Abstract
1. The toxicity of intravenous recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rhTNF), a TNF fragment (TNF114-130), endotoxin and combinations of rhTNF or TNF114-130 were tested in mice. Neither rhTNF nor TNF114-130 was lethal alone, but when combined with a non-lethal dose of endotoxin, rhTNF provoked dose-dependent mortality, as did higher doses of endotoxin alone. 2. Both the toxicity and the vasopermeability changes induced by endotoxin alone were blocked by the platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist BN52021, indomethacin or the dual cyclo-oxygenase/lipoxygenase inhibitor BW755C. 3. The lethality of the combined low dose endotoxin/rhTNF challenge was unaffected by pretreatment with BN52021, indomethacin or BW755C, or by treatment at 6 h intervals with BN52021 or BW755C. 4. The results of these studies suggest that TNF, a putative, early mediator of septic or endotoxin shock, cannot by itself mimic all of the effects of bacterial endotoxin in the model used in this study. Apparently, TNF works synergistically with other mediators whose release is stimulated by endotoxin. 5. The results also suggest that the mechanism of shock production by the rhTNF/endotoxin combination in mice is not dependent on the early stimulation of eicosanoid or PAF synthesis by rhTNF.
Full text
PDF
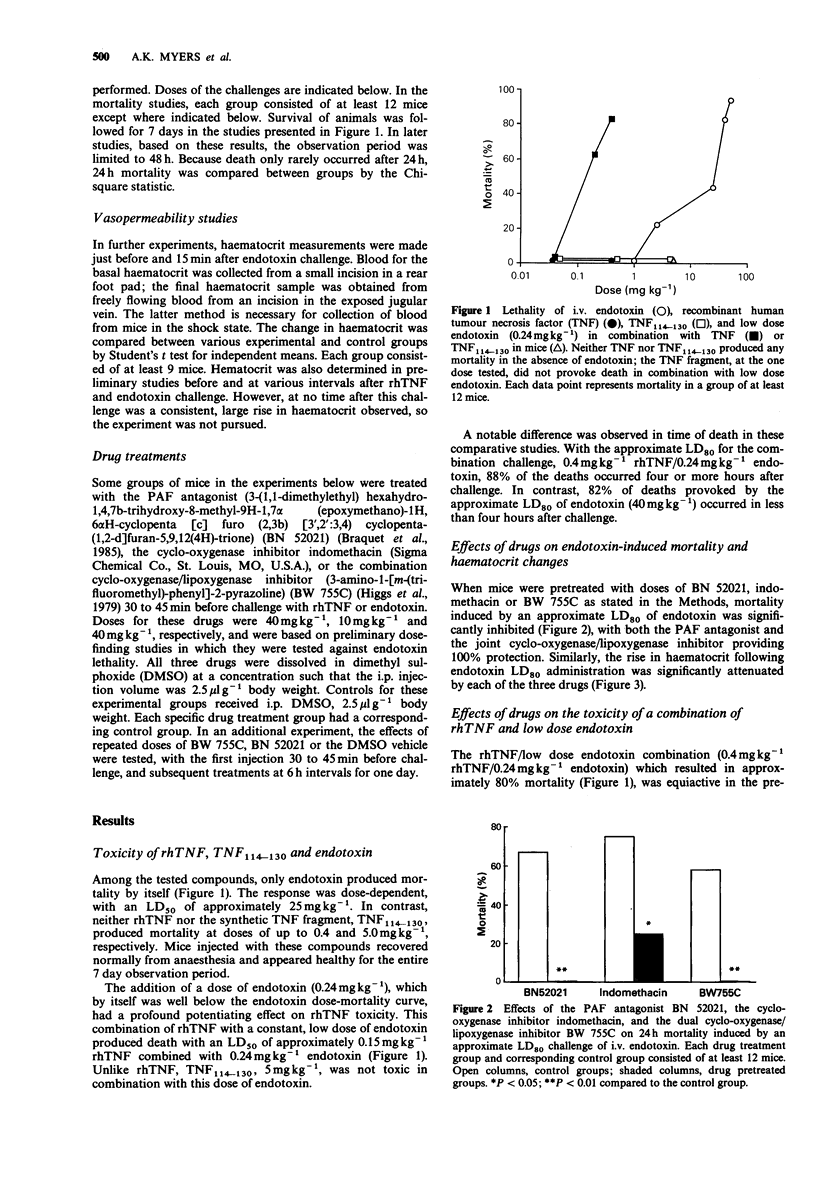
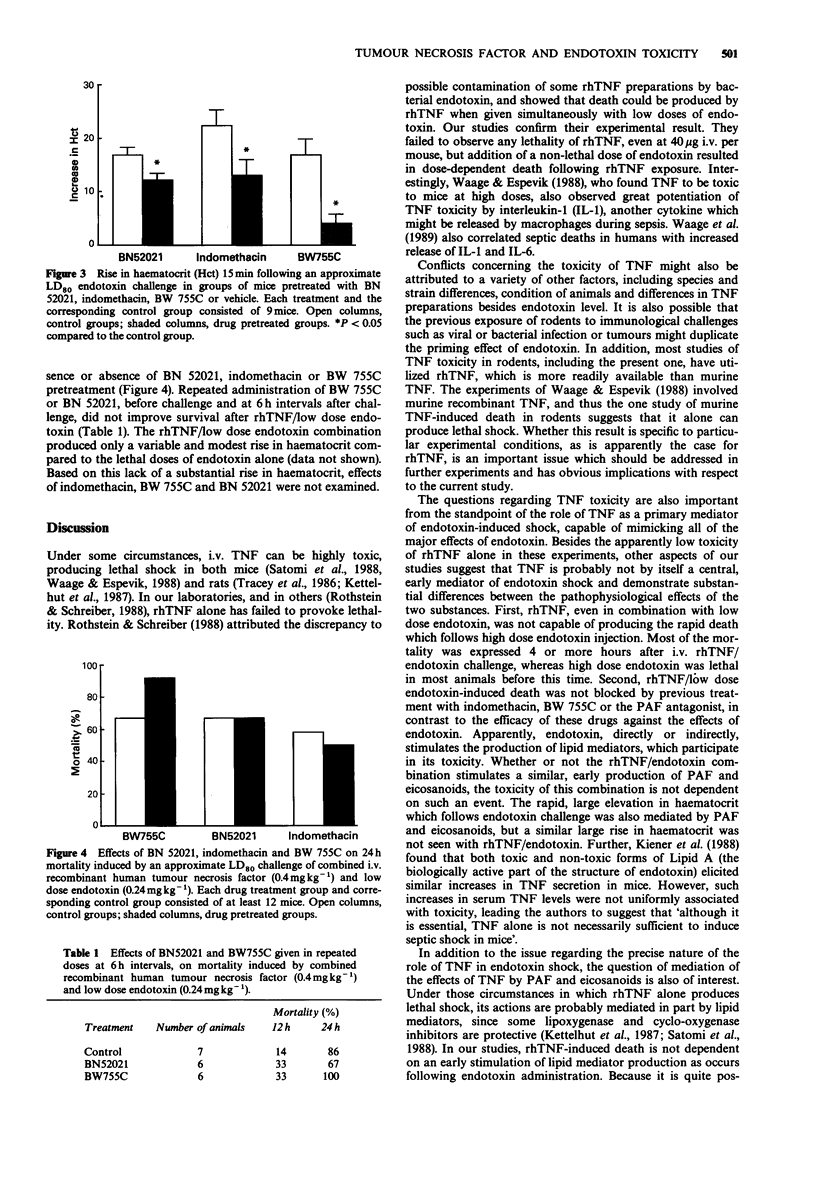

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braquet P., Etienne A., Touvay C., Bourgain R. H., Lefort J., Vargaftig B. B. Involvement of platelet activating factor in respiratory anaphylaxis, demonstrated by PAF-acether inhibitor BN 52021. Lancet. 1985 Jun 29;1(8444):1501–1501. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Van Valen R. G., Melden M. K., Houlihan W. J., Saunders R. N. Biological effects of the orally active platelet activating factor receptor antagonist SDZ 64-412. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Nov;247(2):617–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettelhut I. C., Fiers W., Goldberg A. L. The toxic effects of tumor necrosis factor in vivo and their prevention by cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4273–4277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener P. A., Marek F., Rodgers G., Lin P. F., Warr G., Desiderio J. Induction of tumor necrosis factor, IFN-gamma, and acute lethality in mice by toxic and non-toxic forms of lipid A. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanara E., Vakirtzi-Lemonias C., Kritikou L., Demopoulos C. A. Response of mice and mouse platelets to acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1148–1156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91897-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A., Penhos J., Ramey E., Ramwell P. Thromboxane agonism and antagonism in a mouse sudden death model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Feb;224(2):369–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A., Ramey E., Ramwell P. Glucocorticoid protection against PAF-acether toxicity in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):595–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olanoff L. S., Cook J. A., Eller T., Knapp D. R., Halushka P. V. Protective effects of trans-13-APT, a thromboxane receptor antagonist, in endotoxemia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):114–120. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. L., Schreiber H. Synergy between tumor necrosis factor and bacterial products causes hemorrhagic necrosis and lethal shock in normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):607–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Elsas P. P., Fiers W., Dessein A. J. Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rTNF)2 enhances leukotriene biosynthesis in neutrophils and eosinophils stimulated with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):484–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero V., Baglioni C. Synergistic anti-proliferative activity of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):661–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satomi N., Sakurai A., Haranaka R., Haranaka K. Preventive effects of several chemicals against lethality of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Response Mod. 1988 Feb;7(1):54–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Bowel necrosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in rats is mediated by platelet-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1328–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI113459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashita Z., Imura Y., Nishikawa K., Sumida S. Is platelet activating factor (PAF) a mediator of endotoxin shock? Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Espevik T. Interleukin 1 potentiates the lethal effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin in mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


