Abstract
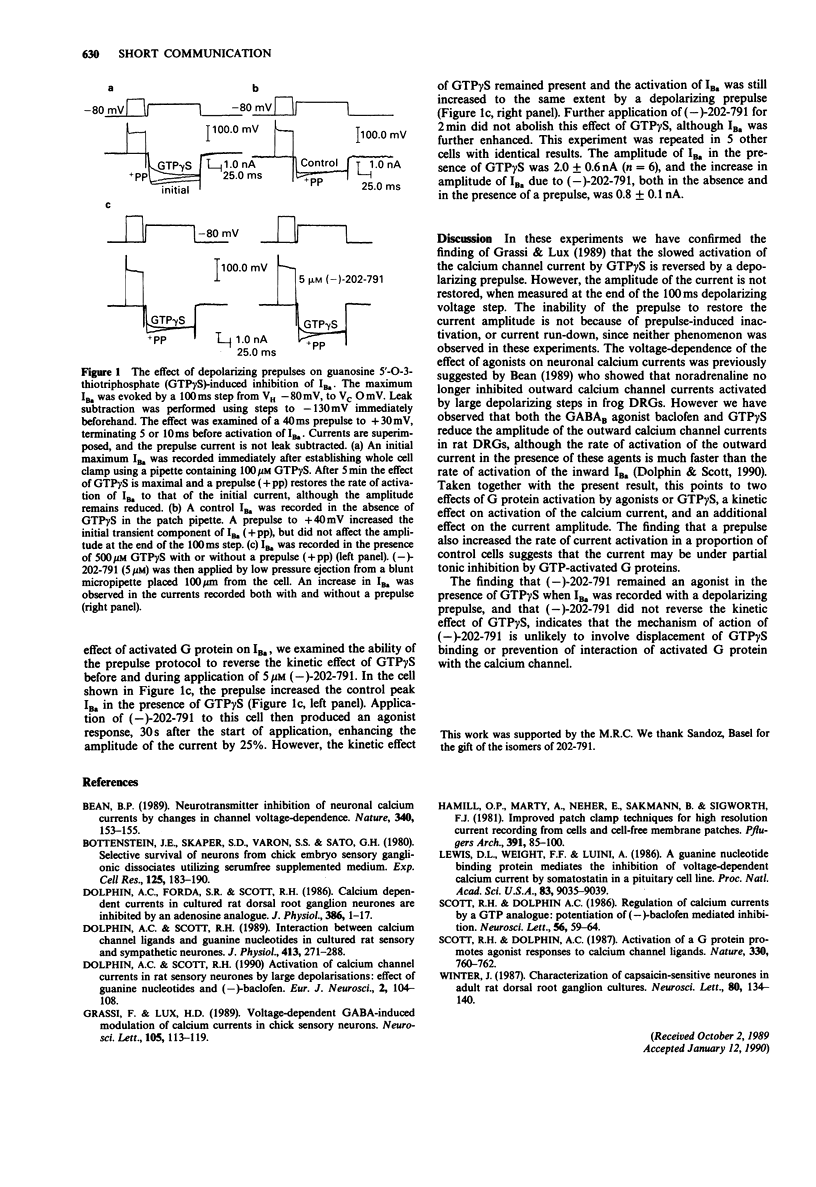
The ability of a depolarizing prepulse to increase the rate of activation of IBa has been examined in cultured sensory neurones of the rat. Both in control neurones and in the presence internally of the guanine nucleotide analogue, guanosine 5'-O-3-thiotriphosphate (GTP gamma S) which markedly slows the rate of activation of IBa and reduces its amplitude, a depolarizing prepulse increased the rate of activation of IBa, but did not increase its amplitude measured at the end of the 100 ms voltage step. The calcium channel antagonist (-)-202-791, which we have previously shown to increase the amplitude of IBa in the presence of GTP gamma S, did not occlude the response to a depolarizing prepulse, suggesting that the mechanism of action of (-)-202-791 is not to disrupt the interaction of the channels with activated G proteins.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Skaper S. D., Varon S. S., Sato G. H. Selective survival of neurons from chick embryo sensory ganglionic dissociates utilizing serum-free supplemented medium. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jan;125(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Scott R. H. Activation of calcium channel currents in rat sensory neurons by large depolarizations: effect of Guanine nucleotides and (-)-baclofen. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(1):104–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Scott R. H. Calcium channel currents and their inhibition by (-)-baclofen in rat sensory neurones: modulation by guanine nucleotides. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Scott R. H. Interaction between calcium channel ligands and guanine nucleotides in cultured rat sensory and sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:271–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi F., Lux H. D. Voltage-dependent GABA-induced modulation of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Dolphin A. C. Activation of a G protein promotes agonist responses to calcium channel ligands. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):760–762. doi: 10.1038/330760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Dolphin A. C. Regulation of calcium currents by a GTP analogue: potentiation of (-)-baclofen-mediated inhibition. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Aug 15;69(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J. Characterization of capsaicin-sensitive neurones in adult rat dorsal root ganglion cultures. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Sep 23;80(2):134–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


