement curves with Hill slopes close to unity suggesting a single site of interaction. 4. The 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptor ligands, 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), RU 24969, and methysergide inhibited the binding of [3H]-yohimbine to rat cortex with high and low affinity, consistent with an interaction with two populations of binding sites. However, inhibition of [3H]-yohimbine binding to human platelets suggested a single site of interaction. The low affinity of 5-HT, 5-carboxyamidotryptamine (5-CT) and dipropyl-5-CT indicated that [3H]-yohimbine was not labelling a 5-HT1-like site in rat cortex.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alabaster V. A., Keir R. F., Peters C. J. Comparison of potency of alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists in vitro: evidence for heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):607–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon N. A., Elliott J. M., Grahame-Smith D. G., St John-Green T., Stump K. A comparison of alpha 2-adrenoreceptor binding characteristics of intact human platelets identified by [3H]-yohimbine and [3H]-dihydroergocryptine. J Auton Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;3(2):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1983.tb00524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadhurst A. M., Alexander B. S., Wood M. D. Heterogeneous 3H-rauwolscine binding sites in rat cortex: two alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes or an additional non-adrenergic interaction? Life Sci. 1988;43(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadhurst A. M., Wyllie M. G. A reassessment of the binding of [3H]rauwolscine to membranes from the rat cortex. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Mar;25(3):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., U'Prichard D. C. Characterization of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1983;24:343–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. [3H]Rauwolscine and [3H]yohimbine binding to rat cerebral and human platelet membranes: possible heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convents A., Convents D., De Backer J. P., De Keyser J., Vauquelin G. High affinity binding of 3H rauwolscine and 3H RX781094 to alpha 2 adrenergic receptors and non-stereoselective sites in human and rabbit brain cortex membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 1;38(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convents A., De Backer J. P., Vauquelin G. Characterization of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors of calf retina membranes by [3H]-rauwolscine and [3H]-RX 781094 binding. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 1;36(15):2497–2503. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiguji M., Meltzer H. Y., U'Prichard D. C. Human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors: labeling with 3H-yohimbine, a selective antagonist ligand. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 15;28(24):2705–2717. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson K. E., McKernan R. M., Miles C. M., Leys K. S., Sever P. S. Heterogeneity of mammalian alpha 2-adrenoceptors delineated by [3H]yohimbine binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 29;120(3):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90469-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diop L., Dausse J. P., Meyer P. Specific binding of [3H]rauwolscine to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat cerebral cortex: comparison between crude and synaptosomal plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):710–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Lohse M. J., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The genomic clone G-21 which resembles a beta-adrenergic receptor sequence encodes the 5-HT1A receptor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):358–360. doi: 10.1038/335358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller D. J., Bylund D. B. Comparison of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and their regulation in rodent and porcine species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Yakubu M. A. [3H]yohimbine and [3H]idazoxan bind to different sites on rabbit forebrain and kidney membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 9;146(2-3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuring R. E., Peroutka S. J. Characterization of a novel 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine binding site subtype in bovine brain membranes. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):894–903. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00894.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Michel T., Brenneman T. B., Lefkowitz R. J. Interactions of agonists with platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Endocrinology. 1982 Mar;110(3):926–932. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-3-926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara R. S., Bylund D. B. Solubilization and characterization of putative alpha-2 adrenergic isoceptors from the human platelet and the rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):603–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerry R., Scrutton M. C., Wallis R. B. Mammalian platelet adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;81(1):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10748.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Homcy C. J., Patenaude C., Graham R. M. Identification of structurally distinct alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14491–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latifpour J., Jones S. B., Bylund D. B. Characterization of [3H]yohimbine binding to putative alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in neonatal rat lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Dec;223(3):606–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Whiting R. L. Methoctramine, a polymethylene tetraamine, differentiates three subtypes of muscarinic receptor in direct binding studies. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 5;145(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Shattil S. J., Insel P. A. Characterization of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors on human platelets using [3H]yohimbine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1562–1570. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Barnett D. B., Cheung Y. D. alpha-Adrenoceptor-effector coupling: affinity states or heterogeneity of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor? Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):39s–42s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrash A. C., Bylund D. B. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes indicated by [3H]yohimbine binding in human brain. Life Sci. 1986 Jun 9;38(23):2129–2137. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouot B., Quennedey M. C., Schwartz J. Characteristics of the [3H]-yohimbine binding on rat brain alpha2-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;321(4):253–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00498509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


