Abstract
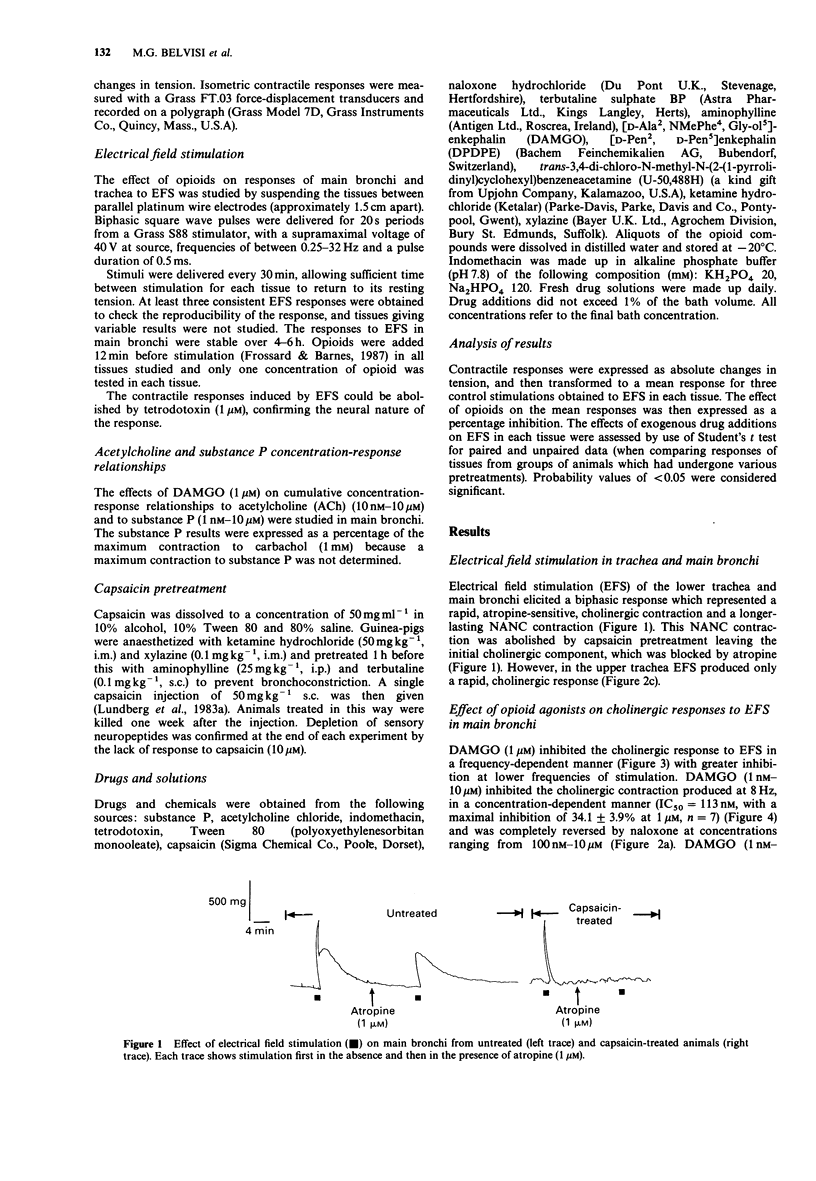
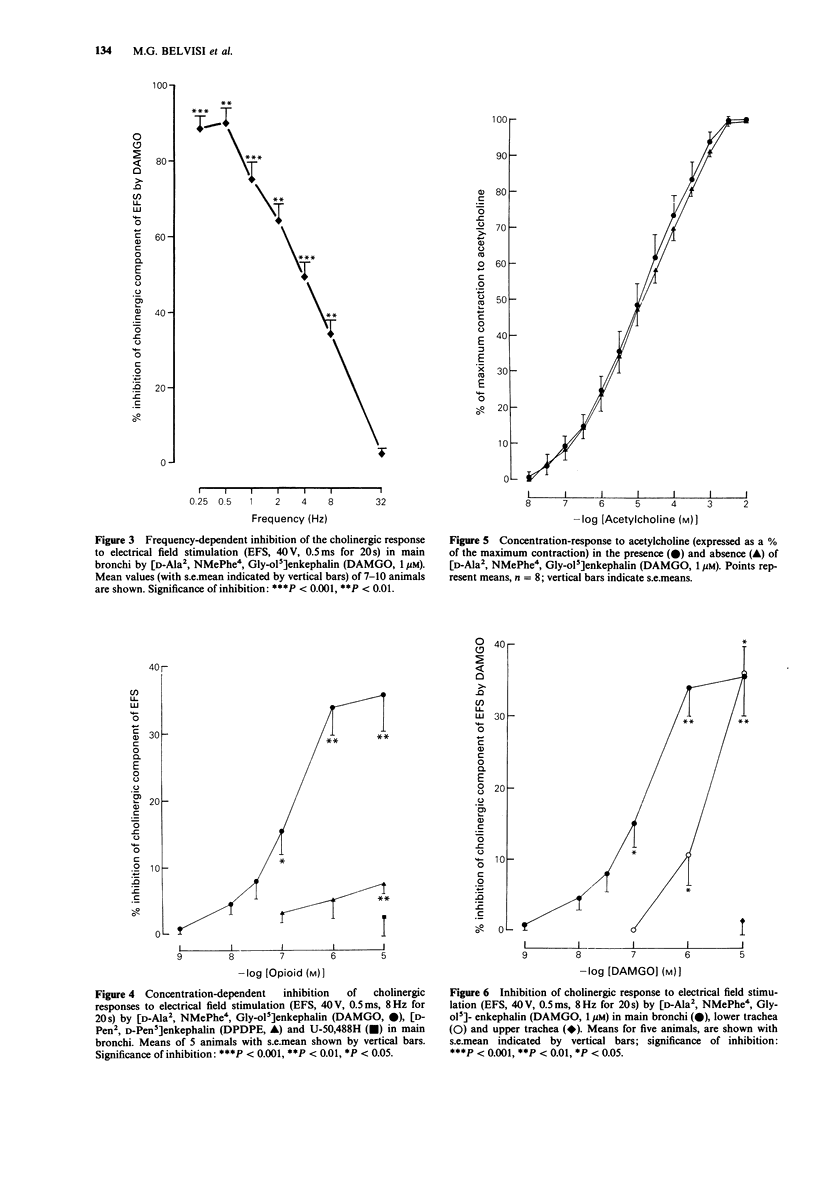
1. Opioid receptors have been localised on sensory fibres in the vagus nerve and opioids have previously been shown to inhibit non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic (NANC) neurotransmission in guinea-pig bronchi in vitro and in vivo. We have now investigated whether an inhibitory effect could be demonstrated on cholinergic neurotransmission. 2. Electrical field stimulation (EFS) (8 Hz, 0.5 ms, 40 V for 20 s) produced only a rapid, cholinergic response in the upper trachea but in the lower trachea and main bronchi a cholinergic response which was atropine-sensitive and a longer lasting NANC contraction that was atropine-insensitive was demonstrated. This slow contraction could be blocked by tetrodotoxin and capsaicin pretreatment. 3. [D-Ala2, NMePhe4, Gly-ol5]enkephalin (DAMGO), a selective mu-opioid receptor agonist, inhibited the cholinergic response to EFS at 8 Hz in a dose-dependent manner in main bronchi (IC50 = 113 nM with a maximal inhibition of 35.7 +/- 5.6% 10 microM, n = 5). In the lower trachea, DAMGO inhibited the cholinergic response to a similar extent (inhibition of 35.8 +/- 3.5% at 10 microM, n = 5). However, DAMGO had no effect on the contractile response to exogenously applied acetylcholine in the main bronchi. By contrast, opioids had no inhibitory effect on cholinergic neurotransmission in the upper trachea. DAMGO (1 microM) inhibited the cholinergic response to EFS in a frequency-dependent manner in the main bronchi with greater inhibition at lower frequencies of stimulation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson R. G., Grundström N. The excitatory non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nervous system of the guinea-pig airways. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;131:141–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthó L., Amann R., Saria A., Szolcsányi J., Lembeck F. Peripheral effects of opioid drugs on capsaicin-sensitive neurones of the guinea-pig bronchus and rabbit ear. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;336(3):316–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00172684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Chung K. F., Jackson D. M., Barnes P. J. Opioid modulation of non-cholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A. L., Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Mode of action of morphine-like drugs on autonomic neuro-effectors. Nature. 