Abstract
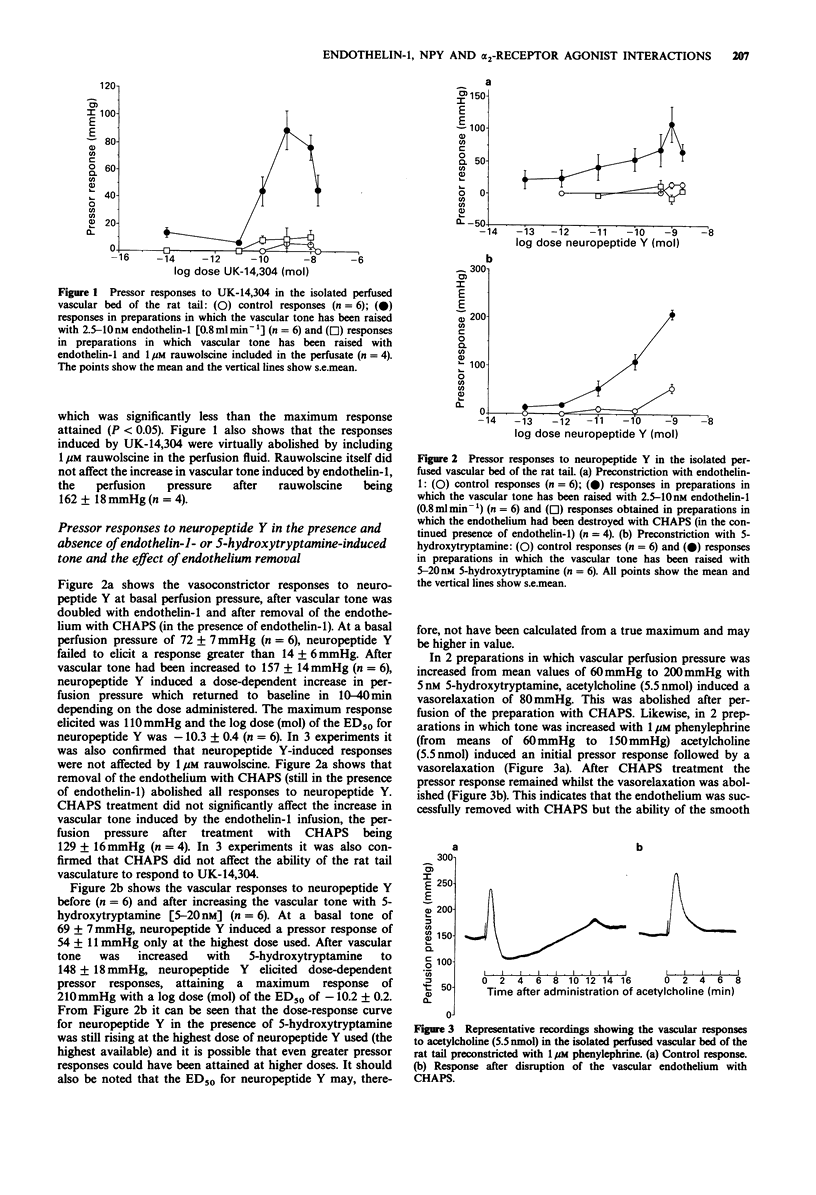
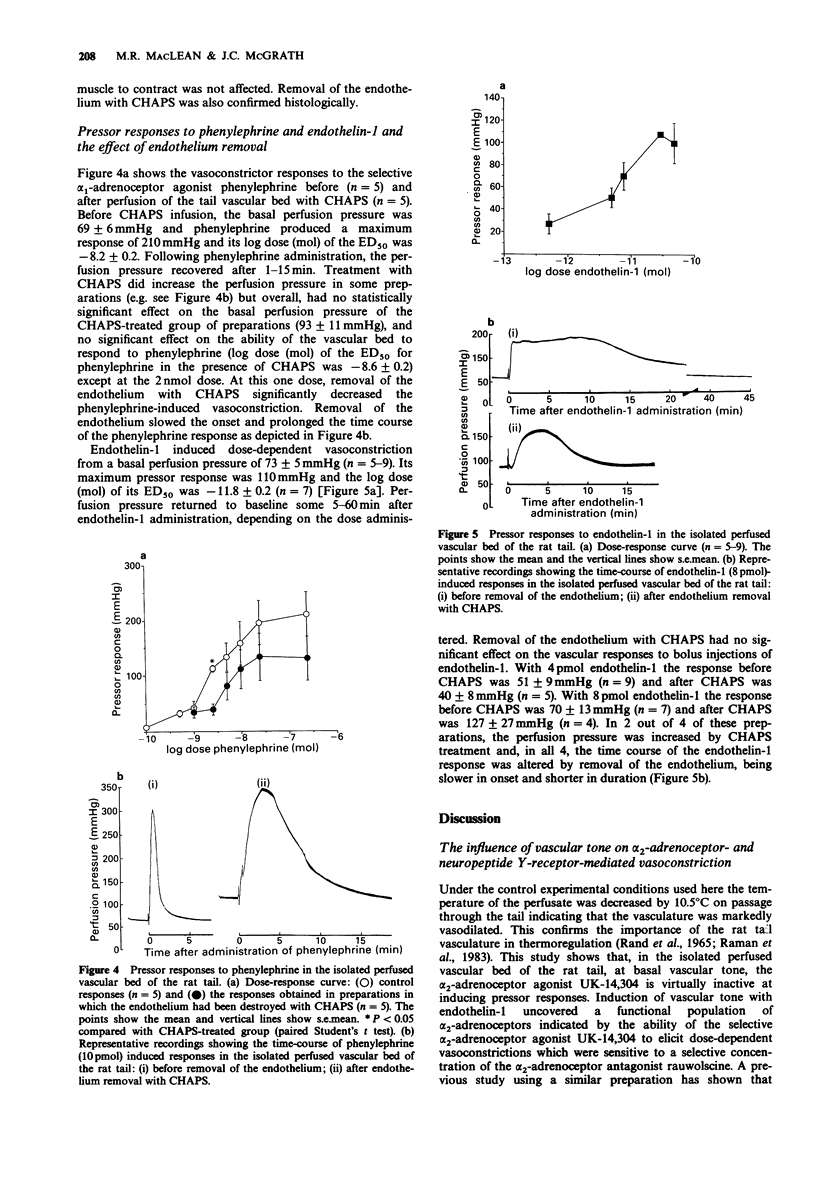
1. The pressor effects to bolus doses of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist UK-14,304 were studied in the isolated vascular bed of the perfused rat tail before and after increasing the perfusion pressure with infusions of endothelin-1. Those of neuropeptide Y were studied before and after pre-constriction with endothelin-1 or 5-hydroxytryptamine. The pressor effects of neuropeptide Y were studied before and after functional disruption of the endothelium with the detergent CHAPS. 2. Endothelin-1 and the alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine induced dose-dependent vasoconstriction, endothelin-1 being some 10(4) times more potent than phenylephrine [log dose (mol) of the ED50 for endothelin-1 and phenylephrine: -11.8 +/- 0.2 (n = 7), -8.2 +/- 0.2 (n = 5) respectively]. 3. Under control conditions, at basal perfusion pressures, UK-14,304 and neuropeptide Y were virtually inactive as vasoconstrictors. Following a sustained increase in perfusion pressure by infusions of endothelin-1 (2.5-10 nM at 0.8 ml min-1), however, both UK-14,304 and neuropeptide Y induced dose-dependent pressor responses and both were some 10(2) times more potent than phenylephrine [log dose (mol) of the ED50 for UK-14304 and neuropeptide Y: -10 +/- 0.5 (n = 6), -10.3 +/- 0.4 (n = 6) respectively]. Responses to neuropeptide Y also were uncovered when vascular tone was increased with 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-20 nM) [log dose (mol) of the ED50 for neuropeptide Y: -10.2 +/- 0.2 (n = 6)]. 4. Pre-constriction-induced pressor responses to UK-14,304 were inhibited by 1 microM rauwolscine whilst those to neuropeptide Y were inhibited by disruption of the endothelium.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Matsuki N., Kasuya Y. Pharmacological and electrophysiological discrimination of contractile responses to selective alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists in rat tail artery. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;45(2):249–261. doi: 10.1254/jjp.45.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert J. F., Waeber B., Rossier B., Geering K., Nussberger J., Brunner H. R. Effects of neuropeptide Y on the blood pressure response to various vasoconstrictor agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1088–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlöf C., Dahlöf P., Lundberg J. M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY): enhancement of blood pressure increase upon alpha-adrenoceptor activation and direct pressor effects in pithed rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly R. N., Hieble J. P. Neuropeptide Y modulates adrenergic neurotransmission by an endothelium dependent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 26;138(3):445–446. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90486-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., MacDonald A., McGrath J. C. Further sub-classification of alpha-adrenoceptors in the cardiovascular system, vas deferens and anococcygeus of the rat [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):421P–422P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. R., McGrath J. C., Wilson V. G. Expression of functional postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rabbit isolated distal saphenous artery--a permissive role for angiotensin II? Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):259–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C. Neuropeptide Y potentiates the effect of various vasoconstrictor agents on rabbit blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Jansen I., Edvinsson L. Neuropeptide Y is a potent inhibitor of cyclic AMP accumulation in feline cerebral blood vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Jul;124(3):467–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T. Precontraction-induced contractile response of isolated canine portal vein to alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):525–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00182726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland C. J. Influence of the endothelium and alpha-adrenoreceptor antagonists on responses to noradrenaline in the rabbit basilar artery. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:205–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. The nature of endothelium-derived vascular relaxant factor. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):645–647. doi: 10.1038/308645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Duesler J. G., Jr, Daly R. N. Effects of neuropeptide Y on the response of isolated blood vessels to norepinephrine and sympathetic field stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Aug;250(2):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Pernow J. Guanethidine-sensitive release of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the cat spleen by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hemsén A., Larsson O., Rudehill A., Saria A., Fredholm B. B. Neuropeptide Y receptor in pig spleen: binding characteristics, reduction of cyclic AMP formation and calcium antagonist inhibition of vasoconstriction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 5;145(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Kuon E., Holtz J., Busse R. Endothelium-mediated dilations contribute to the polarity of the arterial wall in vasomotion induced by alpha 2-adrenergic agonists. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):680–688. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198507000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medgett I. C., Langer S. Z. Heterogeneity of smooth muscle alpha adrenoceptors in rat tail artery in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jun;229(3):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medgett I. C., Langer S. Z. Influence of neuronal uptake on the contribution of smooth muscle alpha 2-adrenoceptors to vasoconstrictor responses to noradrenaline in SHR and WKY isolated tail arteries. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;332(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00633195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. J., Elliott J. M., Cain M. D., Kapoor V., West M. J., Chalmers J. P. Plasma neuropeptide y levels rise in patients undergoing exercise tests for the investigation of chest pain. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1986 May;13(5):437–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1986.tb00923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M., Kapoor V., Chalmers J. Plasma neuropeptide Y concentration is increased after hemorrhage in conscious rats: relative contributions of sympathetic nerves and the adrenal medulla. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987 May;9(5):541–545. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198705000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J. Actions of constrictor (NPY and endothelin) and dilator (substance P, CGRP and VIP) peptides on pig splenic and human skeletal muscle arteries: involvement of the endothelium. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):983–989. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J. Co-release and functional interactions of neuropeptide Y and noradrenaline in peripheral sympathetic vascular control. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1988;568:1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P., BURTON A. C., ING T. THE TAIL OF THE RAT, IN TEMPERATURE REGULATION AND ACCLIMATIZATION. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1965 Mar;43:257–267. doi: 10.1139/y65-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman E. R., Roberts M. F., Vanhuyse V. J. Body temperature control of rat tail blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):R426–R432. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.245.3.R426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Mukoyama M., Imura H. Increased plasma endothelin level in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 18;322(3):205–205. doi: 10.1056/nejm199001183220315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. M., Swamy V. C., Triggle D. J. Postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor characterization and Ca2+ channel antagonist and activator actions in rat tail arteries from normotensive and hypertensive animals. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;64(7):909–921. doi: 10.1139/y86-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulpizio A., Hieble J. P. Demonstration of alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated contraction in the isolated canine saphenous artery treated with Bay K 8644. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 3;135(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton A. G., Macmillan J., McGrath J. C., Storey N. D., Wilson V. G. Evidence for prazosin-resistant, rauwolscine-sensitive alpha-adrenoceptors mediating contractions in the isolated vascular bed of the rat tail. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):563–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesfamariam B., Halpern W., Osol G. Effects of perfusion and endothelium on the reactivity of isolated resistance arteries. Blood Vessels. 1985;22(6):301–305. doi: 10.1159/000158616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Ujiie K., Nakanishi T., Tomura S., Matsuda O., Ando K., Shichiri M., Hirata Y., Marumo F. Plasma endothelin levels in patients with acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1127–1127. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Rat endothelin is a vasodilator in the isolated perfused mesentery of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 17;159(3):325–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Dusting H. K., Reid J. J., Rand M. J. Paradoxical effects of endothelin on cardiovascular noradrenergic neurotransmission. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1989 Apr;16(4):229–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb01548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes S., Bento A. C., de Lima W. T. Responsiveness to epinephrine in adult spontaneously hypertensive rat tail artery: preferential mediation by postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;11(4):473–477. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198804000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