1968 Dec 7;220(5171):1040–1042. doi: 10.1038/2201040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard N., Barnes P. J. Mu-opioid receptors modulate non-cholinergic constrictor nerves in guinea-pig airways. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 23;141(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90578-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. K., Barnes P. J., Meldrum L. A., Maclagan J. Facilitation by tachykinins of neurotransmission in guinea-pig pulmonary parasympathetic nerves. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):274–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Burks T. F., Porreca F. Studies in vitro with ICI 174,864, [D-Pen2, D-Pen5]-enkephalin (DPDPE) and [D-Ala2, NMePhe4, Gly-ol]-enkephalin (DAGO). Neuropeptides. 1985 Feb;5(4-6):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laduron P. M. Axonal transport of opiate receptors in capsaicin-sensitive neurones. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 27;294(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Brodin E., Saria A. Effects and distribution of vagal capsaicin-sensitive substance P neurons with special reference to the trachea and lungs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Nov;119(3):243–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Brodin E., Rosell S., Folkers K. A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martling C. R., Saria A., Andersson P., Lundberg J. M. Capsaicin pretreatment inhibits vagal cholinergic and non-cholinergic control of pulmonary mechanics in the guinea pig. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;325(4):343–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00504379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Simons E. J. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in airways by enkephalin. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Mar;58(3):853–858. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.3.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton C. D., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. The effect of sensory nerve depletion on cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):782P–782P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda N., Muramatsu I., Fujiwara M. Dual effects of dynorphin-(1-13) on cholinergic and substance P-ergic transmissions in the rabbit iris sphincter muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Feb;232(2):545–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


